Abstract
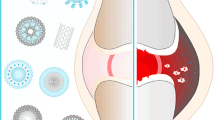
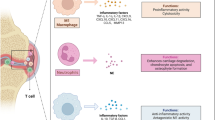
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a disease characterized by degradation of joints with the development of painful osteophytes in the surrounding tissues. Currently, there are a limited number of treatments for this disease, and many of these only provide temporary, palliative relief. In this review, we discuss particle-based drug delivery systems that can provide targeted and sustained delivery of imaging and therapeutic agents to OA-affected sites. We focus on technologies such as polymeric micelles and nano-/microparticles, liposomes, and dendrimers for their potential treatment and/or diagnosis of OA. Several promising studies are highlighted, motivating the continued development of delivery technologies to improve treatments for OA.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loeser RF. Osteoarthritis year in review 2013: biology. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2013;21(10):1436–42.
Valdes AM, Spector TD. Genetic epidemiology of hip and knee osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):23–32.
Issa S, Sharma L. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: an update. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2006;8(1):7–15.
Richette P et al. Benefits of massive weight loss on symptoms, systemic inflammation and cartilage turnover in obese patients with knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(1):139–44.
Tanamas S et al. Does knee malalignment increase the risk of development and progression of knee osteoarthritis? A systematic review. Arth Care Res. 2009;61(4):459–67.
Buckwalter JA, Brown TD. Joint injury, repair, and remodeling: roles in post-traumatic osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;423:7–16.
Lee AS et al. A current review of molecular mechanisms regarding osteoarthritis and pain. Gene. 2013;527(2):440–7.
Zhang Y, Jordan JM. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Clin Geriatr Med. 2010;26(3):355–69.
Turkiewicz A et al. Current and future impact of osteoarthritis on health care: a population-based study with projections to year 2032. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2014;22(11):1826–32.
Kotlarz H et al. Insurer and out-of-pocket costs of osteoarthritis in the US: evidence from national survey data. Arth Rheuma. 2009;60(12):3546–53.
Conaghan, P.G., et al. Impact and therapy of osteoarthritis: the Arthritis Care OA Nation 2012 survey. Clin Rheumatol, 2014.
Fortin PR et al. Timing of total joint replacement affects clinical outcomes among patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. Arth Rheuma. 2002;46(12):3327–30.
Bijlsma JW, Berenbaum F, Lafeber FP. Osteoarthritis: an update with relevance for clinical practice. Lancet. 2011;377(9783):2115–26.
Bradley JD et al. Comparison of an antiinflammatory dose of ibuprofen, an analgesic dose of ibuprofen, and acetaminophen in the treatment of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. N Engl J Med. 1991;325(2):87–91.
Kirwan JR. The effect of glucocorticoids on joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. The arthritis and rheumatism council low-dose glucocorticoid study group. N Engl J Med. 1995;333(3):142–6.
Kirwan JR, Rankin E. 8 Intra-articular therapy in osteoarthritis. Baillière’s Clin Rheumatol. 1997;11(4):769–94.
Derendorf H et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of glucocorticoid suspensions after intra-articular administration. Clin Pharm Ther. 1986;39(3):313–7.
Gerwin N, Hops C, Lucke A. Intraarticular drug delivery in osteoarthritis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006;58(2):226–42.
Larsen C et al. Intra-articular depot formulation principles: role in the management of postoperative pain and arthritic disorders. J Pharm Sci. 2008;97(11):4622–54.
Nanomaterials for the local and targeted delivery of osteoarthritis drugs. J Nanomater, 2012. 2012: 13.
Bertrand N et al. Cancer nanotechnology: the impact of passive and active targeting in the era of modern cancer biology. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2014;66:2–25.
Duncan R. The dawning era of polymer therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2(5):347–60.
Peppas NA et al. Hydrogels in biology and medicine: from molecular principles to bionanotechnology. Adv Mater. 2006;18(11):1345–60.
Kataoka K, Harada A, Nagasaki Y. Block copolymer micelles for drug delivery: design, characterization and biological significance. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;47(1):113–31.
Maibaum L, Dinner AR, Chandler D. Micelle formation and the hydrophobic effect†. J Phys Chem B. 2004;108(21):6778–81.
Eetezadi, S., S.N. Ekdawi, and C. Allen, The challenges facing block copolymer micelles for cancer therapy: In vivo barriers and clinical translation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev, 2014.
O’Reilly RK, Hawker CJ, Wooley KL. Cross-linked block copolymer micelles: functional nanostructures of great potential and versatility. Chem Soc Rev. 2006;35(11):1068–83.
Oe Y et al. Actively-targeted polyion complex micelles stabilized by cholesterol and disulfide cross-linking for systemic delivery of siRNA to solid tumors. Biomaterials. 2014;35(27):7887–95.
Kazunori K et al. Block copolymer micelles as vehicles for drug delivery. J Control Release. 1993;24(1–3):119–32.
Maeda H, Nakamura H, Fang J. The EPR effect for macromolecular drug delivery to solid tumors: improvement of tumor uptake, lowering of systemic toxicity, and distinct tumor imaging in vivo. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(1):71–9.
Torchilin VP. Multifunctional, stimuli-sensitive nanoparticulate systems for drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014;13(11):813–27.
Oerlemans C et al. Polymeric micelles in anticancer therapy: targeting, imaging and triggered release. Pharm Res. 2010;27(12):2569–89.
Choi HS et al. Renal clearance of quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25(10):1165–70.
Yamamoto Y et al. Long-circulating poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(D, L-lactide) block copolymer micelles with modulated surface charge. J Control Release. 2001;77(1–2):27–38.
Papahadjopoulos D et al. Sterically stabilized liposomes: improvements in pharmacokinetics and antitumor therapeutic efficacy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991;88(24):11460–4.
Gao W et al. In situ growth of a stoichiometric PEG-like conjugate at a protein’s N-terminus with significantly improved pharmacokinetics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(36):15231–6.
Li H et al. Matrix metalloproteinase responsive, proximity-activated polymeric nanoparticles for siRNA delivery. Adv Funct Mater. 2013;23(24):3040–52.
Gupta MK et al. Poly(PS-b-DMA) micelles for reactive oxygen species triggered drug release. J Control Release. 2012;162(3):591–8.
Li H et al. Dual MMP7-proximity-activated and folate receptor-targeted nanoparticles for siRNA delivery. Biomacromolecules. 2014;16(1):192–201.
Ponta A, Bae Y. PEG-poly (amino acid) block copolymer micelles for tunable drug release. Pharm Res. 2010;27(11):2330–42.
Wu C et al. Fabrication of complex micelles with tunable shell for application in controlled drug release. Macromol Biosci. 2009;9(12):1185–93.
Li J et al. A reduction and pH dual-sensitive polymeric vector for long-circulating and tumor-targeted siRNA delivery. Adv Mater. 2014;26(48):8217–24.
Dahlman JE et al. In vivo endothelial siRNA delivery using polymeric nanoparticles with low molecular weight. Nat Nano. 2014;9(8):648–55.
Convertine AJ et al. Development of a novel endosomolytic diblock copolymer for siRNA delivery. J Control Release. 2009;133(3):221–9.
Convertine AJ et al. pH-responsive polymeric micelle carriers for siRNA drugs. Biomacromolecules. 2010;11(11):2904–11.
Nelson CE et al. Balancing cationic and hydrophobic content of PEGylated siRNA polyplexes enhances endosome escape, stability, blood circulation time, and bioactivity in vivo. ACS Nano. 2013;7(10):8870–80.
Miteva M et al. Tuning PEGylation of mixed micelles to overcome intracellular and systemic siRNA delivery barriers. Biomaterials. 2015;38:97–107.
Pittella F et al. Enhanced endosomal escape of siRNA-incorporating hybrid nanoparticles from calcium phosphate and PEG-block charge-conversional polymer for efficient gene knockdown with negligible cytotoxicity. Biomaterials. 2011;32(11):3106–14.
PANYAM J et al. Rapid endo-lysosomal escape of poly(dl-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles: implications for drug and gene delivery. FASEB J. 2002;16(10):1217–26.
Allen TM, Chonn A. Large unilamellar liposomes with low uptake into the reticuloendothelial system. FEBS Lett. 1987;223(1):42–6.
Allen TM, Cullis PR. Liposomal drug delivery systems: from concept to clinical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(1):36–48.
Torchilin VP. Recent advances with liposomes as pharmaceutical carriers. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4(2):145–60.
Gubernator J. Active methods of drug loading into liposomes: recent strategies for stable drug entrapment and increased in vivo activity. Expert Opinion Drug Deliv. 2011;8(5):565–80.
Akbarzadeh A et al. Liposome: classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2013;8(1):102.
Abraham SA et al. The liposomal formulation of doxorubicin. Methods Enzymol. 2005;391:71–97.
Slingerland M, Guchelaar HJ, Gelderblom H. Liposomal drug formulations in cancer therapy: 15 years along the road. Drug Discov Today. 2012;17(3–4):160–6.
Mulder WJM et al. Lipid-based nanoparticles for contrast-enhanced MRI and molecular imaging. NMR Biomed. 2006;19(1):142–64.
van den Hoven JM et al. Liposomal drug formulations in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Pharm. 2011;8(4):1002–15.
Zimmerman, S.C, and Lawless L.J. Supramolecular chemistry of dendrimers. In Dendrimers IV. 2001, Springer. 95–120.
Dufès C, Uchegbu IF, Schätzlein AG. Dendrimers in gene delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005;57(15):2177–202.
Gillies ER, Fréchet JMJ. Dendrimers and dendritic polymers in drug delivery. Drug Discov Today. 2005;10(1):35–43.
Patil ML et al. Surface-modified and internally cationic polyamidoamine dendrimers for efficient siRNA delivery. Bioconjug Chem. 2008;19(7):1396–403.
Lee CC et al. Designing dendrimers for biological applications. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23(12):1517–26.
Li, Y., et al. A smart and versatile theranostic nanomedicine platform based on nanoporphyrin. Nat Commun, 2014. 5.
Miller TM et al. Synthesis and characterization of a series of monodisperse, 1,3,5-phenylene-based hydrocarbon dendrimers including C276H186 and their fluorinated analogs. J Am Chem Soc. 1992;114(3):1018–25.
Tyssen D et al. Structure activity relationship of dendrimer microbicides with dual action antiviral activity. PLoS ONE. 2010;5(8):e12309.
Patri AK, Kukowska-Latallo JF, Baker Jr JR. Targeted drug delivery with dendrimers: comparison of the release kinetics of covalently conjugated drug and non-covalent drug inclusion complex. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005;57(15):2203–14.
Svenson S. Dendrimers as versatile platform in drug delivery applications. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2009;71(3):445–62.
Midoux P et al. Polymer-based gene delivery: a current review on the uptake and intracellular trafficking of polyplexes. Curr Gene Ther. 2008;8(5):335–52.
Gajbhiye V et al. Dendrimers as therapeutic agents: a systematic review. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2009;61(8):989–1003.
Joshi N, Grinstaff M. Applications of dendrimers in tissue engineering. Curr Top Med Chem. 2008;8(14):1225–36.
Napoli A et al. Oxidation-responsive polymeric vesicles. Nat Mater. 2004;3(3):183–9.
Poole KM et al. ROS-responsive microspheres for on demand antioxidant therapy in a model of diabetic peripheral arterial disease. Biomaterials. 2015;41:166–75.
Joshi RV et al. Dual pH- and temperature-responsive microparticles for protein delivery to ischemic tissues. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(5):6526–34.
Schubert S, Delaney Jr JT, Schubert US. Nanoprecipitation and nanoformulation of polymers: from history to powerful possibilities beyond poly (lactic acid). Soft Matter. 2011;7(5):1581–8.
Hornig S et al. Synthetic polymeric nanoparticles by nanoprecipitation. J Mater Chem. 2009;19(23):3838–40.
Tseng CHT et al. Continuous precipitation of ceria nanoparticles from a continuous flow micromixer. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2013;64(1–4):579–86.
Zhu Z. Flash nanoprecipitation: prediction and enhancement of particle stability via drug structure. Mol Pharm. 2014;11(3):776–86.
Bensaid S et al. Flow field simulation and mixing efficiency assessment of the multi-inlet vortex mixer for molybdenum sulfide nanoparticle precipitation. Chem Eng J. 2014;238:66–77.
Fang RH et al. Large-scale synthesis of lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles using a multi-inlet vortex reactor. Langmuir. 2012;28(39):13824–9.
Capretto L et al. Microfluidic and lab-on-a-chip preparation routes for organic nanoparticles and vesicular systems for nanomedicine applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(11):1496–532.
Adolph EJ et al. Enhanced performance of plasmid DNA polyplexes stabilized by a combination of core hydrophobicity and surface pegylation. J Mater Chem B Mater Biol Med. 2014;2(46):8154–64.
Immordino ML, Dosio F, Cattel L. Stealth liposomes: review of the basic science, rationale, and clinical applications, existing and potential. Int J Nanomedicine. 2006;1(3):297–315.
Haag R, Kratz F. Polymer therapeutics: concepts and applications. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2006;45(8):1198–215.
Rothenfluh DA et al. Biofunctional polymer nanoparticles for intra-articular targeting and retention in cartilage. Nat Mater. 2008;7(3):248–54.
Hayder M et al. A phosphorus-based dendrimer targets inflammation and osteoclastogenesis in experimental arthritis. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3(81):81ra35.
Singer II et al. VDIPEN, a metalloproteinase-generated neoepitope, is induced and immunolocalized in articular cartilage during inflammatory arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1995;95(5):2178–86.
Crielaard BJ et al. Glucocorticoid-loaded core-cross-linked polymeric micelles with tailorable release kinetics for targeted therapy of rheumatoid arthritis. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2012;51(29):7254–8.
Zhang J et al. Local delivery of indomethacin to arthritis-bearing rats through polymeric micelles based on amphiphilic polyphosphazenes. Pharm Res. 2007;24(10):1944–53.
Koo O, Rubinstein I, Önyüksel H. Actively targeted low-dose camptothecin as a safe, long-acting, disease-modifying nanomedicine for rheumatoid arthritis. Pharm Res. 2011;28(4):776–87.
Coimbra M et al. Antitumor efficacy of dexamethasone-loaded core-crosslinked polymeric micelles. J Control Release. 2012;163(3):361–7.
Wilson DR et al. Synthesis and evaluation of cyclosporine a-loaded polysialic acid–polycaprolactone micelles for rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2014;51:146–56.
Dagar S et al. VIP grafted sterically stabilized liposomes for targeted imaging of breast cancer: in vivo studies. J Control Release. 2003;91(1–2):123–33.
Sethi V et al. Novel, biocompatible, and disease modifying VIP nanomedicine for rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Pharm. 2013;10(2):728–38.
Letchford K, Burt H. A review of the formation and classification of amphiphilic block copolymer nanoparticulate structures: micelles, nanospheres, nanocapsules and polymersomes. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2007;65(3):259–69.
Butoescu N et al. Dexamethasone-containing biodegradable superparamagnetic microparticles for intra-articular administration: physicochemical and magnetic properties, in vitro and in vivo drug release. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2009;72(3):529–38.
Pradal J, Jordan O, Allémann E. Intra-articular drug delivery for arthritis diseases: the value of extended release and targeting strategies. J Drug Del Sci Technol. 2012;22(5):409–19.
van den Hoven JM et al. Liposomal drug formulations in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Pharm. 2011;8(4):1002–15.
Elron-Gross I, Glucksam Y, Margalit R. Liposomal dexamethasone–diclofenac combinations for local osteoarthritis treatment. Int J Pharm. 2009;376(1–2):84–91.
Cho H et al. Theranostic immunoliposomes for osteoarthritis. Nanomedicine. 2014;10(3):619–27.
Cho, H., et al. Detection of early cartilage damage using targeted nanosomes in a post-traumatic osteoarthritis mouse model. Nanomed: Nanotechnol Biol Med, 2015.
Hofkens W et al. Liposomal targeting of prednisolone phosphate to synovial lining macrophages during experimental arthritis inhibits M1 activation but does not favor M2 differentiation. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(2):e54016.
Dong J et al. Intra-articular delivery of liposomal celecoxib–hyaluronate combination for the treatment of osteoarthritis in rabbit model. Int J Pharm. 2013;441(1):285–90.
Vanniasinghe AS et al. Targeting fibroblast-like synovial cells at sites of inflammation with peptide targeted liposomes results in inhibition of experimental arthritis. Clin Immunol. 2014;151(1):43–54.
Hayder M et al. Anti-inflammatory properties of dendrimers per se. ScientificWorldJournal. 2011;11:1367–82.
Singh A et al. Nanoengineered particles for enhanced intra-articular retention and delivery of proteins. Adv Healthcare Mater. 2014;3(10):1562–7.
Grund S, Bauer M, Fischer D. Polymers in drug delivery—state of the art and future trends. Adv Eng Mater. 2011;13(3):B61–87.
Kawadkar J, Chauhan MK. Intra-articular delivery of genipin cross-linked chitosan microspheres of flurbiprofen: Preparation, characterization, in vitro and in vivo studies. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2012;81(3):563–72.
Ryan SM et al. An intra-articular salmon calcitonin-based nanocomplex reduces experimental inflammatory arthritis. J Control Release. 2013;167(2):120–9.
Lu Y et al. Preparation and evaluation of biodegradable flubiprofen gelatin micro-spheres for intra-articular administration. J Microencapsul. 2007;24(6):515–24.
Janssen M et al. Drugs and polymers for delivery systems in oa joints: clinical needs and opportunities. Polymers. 2014;6(3):799–819.
Kumar A et al. Sustained efficacy of intra-articular FX006 in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2012;20:S289.
Whitmire RE et al. Self-assembling nanoparticles for intra-articular delivery of anti-inflammatory proteins. Biomaterials. 2012;33(30):7665–75.
Safinya CR, Ewert KK. Materials chemistry: liposomes derived from molecular vases. Nature. 2012;489(7416):372–4.
Morachis JM, Mahmoud EA, Almutairi A. Physical and chemical strategies for therapeutic delivery by using polymeric nanoparticles. Pharmacol Rev. 2012;64(3):505–19.
Liggins R et al. Intra-articular treatment of arthritis with microsphere formulations of paclitaxel: biocompatibility and efficacy determinations in rabbits. Inflamm Res. 2004;53(8):363–72.
Liang LS et al. Methotrexate loaded poly (l-lactic acid) microspheres for intra-articular delivery of methotrexate to the joint. J Pharm Sci. 2004;93(4):943–56.
Bédouet L et al. Synthesis of hydrophilic intra-articular microspheres conjugated to ibuprofen and evaluation of anti-inflammatory activity on articular explants. Int J Pharm. 2014;459(1–2):51–61.
Gaignaux A et al. Development and evaluation of sustained-release clonidine-loaded PLGA microparticles. Int J Pharm. 2012;437(1):20–8.
Zhang Z et al. Enhanced targeting efficiency of PLGA microspheres loaded with Lornoxicam for intra-articular administration. Drug Deliv. 2011;18(7):536–44.
Zhang Z, Huang G. Intra-articular lornoxicam loaded PLGA microspheres: enhanced therapeutic efficiency and decreased systemic toxicity in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Drug Deliv. 2012;19(5):255–63.
Bozdag S et al. In vitro evaluation and intra-articular administration of biodegradable microspheres containing naproxen sodium. J Microencapsul. 2001;18(4):443–56.
Fernandez-Carballido A et al. Sterilized ibuprofen-loaded poly (D, L-lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres for intra-articular administration: effect of γ-irradiation and storage. J Microencapsul. 2004;21(6):653–65.
Panusa A et al. Methylprednisolone loaded PLGA microspheres: a new formulation for sustained release via intra articular administration. A comparison study with methylprednisolone acetate in rats. J Pharma Sci. 2011;100(11):4580–6.
Horisawa E et al. Prolonged anti-inflammatory action of DL-lactide/glycolide copolymer nanospheres containing betamethasone sodium phosphate for an intra-articular delivery system in antigen-induced arthritic rabbit. Pharm Res. 2002;19(4):403–10.
Zille H et al. Evaluation of intra-articular delivery of hyaluronic acid functionalized biopolymeric nanoparticles in healthy rat knees. Bio-med Mat Eng. 2010;20(3):235–42.
Eswaramoorthy R et al. Sustained release of PTH(1–34) from PLGA microspheres suppresses osteoarthritis progression in rats. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(6):2254–62.
Ko J-Y et al. Sulforaphane–PLGA microspheres for the intra-articular treatment of osteoarthritis. Biomaterials. 2013;34(21):5359–68.
Presumey J et al. PLGA microspheres encapsulating siRNA anti-TNFalpha: efficient RNAi-mediated treatment of arthritic joints. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2012;82(3):457–64.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interests for the production of this review article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kavanaugh, T.E., Werfel, T.A., Cho, H. et al. Particle-based technologies for osteoarthritis detection and therapy. Drug Deliv. and Transl. Res. 6, 132–147 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-015-0234-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13346-015-0234-2