Abstract
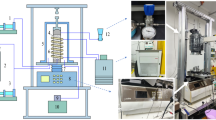
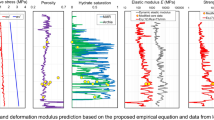
A triaxial system is designed with a temperature range from −20 °C to 25 °C and a pressure range from 0 MPa to 30 MPa in order to improve the understanding of the mechanical properties of gas hydrate-bearing sediments. The mechanical properties of synthetic gas hydrate-bearing sediments (gas hydrate-kaolin clay mixture) were measured by using current experimental apparatus. The results indicate that: (1) the failure strength of gas hydrate-bearing sediments strongly depends on the temperature. The sediment’s strength increases with the decreases of temperature. (2) The maximum deviator stress increases linearly with the confining pressure at a low-pressure stage. However, it fluctuates at a high-pressure stage. (3) Maximum deviator stress increases with increasing strain rate, whereas the strain-stress curve has no tremendous change until the axial strain reaches approximately 0.5%. (4) The internal friction angles of gas hydrate-bearing sediments are not sensitive to kaolin volume ratio. The cohesion shows a high kaolin volume ratio dependency.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkire, D. B. and Andersland, B. O., 1973. The effect of confining pressure on the mechanical properties of sand-ice materials, J. Glaciol., 12(66): 469–481.
Baker, T. H. W., 1979. Strain rate effect on the compressive strength of frozen sand, Eng. Geol., 13(1–4): 223–231.
Boswell, R., 2009. Is Gas Hydrate Energy Within Reach?, Science, 325(5943): 957–958.
Brown, H. E., Holbrook, W. S., Hornbach, M. J. and Nealon, J., 2006. Slide structure and role of gas hydrate at the northern boundary of the Storegga Slide, offshore Norway, Mar. Geol., 229(3–4): 179–186.
Chamberlain, E., Groves, C. and Perham, R., 1972. The mechanical behaviour of frozen earth materials under high-pressure triaxial test conditions, Geotechnique, 22(3): 469–483.
Dawe, R. A. and Thomas, S., 2007. A large potential methane source — Natural gas hydrates, Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, 29(3): 217–229.
Dickens, G. R., Oneil, J. R., Rea, D. K. and Owen, R. M., 1995. Dissociation of oceanic methane hydrate as a cause of the carbon isotope excursion at the end of the paleocene, Paleoceanography, 10(6): 965–971.
Durham, W. B., Kirby, S. H., Stern, L. A. and Zhang, W., 2003. The strength and rheology of methane clathrate hydrate, J. Geophys. Res., 108(B4): ECV2-1–11.
Glasby, G. P., 2003. Potential impact on climate of the exploitation of methane hydrate deposits offshore, Mar. Petrol. Geol., 20(2): 163–175.
Handa, Y. P. and Stupin, D. Y., 1992. Thermodynamic properties and dissociation characteristics of methane and propane hydrates in 70-.ANG.-radius silica gel pores, The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 96(21): 8599–8603.
Hawkes, I. and Mellor, M., 1972. Deformation and fracture of ice under uniaxial stress, J Glaciol, 11(61): 103–131.
Hyodo, M., Hyde, A., Nakata, Y., Yoshimoto, N., Fukunaga, M., Kubo, K., Nanjo, Y., Matsuo, T. and Nakamura K., 2002. Triaxial compressive strength of methane hydrate, 12th International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference (ISOPE-2002), Japan, 1, 422–428.
Hyodo, M., Nakata, Y., Yoshimoto, N. and Ebinuma, T., 2005. Basic research on the mechanical behavior of methane hydrate-sediments mixture, Soils Found., 45(1): 75–85.
Lee, J. Y., Santamarina, J. C. and Ruppel, C., 2008. Mechanical and electromagnetic properties of northern Gulf of Mexico sediments with and without THF hydrates, Mar. Petrol. Geol., 25(9): 884–895.
Lee, J. Y., Yun, T. S., Santamarina, J. C. and Ruppel, C., 2007. Observations related to tetrahydrofuran and methane hydrates for laboratory studies of hydrate-bearing sediments, Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst., 8(6): Q06003, doi: 10.1029/2006GC001531.
Long, D., Jackson, P. D., Lovell, M. A., Rochelle, C. A., Francis, T. J. G. and Schultheiss, P. J., 2005. Methane hydrates: problems in unlocking their potential, Petroleum Geology Conference Series, London, 6, 723–730.
Lu, X. B., Wang, L., Wang, S. Y. and Li, Q. P., 2008. Study on the mechanical properties of the Tetrahydrofuran hydrate deposit, 18th (2008) International Offshore and Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference Proceedings, Canada, 57–60.
Masui, A., Haneda, H., Ogata, Y. and Aoki, K., 2007. Mechanical properties of sandy sediment containing marine gas hydrates in deep sea offshore Japan, International Society Offshore & Polar Engineers, Lisbon, 53–56.
Masui, A., Miyazaki, K., Haneda, H., Ogata, Y. and Aoki, K., 2008a. Mechanical properties of natural gas hydrate bearing sediments retrieved from Eastern Nankai Trough, Offshore Technology Conference, Houston.
Masui, A., Miyazaki, K., Haneda, H., Ogata, Y. and Aoki, K., 2008b. Mechanical characteristics of natural and artificial gas hydrate bearing sediments, Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Gas Hydrates (ICGH 2008), Canada.
Milkov, A.V., 2004. Global estimates of hydrate-bound gas in marine sediments: how much is really out there? Earth-Sci. Rev., 66(3–4): 183–197.
Pierce, J., 2005. Gas pressure [methane hydrate exploration and extraction], Engineer, 293(7672): 16–17.
Ripmeester, J. A. and Ratcliffe, C. I., 1988. Low-temperature cross-polarization/magic angle spinning 13C NMR of solid methane hydrates: structure, cage occupancy, and hydration number, J. Phys. Chem., 92(2): 337–339.
Ripmeester, J. A., Tse, J. S., Ratcliffe, C. I. and Powell, B. M., 1987. A new clathrate hydrate structure, Nature, 325(6100): 135–136.
Sloan, E. D., 1998. Gas hydrates: review of physical/chemical properties, Energ. Fuel., 12(2): 191–196.
Stern, L. A., Kirby, S. H. and Durham, W. B., 1996. Peculiarities of methane clathrate hydrate formation and solid-state deformation, including possible superheating of water ice, Science, 273(5283): 1843–1848.
Vanoudheusden, E., Sultan, N. and Cochonat, P., 2004. Mechanical behaviour of unsaturated marine sediments: experimental and theoretical approaches, Mar. Geol., 213(1–4): 323–342.
Wang, D., Ma, W. and Chang, X., 2004. Analyses of behavior of stress-strain of frozen Lanzhou loess subjected to K0 consolidation, Cold Reg. Sci. Technol., 40(1–2): 19–29.
Winters, W. J., Pecher, I. A., Waite, W. F. and Mason, D. H., 2004. Physical properties and rock physics models of sediment containing natural and laboratory-formed methane gas hydrate, Am. Mineral., 89(8–9): 1221–1227.
Winters, W. J., Waite, W. F., Mason, D. H., Gilbert, L. Y. and Pecher, I. A., 2007. Methane gas hydrate effect on sediment acoustic and strength properties, J. Petrol. Sci. Eng., 56(1–3): 127–135.
Yun, T. S., Santamarina, J. C. and Ruppel, C., 2007. Mechanical properties of sand, silt, and clay containing tetrahydrofuran hydrate, J. Geophys. Res., 112(B4): B04106.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, Grant No. 2006AA09A209), the Major National S&T Program (Grant No. 2008ZX05026-004), the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program, Grant No. 2009CB219507) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 91010015).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Yh., Song, Yc., Yu, F. et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties of gas hydrate-bearing sediments using kaolin clay. China Ocean Eng 25, 113–122 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13344-011-0009-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13344-011-0009-6