Abstract
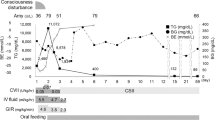
A 36-year-old woman presented to the emergency room with a consciousness disorder after developing abdominal pain with diarrhea for 2 days. She presented with marked hyperglycemia, ketoacidosis, and increased serum free fatty acid (FFA) levels; however, no elevation in the glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels was observed. Based on the marked depletion of insulin secretion, the patient was diagnosed as diabetic ketoacidosis attributed to fulminant type 1 diabetes (FT1D). Computed tomography on admission revealed severe fatty liver (FL), which improved 17 h following insulin treatment. Insulin treatment also suppressed the serum FFA levels. Some cases of FT1D with FL and liver dysfunction have been reported previously; however, its pathogenesis and clinical course remain unclear. Compared to previous reports, this case reported the shortest time for FL improvement. In this case, rapid and severe insulin deficiency led to a markedly high FFA level and significant accumulation of triglycerides in the hepatocytes, resulting in severe FL. A rapid and large dose of insulin was administered when systemic insulin sensitivity was nearly maximal owing to insulin deficiency, increased insulin efficacy, early reduction of FFA, suppressed triglyceride accumulation in the hepatocytes, and increased triglyceride excretion from the liver. All these factors could have contributed to the rapid improvement in FL.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Clinical data from the corresponding author are available upon request.
References
Takaike H, Uchigata Y, Iwamoto Y, Imagawa A, Iwahashi H, Kanatsuka A, Kawakaki E, Kobayashi T, Shimada A, Shimizu I, Maruyama T, Hanafusa T, Makino H. Nationwide survey to compare the prevalence of transient elevation of liver transaminase during treatment of diabetic ketosis or ketoacidosis in new-onset acute and fulminant type 1 diabetes mellitus. Ann Med. 2008;40(5):395–400.
Takaike H, Uchigata Y, Iwasaki N, Iwamoto Y. Transient elevation of liver transaminase after starting insulin therapy for diabetic ketosis or ketoacidosis in newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2004;64:27–32.
Kwong TC, Sparks JD, Cianci JF, Sparks CE. Inhibition of apolipoprotein B net synthesis and secretion from cultured rat hepatocytes by the calcium-channel blocker diltiazem. Europe PMC. 1989;263(2):411–5.
Sparks JD, Zolfaghari R, Sparks CE, Smith HC, Fisher EA. Impaired hepatic apolipoprotein B and E translation in streptozotocin diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1992;89(5):1418–30.
Eric F, Elizabeth L, Roger SM. Apolipoprotein B100 quality control and the regulation of hepatic very low density lipoprotein secretion. J Biomed Res. 2014;28(3):178–93.
Tamura S, Shimomura I. Contribution of adipose tissue and de novo lipogenesis to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:1139–42.
Ginsberg HN, Zhang YL, Hernandez-Ono A. Regulation of plasma triglycerides in insulin resistance and diabetes. Arch Med Res. 2005;36(3):232–40.
Chatila R, West AB. Hepatomegaly and abnormal liver tests due to glycogenosis in adults with diabetes. Medicine. 1996;75(6):327–33.
Sherigar JM, Castro JD, Yin YM, Guss D, Mohanty SR. Glycogenic hepatopathy: a narrative review. World J Hepatol. 2018;10(2):172–85.
Rogal SS, Ukomadu C, Levy BD, Loscalzo J. A sweet source of abdominal pain. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(18):1762–7 (Clinical problem-solving).
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the work of the past and present members of our department.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Noda, S., Harai, N., Komai, S. et al. Rapid improvement of severe fatty liver in a case of fulminant type 1 diabetes following insulin treatment. Diabetol Int 15, 297–301 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-023-00675-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-023-00675-5