Abstract
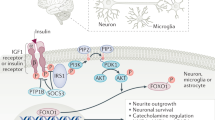
Various humoral factors are involved in the regulation of energy and glucose metabolism mediated by the interaction between the central nervous system and peripheral tissues. Insulin, which strictly regulates glucose metabolism in the liver, skeletal muscles, and adipose tissue, also plays a role in brain-mediated regulation of energy and glucose metabolism. Through the hypothalamus, insulin regulates not only diet intake and postprandial thermogenesis, but also glucose metabolism in the liver and skeletal muscles. Insulin exerts its action on the liver via the vagus nerve by activating phosphoinositide-3-kinase and KATP channels in the hypothalamic neurons. Central insulin action enhances the secretion of interleukin-6 from hepatic Kupffer cells and activates the transcription factor signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), which suppresses the expression of gluconeogenic enzyme genes in hepatocytes and thereby reducies hepatic glucose production. Brain-mediated suppression of hepatic glucose production also arises from an increase in the plasma histidine level. Histidine is converted to histamine in the hypothalamus, which activates hepatic STAT3 and thereby suppresses the expression of gluconeogenic enzyme genes via hypothalamic histamine H1 receptors. In obesity and type 2 diabetes, suppression of hepatic glucose production by central insulin action is impaired, potentially increasing hepatic glucose production. However, further studies are needed to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying the interaction between the central nervous system and peripheral tissues.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schwartz MW, Figlewicz DP, Baskin DG, Woods SC, Porte D Jr. Insulin in the brain: a hormonal regulator of energy balance. Endocr Rev. 1992;13:387–414.
Kaiyala KJ, Woods SC, Schwartz MW. New model for the regulation of energy balance and adiposity by the central nervous system. Am J Clin Nutr. 1995;62:1123S–34S.
Qi Y, Takahashi N, Hileman SM, Patel HR, Berg AH, Pajvani UB, Scherer PE, Ahima RS. Adiponectin acts in the brain to decrease body weight. Nat Med. 2004;10:524–9.
Kubota N, Yano W, Kubota T, Yamauchi T, Itoh S, Kumagai H, Kozono H, Takamoto I, Okamoto S, Shiuchi T, Suzuki R, Satoh H, Tsuchida A, Moroi M, Sugi K, Noda T, Ebinuma H, Ueta Y, Kondo T, Araki E, Ezaki O, Nagai R, Tobe K, Terauchi Y, Ueki K, Minokoshi Y, Kadowaki T. Adiponectin stimulates AMP-activated protein kinase in the hypothalamus and increases food intake. Cell Metab. 2007;6:55–68.
Field BC, Chaudhri OB, Bloom SR. Bowels control brain: gut hormones and obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2010;6:444–53.
Plum L, Belgardt BF, Bruning JC. Central insulin action in energy and glucose homeostasis. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:1761–6.
Obici S, Zhang BB, Karkanias G, Rossetti L. Hypothalamic insulin signaling is required for inhibition of glucose production. Nat Med. 2002;8:1376–82.
Corp ES, Woods SC, Porte D Jr, Dorsa DM, Figlewicz DP, Baskin DG. Localization of 125I-insulin binding sites in the rat hypothalamus by quantitative autoradiography. Neurosci Lett. 1986;70:17–22.
van Houten M, Posner BI, Kopriwa BM, Brawer JR. Insulin binding sites localized to nerve terminals in rat median eminence and arcuate nucleus. Sci. 1980;207:1081–3.
Marks JL, Porte D Jr, Stahl WL, Baskin DG. Localization of insulin receptor mRNA in rat brain by in situ hybridization. Endocrinol. 1990;127:3234–6.
Woods SC, Lotter EC, McKay LD, Porte D Jr. Chronic intracerebroventricular infusion of insulin reduces food intake and body weight of baboons. Nature. 1979;282:503–5.
Air EL, Strowski MZ, Benoit SC, Conarello SL, Salituro GM, Guan XM, Liu K, Woods SC, Zhang BB. Small molecule insulin mimetics reduce food intake and body weight and prevent development of obesity. Nat Med. 2002;8:179–83.
Bruning JC, Gautam D, Burks DJ, Gillette J, Schubert M, Orban PC, Klein R, Krone W, Muller-Wieland D, Kahn CR. Role of brain insulin receptor in control of body weight and reproduction. Sci. 2000;289:2122–5.
Niswender KD, Baskin DG, Schwartz MW. Insulin and its evolving partnership with leptin in the hypothalamic control of energy homeostasis. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2004;15:362–9.
Schwartz MW, Sipols AJ, Marks JL, Sanacora G, White JD, Scheurink A, Kahn SE, Baskin DG, Woods SC, Figlewicz DP. Inhibition of hypothalamic neuropeptide Y gene expression by insulin. Endocrinol. 1992;130:3608–16.
Ogawa W, Matozaki T, Kasuga M. Role of binding proteins to IRS-1 in insulin signalling. Mol Cell Biochem. 1998;182:13–22.
Landsberg L. Insulin-mediated sympathetic stimulation: role in the pathogenesis of obesity-related hypertension (or, how insulin affects blood pressure, and why). J Hypertens. 2001;19:523–8.
Hogan S, Himms-Hagen J. Brown adipose tissue of mice with gold thioglucose-induced obesity: effect of cold and diet. Am J Physiol. 1983;244:E581–8.
Rahmouni K, Morgan DA, Morgan GM, Liu X, Sigmund CD, Mark AL, Haynes WG. Hypothalamic PI3 K and MAPK differentially mediate regional sympathetic activation to insulin. J Clin Invest. 2004;114:652–8.
Koch L, Wunderlich FT, Seibler J, Konner AC, Hampel B, Irlenbusch S, Brabant G, Kahn CR, Schwenk F, Bruning JC. Central insulin action regulates peripheral glucose and fat metabolism in mice. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:2132–47.
Ader M, Bergman RN. Peripheral effects of insulin dominate suppression of fasting hepatic glucose production. Am J Physiol. 1990;258:E1020–32.
Lewis GF, Zinman B, Groenewoud Y, Vranic M, Giacca A. Hepatic glucose production is regulated both by direct hepatic and extrahepatic effects of insulin in humans. Diabetes. 1996;45:454–62.
Prager R, Wallace P, Olefsky JM. Direct and indirect effects of insulin to inhibit hepatic glucose output in obese subjects. Diabetes. 1987;36:607–11.
Ramnanan CJ, Edgerton DS, Cherrington AD. Evidence against a physiologic role for acute changes in cns insulin action in the rapid regulation of hepatic glucose production. Cell Metab. 2012;15:656–64.
Pocai A, Lam TK, Gutierrez-Juarez R, Obici S, Schwartz GJ, Bryan J, Aguilar-Bryan L, Rossetti L. Hypothalamic K(ATP) channels control hepatic glucose production. Nature. 2005;434:1026–31.
Inoue H, Ogawa W, Asakawa A, Okamoto Y, Nishizawa A, Matsumoto M, Teshigawara K, Matsuki Y, Watanabe E, Hiramatsu R, Notohara K, Katayose K, Okamura H, Kahn CR, Noda T, Takeda K, Akira S, Inui A, Kasuga M. Role of hepatic STAT3 in brain-insulin action on hepatic glucose production. Cell Metab. 2006;3:267–75.
Gelling RW, Morton GJ, Morrison CD, Niswender KD, Myers MG Jr, Rhodes CJ, Schwartz MW. Insulin action in the brain contributes to glucose lowering during insulin treatment of diabetes. Cell Metab. 2006;3:67–73.
Konner AC, Janoschek R, Plum L, Jordan SD, Rother E, Ma X, Xu C, Enriori P, Hampel B, Barsh GS, Kahn CR, Cowley MA, Ashcroft FM, Bruning JC. Insulin action in AgRP-expressing neurons is required for suppression of hepatic glucose production. Cell Metab. 2007;5:438–49.
Hill JW, Elias CF, Fukuda M, Williams KW, Berglund ED, Holland WL, Cho YR, Chuang JC, Xu Y, Choi M, Lauzon D, Lee CE, Coppari R, Richardson JA, Zigman JM, Chua S, Scherer PE, Lowell BB, Bruning JC, Elmquist JK. Direct insulin and leptin action on pro-opiomelanocortin neurons is required for normal glucose homeostasis and fertility. Cell Metab. 2010;11:286–97.
Spanswick D, Smith MA, Mirshamsi S, Routh VH, Ashford ML. Insulin activates ATP-sensitive K + channels in hypothalamic neurons of lean, but not obese rats. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:757–8.
Kishore P, Boucai L, Zhang K, Li W, Koppaka S, Kehlenbrink S, Schiwek A, Esterson YB, Mehta D, Bursheh S, Su Y, Gutierrez-Juarez R, Muzumdar R, Schwartz GJ, Hawkins M. Activation of K(ATP) channels suppresses glucose production in humans. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:4916–20.
Coomans CP, Biermasz NR, Geerling JJ, Guigas B, Rensen PC, Havekes LM, Romijn JA. Stimulatory Effect of Insulin on Glucose Uptake by Muscle Involves the Central Nervous System in Insulin-Sensitive Mice. Diabetes. 2011;60:3132–40.
Akira S. IL-6-regulated transcription factors. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1997;29:1401–18.
Ramnanan CJ, Saraswathi V, Smith MS, Donahue EP, Farmer B, Farmer TD, Neal D, Williams PE, Lautz M, Mari A, Cherrington AD, Edgerton DS. Brain insulin action augments hepatic glycogen synthesis without suppressing glucose production or gluconeogenesis in dogs. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:3713–23.
Inoue H, Ogawa W, Ozaki M, Haga S, Matsumoto M, Furukawa K, Hashimoto N, Kido Y, Mori T, Sakaue H, Teshigawara K, Jin S, Iguchi H, Hiramatsu R, LeRoith D, Takeda K, Akira S, Kasuga M. Role of STAT-3 in regulation of hepatic gluconeogenic genes and carbohydrate metabolism in vivo. Nat Med. 2004;10:168–74.
Ramadoss P, Unger-Smith NE, Lam FS, Hollenberg AN. STAT3 targets the regulatory regions of gluconeogenic genes in vivo. Mol Endocrinol. 2009;23:827–37.
O’Brien RM, Streeper RS, Ayala JE, Stadelmaier BT, Hornbuckle LA. Insulin-regulated gene expression. Biochem Soc Trans. 2001;29:552–8.
Herzig S, Long F, Jhala US, Hedrick S, Quinn R, Bauer A, Rudolph D, Schutz G, Yoon C, Puigserver P, Spiegelman B, Montminy M. CREB regulates hepatic gluconeogenesis through the coactivator PGC-1. Nature. 2001;413:179–83.
Awazawa M, Ueki K, Inabe K, Yamauchi T, Kubota N, Kaneko K, Kobayashi M, Iwane A, Sasako T, Okazaki Y, Ohsugi M, Takamoto I, Yamashita S, Asahara H, Akira S, Kasuga M, Kadowaki T. Adiponectin enhances insulin sensitivity by increasing hepatic IRS-2 expression via a macrophage-derived IL-6-dependent pathway. Cell Metab. 2011;13:401–12.
Eldar-Finkelman H. Glycogen synthase kinase 3: an emerging therapeutic target. Trends Mol Med. 2002;8:126–32.
Wallenius V, Wallenius K, Ahrén B, Rudling M, Carlsten H, Dickson SL, Ohlsson C, Jansson JO. Interleukin-6-deficient mice develop mature-onset obesity. Nat Med. 2002;8:75–9.
Kimura K, Nakamura Y, Inaba Y, Matsumoto M, Kido Y, Asahara SI, Matsuda T, Watanabe H, Maeda A, Inagaki F, Mukai C, Takeda K, Akira S, Ota T, Nakabayashi H, Kaneko S, Kasuga M, Inoue H. Histidine augments the suppression of hepatic glucose production by central insulin action. Diabetes. 2013;62:2266–77.
Cota D, Proulx K, Seeley RJ. The role of CNS fuel sensing in energy and glucose regulation. Gastroenterol. 2007;132:2158–68.
Lam TK, Gutierrez-Juarez R, Pocai A, Rossetti L. Regulation of blood glucose by hypothalamic pyruvate metabolism. Science. 2005;309:943–7.
Obici S, Feng Z, Morgan K, Stein D, Karkanias G, Rossetti L. Central administration of oleic acid inhibits glucose production and food intake. Diabetes. 2002;51:271–5.
Stancakova A, Civelek M, Saleem NK, Soininen P, Kangas AJ, Cederberg H, Paananen J, Pihlajamaki J, Bonnycastle LL, Morken MA, Boehnke M, Pajukanta P, Lusis AJ, Collins FS, Kuusisto J, Ala-Korpela M, Laakso M. Hyperglycemia and a common variant of GCKR are associated with the levels of eight amino acids in 9,369 Finnish men. Diabetes. 2012;61:1895–902.
Newgard CB, An J, Bain JR, Muehlbauer MJ, Stevens RD, Lien LF, Haqq AM, Shah SH, Arlotto M, Slentz CA, Rochon J, Gallup D, Ilkayeva O, Wenner BR, Yancy WS Jr, Eisenson H, Musante G, Surwit RS, Millington DS, Butler MD, Svetkey LP. A branched-chain amino acid-related metabolic signature that differentiates obese and lean humans and contributes to insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2009;9:311–26.
Anderson GH. Diet, neurotransmitters and brain function. Br Med Bull. 1981;37:95–100.
Su Y, Lam TK, He W, Pocai A, Bryan J, Aguilar-Bryan L, Gutierrez-Juarez R. Hypothalamic leucine metabolism regulates liver glucose production. Diabetes. 2012;61:85–93.
Lin HV, Accili D. Hormonal regulation of hepatic glucose production in health and disease. Cell Metab. 2011;14:9–19.
Ono H, Pocai A, Wang Y, Sakoda H, Asano T, Backer JM, Schwartz GJ, Rossetti L. Activation of hypothalamic S6 kinase mediates diet-induced hepatic insulin resistance in rats. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:2959–68.
Milanski M, Arruda AP, Coope A, Ignacio-Souza LM, Nunez CE, Roman EA, Romanatto T, Pascoal LB, Caricilli AM, Torsoni MA, Prada PO, Saad MJ, Velloso LA. Inhibition of hypothalamic inflammation reverses diet-induced insulin resistance in the liver. Diabetes. 2012;61:1455–62.
Kimura K, Ymada T, Matusmoto M, Kido Y, Hosooka T, Asahara S, Matsuda T, Ota T, Watanabe H, Sai Y, Miyamoto K, Kaneko S, Kasuga M, Inoue H. Endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibits STAT3-dependent suppression of hepatic gluconeogenesis via dephosphorylation and deacetylation. Diabetes. 2012;61:61–73.
Dentin R, Hedrick S, Xie J, Yates J 3rd, Montminy M. Hepatic glucose sensing via the CREB coactivator CRTC2. Sci. 2008;319:1402–5.
Acknowledgments
This review was presented as a part of the Lilly Award Lecture at the Japan Diabetes Society 2014, Osaka, Japan. I would like to sincerely acknowledge the inspiring guidance and continued support of my mentor, Masato Kasuga. I also thank my colleagues and collaborators who have contributed to the work performed over the past 15 years. Finally, I would like to acknowledge the commitment and generosity of the Frontier Science Organization and the College of Medical, Pharmaceutical and Health Sciences of Kanazawa University. I thank ThinkSCIENCE, Inc. (Tokyo, Japan) for help preparing the manuscript. This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI Grant Numbers 25126709, 26282022, and 26670599, and by the Daininaika-Doumonkai grant to H.I.
Conflict of interest
I declare that I have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, H. Molecular basis of brain-mediated regulation of hepatic glucose metabolism. Diabetol Int 5, 158–164 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-014-0185-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-014-0185-8