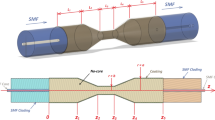
Abstract
The deposition of tetrakis (4-sulonatophenyl) porphyrin (TPPS) thin film on optical fibers presents many possibilities for sensing applications. The J-form aggregation with a narrow and sharp spectral feature at about 490 nm and its sensitivity to humidity have been discussed; a fast change of wavelength occurs according with variation in the humidity level. The reproducibility and high sensitivity of TPPS-coated fibers, along with the capabilities of optical fibers, suggest the device as a good candidate for humidity sensing in harsh environments.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References
T. L. Yeo, T. Sun, and K. T. V. Grattan, “Fibre-optic sensor technologies for humidity and moisture measurement,” Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2008, 144(2): 280–295.
M. Giordano, M. Russo, A. Cusano, A. Cutolo, G. Mensitieri, and L. Nicolais, “Optical sensor based on ultrathin films of δ-form syndiotactic polystyrene for fast and high resolution detection of chloroform,” Applied Physics Letters, 2004, 85(22): 5349–5351.
A. Cusano, P. Pilla, L. Contessa, A. Iadicicco, S. Campopiano, A. Cutolo, et al., “High-sensitivity optical chemosensor based on coated long-period gratings for sub-ppm chemical detection in water,” Applied Physics Letters, 2005, 87(23): 234105-1–234105-3.
S. Otsuki, K. Adachi, and T. Taguchi, “A novel fibre-optic gas sensing arrangement based on an air gap setting and an application to optical detection of humidity,” Analytical Sciences, 1998, 14(3): 633–635.
S. J. Glenn, B. M. Cullum, R. B. Nair, D. A. Nivens, C. J. Murphy, and S. M. Angel, “Lifetime-based fiber-optic water sensor using a luminescent complex in a lithium-treated Nafion (TM) membrane,” Analytica Chimica Acta, 2001, 448(1–2): 1–8.
S. Q. Tao, C. B. Winstead, R. Jindal, and J. P. Singh, “Optical-fibre sensor using tailored porous sol-gel fiber core,” IEEE Sensors Journal, 2004, 4(3): 322–328.
M. Bedoya, M. T. Díez, M. C. M. Bondi, and G. Orellana, “Humidity sensing with a luminescent Ru (II) complex and phase-sensitive detection,” Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2006, 113(2): 573–581.
S. Muto, O. Suzuki, T. Amano, and M. Morisawa, “A plastic optical fiber sensor for real-time humidity monitoring,” Measurement Science and Technology, 2003, 14(6): 746–750.
F. J. Arregui, Z. Ciaurriz, M. Oneca, and I. R. Matias, “An experimental study about hydrogels for the fabrication of optical fiber humidity sensors,” Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2003, 96(1–2): 165–172.
A. Gastón, F. Pérez, and J. Sevilla, “Optical fiber relative-humidity sensor with polyvinyl alcohol film,” Applied Optics, 2004, 43(21): 4127–4132.
A. A. Herrero, H. Guerrero, and D. Levy, “High-sensitivity sensor of low relative humidity based on overlay on side-polished fibers,” IEEE Sensors Journal, 2004, 4(1): 52–56.
L. Xu, J. C. Fanguy, K. Soni, and S. Tao, “Optical fiber humidity sensor based on evanescent-wave scattering,” Optics Letters, 2004, 29(11): 1191–1193.
J. M. Corres, J. Bravo, I. R. Matias, and F. J. Arregui, “Nonadiabatic tapered single-mode fiber coated with humidity sensitive nanofilms,” IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2006, 18(8): 935–937.
P. Kronenberg, P. K. Rastogi, P. Giaccari, and H. G. Limberger, “Relative humidity sensor with optical fiber Bragg gratings,” Optics Letters, 2002, 27(16): 1385–1387.
S. Luo, Y. Liu, A. Sucheta, M. Evans, and R. V. Tassell, “Applications of LPG fiber optical sensors for relative humidity and chemical-warfare-agents monitoring,” Advanced Sensor Systems and Applications, 2002, 4920: 193–205.
K. M. Tan, C. M. Tay, S. C. Tjin, C. C. Chan, and H. Rahardjo, “High relative humidity measurements using gelatin coated long-period grating sensors,” Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2005, 110(2): 335–341.
M. Konstantaki, S. Pissadakis, S. Pispas, N. Madamopoulos, and N. A. Vainos, “Optical fiber long-period grating humidity sensor with poly (ethylene oxide)/cobalt chloride coating,” Applied Optics, 2006, 45(19): 4567–4571.
S. H. Lim, L. Feng, J. W. Kemling, C. J. Musto, and K. S. Suslick, “An optoelectronic nose for detection of toxic gases,” Nature Chemistry, 2009, 1(7): 562–567.
K. M. Kadish, K. M. Smith, and R. Guilard, Handbook of the Porphyrin: inorganic, organometallic and coordination chemistry. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 2000.
X. B. Zhang, Z. Z. Li, C. C. Guo, S. H. Chen, G. L. Shen, and R. Q. Yu, “Porphyrin-metalloporphyrin composite based optical fiber sensor for the determination of berberine,” Analytica Chimica Acta, 2001, 439(1): 65–71.
X. B. Zhang, C. C. Guo, Z. Z. Li, G. L. Shen, and R. Q. Yu, “An optical fiber chemical sensor for mercury ions based on a porphyrin dimer,” Analytical Chemistry, 2002, 74(4): 821–825.
R. Ni, R. B. Tong, C. C. Guo, G. L. Shen, and R. Q. Yu, “An anthracene/porphyrin dimer fluorescence energy transfer sensing system for picric acid,” Talanta, 2004, 63(2): 251–257.
G. Huyang, J. Canning, M. L. Aslund, D. Stocks, T. Khoury, and M. J, Crossley, “Evaluation of optical fiber microcell reactor for use in remote acid sensing,” Optics Letters, 2010, 35(6): 817–819.
R. Selyanchyn, S. Korposh, W. Yasukochi, and S. W. Lee, “A preliminary test for skin gas assessment using a porphyrin based evanescent wave optical fiber sensor,” Sensors & Transducers, 2011, 125(2): 54–67.
S. Stelitano, G. De Luca, S. Savasta, and S. Patané, “Polarized emission from high quality microcavity based on active organic layered domains,” Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 93(19): 193302-1–193302-3.
K. Araki, M. J. Wagner, and M. S. Wrighton, “Layer-by-layer growth of electrostatically assembled multilayer porphyrin films,” Langmuir, 1996, 12(22): 5393–5398.
Z. J. Zhang, S. F. Hou, Z. H. Zhu, and Z. F. Liu, “Preparation and characterization of a porphyrin self-assembled monolayer with a controlled orientation on gold,” Langmuir, 2000, 16(2): 537–540.
L. M. Scolaro, A. Romeo, M. A. Castriciano, G. De Luca, S. Patanè, and N. Micali, “Porphyrin deposition induced by UV irradiation,” Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(8): 2040–2041.
G. D. Luca, G. Pollicino, A. Romeo, S. Patanè, and L. M. Scolaro, “Control over the optical and morphological properties of UV-deposited porphyrin structures,” Chemistry of Materials, 2006, 18(23): 5429–5436.
G. D. Luca, G. Pollicino, A. Romeo, and L. M. Scolaro, “Sensing behavior of tetrakis (4-sulfonatophenyl) porphyrin thin films,” Chemistry of Materials, 2006, 18(8): 2005–2007.
D. P. Bhopate, K. Kim, P. G. Mahajan, A. H. Gore, S. R. Patil, S. M. Majhi, et al., “Fluorescent chemosensor for quantitation of multiple atmospheric gases,” Journal of Nanomed Nanotechnol, 2017, 8(2): 1–9.
A. Bahrampour, A. Iadicicco, G. D. Luca, M. Giordano, A. Borriello, A. Cutolo, et al., “Porphyrin thin films on fibre optic probes through UV-light induced deposition,” Optics & Laser Technology, 2013, 49: 279–283.
A. Bahrampour, A. Iadicicco, G. D. Luca, M. Giordano, A. Cutolo, L. M. Scolaro, et al., “Sensing characteristics to acid vapors of a TPPS coated fiber optic: a preliminary analysis,” World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, International Journal of Chemical, Molecular, Nuclear, Materials and Metallurgical Engineering, 2012, 6(11): 989–992.
G. De Luca, A. Romeo, V. Villari, N. Micali, I. Foltran, E. Foresti, et al., “Self-organizing functional materials via ionic self assembly: porphyrins H- and J-aggregates on synthetic chrysotile nanotubes,” Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(20): 6920–6921.
G. Scheibe, “Variability of the absorption spectra of some sensitizing dyes and its cause,” Angewandte Chemie, 1936, 49: 563–564.
G. Scheibe, “Über die veränderlichkeit der absorptionsspektren in lösungen und die nebenvalenzen als ihre ursache,” Angewandte Chemie, 1937, 50(11): 212–219.
E. E. Jelley, “Spectral absorption and fluorescence of dyes in the molecular state,” Nature, 1936, 138(3502): 1009–1010.
J. S. Briggs and A. Herzenberg, “Sum rules for the vibronic spectra of helical polymers,” Journal of Physics B: Atomic and Molecular Physics, 1970, 3(12): 1663–1676.
F. C. Spano and C. Silva, “H-and J-aggregate behavior in polymeric semiconductors,” Annual Review of Physical Chemistry, 2014, 65: 477–500.
M. Sauer and J. Hofkens, Handbook of fluorescence spectroscopy and imaging: from ensemble to single molecules. Hoboken, New Jersey, USA: John Wiley & Sons, 2010: 1–290.
A. Eisfeld and J. S. Briggs, “The J- and H-bands of organic dye aggregates,” Chemical Physics, 2006, 324(2–3): 376–384.
R. H. Tredgold, “Langmuir-blodgett films: organic monolayer imaged,” Nature, 1985: 313(6001): 348–348.
K. M. Lenahan, Y. X. Wang, Y. Liu, R. O. Claus, J. R. Heflin, D. Marciu, et al., “Novel polymer dyes for nonlinear optical applications using ionic self-assembled monolayer technology,” Advanced Materials, 1998, 10(11): 853–855.
A. Bahrampour, “New hollow core fiber design and porphyrin thin film deposition method towards enhanced optical fiber sensors,” Ph.D. dissertation, University of Naples, Italy, 2013.
R. F. Pasternack, P. R. Huber, P. Boyd, G. Engasser, L. Francesconi, E. Gibbs, et al., “Aggregation of meso-substituted water-soluble porphyrins,” Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1972, 94(13): 4511–4517.
P. J. Collings, E. J. Gibbs, T. E. Starr, O. Vafek, C. Yee, L. A. Pomerance, et al., “Resonance light scattering and its application in determining the size, shape, and aggregation number for supramolecular assemblies of chromophores,” The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 1999, 103(40): 8474–8481.
A. G. Ardakani, S. M. Mahdavi, and A. R. Bahrampour, “Time-dependent theory for random lasers in the presence of an inhomogeneous broadened gain medium such as PbSe quantum dots,” Applied Optics, 2013, 52(6): 1317–1324.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://doi.org/creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Dehghani Sanij, M., Bahrampour, A. & Bahrampour, A.R. Resonant Light Scattering Toward Optical Fiber Humidity Sensors. Photonic Sens 9, 60–68 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13320-018-0519-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13320-018-0519-4