Abstract
Background and Objective
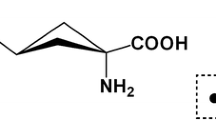
Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) is a binary cancer treatment that combines boron administration and neutron irradiation. The tumor cells take up the boron compound and the subsequent neutron irradiation results in a nuclear fission reaction caused by the neutron capture reaction of the boron nuclei. This produces highly cytocidal heavy particles, leading to the destruction of tumor cells. p-boronophenylalanine (BPA) is widely used in BNCT but is insoluble in water and requires reducing sugar or sugar alcohol as a dissolvent to create an aqueous solution for administration. The purpose of this study was to investigate the pharmacokinetics of 14C-radiolabeled BPA using sorbitol as a dissolvent, which has not been reported before, and confirm whether neutron irradiation with a sorbitol solution of BPA can produce an antitumor effect of BNCT.
Materials and Methods
In this study, we evaluated the sugar alcohol, sorbitol, as a novel dissolution aid and examined the consequent stability of the BPA for long-term storage. U-87 MG and SAS tumor cell lines were used for in vitro and in vivo experiments. We examined the pharmacokinetics of 14C-radiolabeled BPA in sorbitol solution, administered either intravenously or subcutaneously to a mouse tumor model. Neutron irradiation was performed in conjunction with the administration of BPA in sorbitol solution using the same tumor cell lines both in vitro and in vivo.
Results
We found that BPA in sorbitol solution maintains stability for longer than in fructose solution, and can therefore be stored for a longer period. Pharmacokinetic studies with 14C-radiolabeled BPA confirmed that the sorbitol solution of BPA distributed through tumors in much the same way as BPA in fructose. Neutron irradiation was found to produce dose-dependent antitumor effects, both in vitro and in vivo, after the administration of BPA in sorbitol solution.
Conclusion
In this report, we demonstrate the efficacy of BPA in sorbitol solution as the boron source in BNCT.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barth RF, Coderre JA, Vicente MGH, Blue TE. Boron neutron capture therapy of cancer: current status and future prospects. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:3987–4002.
Barth RF, Vicente MGH, Harling OK, Kiger WS 3rd, Riley KJ, Binns PJ, et al. Current status of boron neutron capture therapy of high grade gliomas and recurrent head and neck cancer. Radiat Oncol. 2012;7:146.
Locher GL. Biological effects of therapeutic possibilities of neutrons. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther. 1936;36:1–13.
Mishima Y, Honda C, Ichihashi M, Obara H, Hiratsuka J, Fukuda H, et al. Treatment of malignant melanoma by single thermal neutron capture therapy with melanoma-seeking 10B-compound. Lancet. 1989;2:388–9.
Hirose K, Konno A, Hiratsuka J, Yoshimoto S, Kato T, Ono K, et al. Boron neutron capture therapy using cyclotron-based epithermal neutron source and borofalan (10B) for recurrent or locally advanced head and neck cancer (JHN002): an open-label phase II trial. Radiother Oncol. 2021;155:182–7.
Mori Y, Suzuki A, Yoshino K, Kakihana H. Complex formation of p-boronophenylalanine with some monosaccharides. Pigment Cell Res. 1989;2:273–7.
Yoshino K, Suzuki A, Mori Y, Kakihana H, Honda C, Mishima Y, et al. Improvement of solubility of p-boronophenylalanine by complex formation with monosaccharides. Strahlenther Onkol. 1989;165:127–9.
Zhang Q, Ames JM, Smith RD, Baynes JW, Metz TO. A perspective on the Maillard reaction and the analysis of protein glycation by mass spectrometry: probing the pathogenesis of chronic disease. J Proteome Res. 2009;8:754–69.
van Rij CM, Sinjewel A, van Loenen AC, Sauerwein WAG, Wittig A, Kriz O, et al. Stability of 10B-l-boronophenylalanine-fructose injection. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2005;62:2608–10.
Halbert G, Elliott M, Ford S, Dick L, Schmidt E. Improved pharmaceutical stability of a boronphenylalanine mannitol formulation for boron neutron capture therapy. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2013;48:735–9.
Coderre JA, Button TM, Micca PL, Fisher CD, Nawrocky MM, Liu HB. Neutron capture therapy of the 9L rat gliosarcoma using the p-boronophenylalanine-fructose complex. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1994;30:643–52.
International Atomic Energy Agency. Current Status of Neutron Capture Therapy. IAEA-TECDOC-1223 (Internet). 2001; Available from: https://www.iaea.org/publications/6168/current-status-of-neutron-capture-therapy
Hiratsuka J, Fukuda H, Kobayashi T, Karashima H, Yoshino K, Imajo Y, et al. The relative biological effectiveness of 10B-neutron capture therapy for early skin reaction in the hamster. Radiat Res. 1991;128:186–91.
Fukuda H, Hiratsuka J, Honda C, Kobayashi T, Yoshino K, Karashima H, et al. Boron neutron capture therapy of malignant melanoma using 10B-paraboronophenylalanine with special reference to evaluation of radiation dose and damage to the normal skin. Radiat Res. 1994;138:435–42.
Heikkinen S, Savolainen S, Melkko P. In vitro studies on stability of L-p-boronophenylalanine-fructose complex (BPA-F). J Radiat Res. 2011;52:360–4.
Watanabe T, Hattori Y, Ohta Y, Ishimura M, Nakagawa Y, Sanada Y, et al. Comparison of the pharmacokinetics between L-BPA and L-FBPA using the same administration dose and protocol: a validation study for the theranostic approach using [18F]-L-FBPA positron emission tomography in boron neutron capture therapy. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:859.
Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency, Japan. Report on the Deliberation Results for Steboronine 9000 mg/300 mL for Infusion (March 3, 2020). Available from: https://www.pmda.go.jp/files/000237990.pdf
Ono K, Tanaka H, Tamari Y, Watanabe T, Suzuki M, Masunaga S-I. Proposal for determining absolute biological effectiveness of boron neutron capture therapy-the effect of 10B(n,α)7Li dose can be predicted from the nucleocytoplasmic ratio or the cell size. J Radiat Res. 2019;60:29–36.
Takeno S, Tanaka H, Ono K, Mizowaki T, Suzuki M. Analysis of boron neutron capture reaction sensitivity using Monte Carlo simulation and proposal of a new dosimetry index in boron neutron capture therapy. J Radiat Res. 2022;63:780–91.
Yokoyama K, Miyatake S-I, Kajimoto Y, Kawabata S, Doi A, Yoshida T, et al. Analysis of boron distribution in vivo for boron neutron capture therapy using two different boron compounds by secondary ion mass spectrometry. Radiat Res. 2007;167:102–9.
Soldin OP, Mattison DR. Sex differences in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2009;48:143–57.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for this work.
Conflict of interest
Three of the authors (T.Y., T.H., and K.U.) declare conflicts of interest based on their relationships with Stella Pharma Corporation. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Availability of data and materials
The raw data before analysis can be downloaded as supplementary data in this manuscript.
Code availability
Not applicable. No special codes were used in the analysis of this study’s data.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Author contributions
K.O., T.H., and K.U. conceived and designed the study. T.Y., H.T., Y.K., G.K., S.-I. M., and S. M. performed experiments and data analyses. T.W. performed additional data analyses. K.O., and S. M. supervised the project. T.W., T.H., and K.U. wrote the manuscript. All authors edited and approved the manuscript.
Ethics approval
The mice used in this study were cared for and treated according to the Recommendations for the Handling of Laboratory Animals for Biomedical Research by the Committee on Ethical Handling Regulations for Laboratory Animal Experiments, Kyoto University. Additionally, all animal experiments were approved by Ethical Handling Regulations for Laboratory Animal Experiments, Kyoto University (approval no. 200813) and conducted per the laboratory animal handling guidelines of our institution.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, T., Yoshikawa, T., Tanaka, H. et al. Pharmacokinetic Study of 14C-Radiolabeled p-Boronophenylalanine (BPA) in Sorbitol Solution and the Treatment Outcome of BPA-Based Boron Neutron Capture Therapy on a Tumor-Bearing Mouse Model. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 48, 443–453 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-023-00830-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-023-00830-y