Abstract
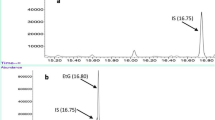
The objective of this work was to analyze transformation and excretion of β-asarone in rabbits with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS). The rabbits were administered IV at a dose of 30 mg/kg body weight β-asarone–water–propylene glycol (6:34:60, v/v/v), and urine and feces were collected within 6, 12 and 24 h. At 24 h, the animals were killed and bile was collected. Urine (2 mL) and bile (2 mL) samples were extracted with ether (4 mL), and the feces samples (2 g) were prepared by making an ether-feces (2:1, v/w) homogenate. Ether phase was evaporated and 25 µL psoralen–ether (2.95:1 w/v) was added. All samples were measured with GC–MS. β-Asarone was excreted in urine, feces and bile, and the excretion efficiency was about 62% in urine, 22% in feces, and 16% in bile. About 22% β-asarone was converted into α-asarone. Most β-asarone were excreted in 12 h. Gender differences accounted for no significant influence on the transformation and excretion of β-asarone.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cho J, Joo NE, Kong J-Y, Jeong D-Y, Lee KD, Kang B-S (2000) Inhibition of excitotoxic neuronal death by methanol extract of Acori graminei rhizoma in cultured rat cortical neurons. J Ethnopharmacol 73:31–37
Cho J, Ho Kim Y, Kong JY (2002) Protection of cultured rat cortical neurons from excitotoxicity by asarone, a major essential oil component in the rhizomes of Acorus gramineus. Life Sci 71(5):591
Fang YQ, Li L, Wu QD (2003) Effects of beta-asarone on gene expression in mouse brain. Zhong Yao Cai 26(9):650–652
Fang YQ, Fang RM, Fang GL, Jiang Y, Fu SY (2008) Effects of beta-asarone on expression of c-fos in kindling epilepsy rat brain. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 33(5):534–536
Fang YQ, Shi C, Liu L, Fang RM (2012) Pharmacokinetics of β-asarone in rabbit blood, hippocampus, cortex, brain stem, thalamus and cerebellum. Pharmazie 67:1–4. doi:10.1691/ph.2012.1100
Geng Y, Li C, Liu J, Xing G, Zhou L, Dong M, Li X, Niu Y (2010) Beta-asarone improves cognitive function by suppressing neuronal apoptosis in the beta-amyloid hippocampus injection rats. Biol Pharm Bull 33(5):836–843
Irie Y, Keung WM (2003) Rhizoma acori graminei and its active principles protect PC-12 cells from the toxic effect of amyloid-β peptide. Brain Res 963:282
Li C, Xing G, Dong M, Zhou L, Li J, Wang G, Zou D, Wang R, Liu J, Niu Y (2010) Beta-asarone protection against beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells via JNK signaling and modulation of Bcl-2 family proteins. Eur J Pharmacol 635(1–3):96–102
Liu L, Fang YQ (2011) Analysis of the distribution of β-asarone in rat hippocampus, brainstem, cortex and cerebellum with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS). J Med Plant Res 5(9):1728–1734
Liu J, Li C, Xing G, Zhou L, Dong M, Geng Y, Li X, Li J, Wang G, Zou D, Niu Y (2010) Beta-asarone attenuates neuronal apoptosis induced by beta amyloid in rat hippocampus. Yakugaku Zasshi 130(5):737–746
Zanoli P, Avallone R, Baraldi M (1998) Sedative and hypothermic effects induced by β-asarone, a main component of Acorus calamus. Phytother Res 12:S114–S116
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Guangdong Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 2003C34403). We would like to express our sincere thanks to the reviewers and editors for the constructive and positive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
C. Shi and L. Liu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, Y.Q., Shi, C., Liu, L. et al. Analysis of transformation and excretion of β-asarone in rabbits with GC–MS. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 37, 187–190 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-012-0083-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-012-0083-z