Abstract
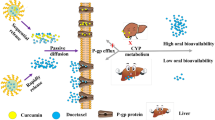
The present study investigated the effects of a curcumin self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) on the pharmacokinetics of orally administered docetaxel in rats. A single dose of docetaxel was orally administered (30 mg/kg) alone or after oral curcumin SEDDS (25, 50, 100 and 150 mg/kg) administration with time intervals of 0, 15 and 30 min, respectively. After oral administration, the C max and the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) of docetaxel were significantly increased (0 min, p < 0.05; 15 and 30 min, p < 0.01) by 2.2, 4.7 and 4.6 times and 2.0, 3.8 and 4.1 times compared to that of control group, respectively, after treatment with curcumin SEDDS (100 mg/kg) for each interval. Moreover, The C max of docetaxel was increased by 2.6 and 4.4 times in response to 25 and 50 mg/kg curcumin SEDDS treatment, respectively, the corresponding AUC was increased by about 2.4 and 3.1 times, and consequently the absolute bioavailabilities of docetaxel in these two treatment groups were 7.9 and 10.4%, respectively, which showed a significant increase of about 2.4- and 3.2-fold in comparison to the control value (3.3%). However, no further increase in either AUC or C max values of docetaxel was observed as the curcumin SEDDS dose was increased from 50 to 150 mg/kg. It is worth noting that the presence of curcumin SEDDS did not significantly decrease the systemic clearance, which was shown by the almost unchanged terminal half-life (t 1/2) of docetaxel in all treatment groups. Thus, the enhanced bioavailability of oral docetaxel by curcumin SEDDS seemed to be likely due to an inhibition function of cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A and P-glycoprotein (Pgp) in the intestines of the rats. However, further in vivo studies are needed to verify these hypotheses.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amit AK, Vandana BP (2008) Design and evaluation of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) of nimodipine. AAPS PharmSciTech 9:191–196
Anuchapreeda S, Leechanachai P, Smith MM, Ambudkar SV, Limtrakul PN (2002) Modulation of P-glycoprotein expression and function by curcumin in multidrug-resistant human KB cells. Biochem Pharmacol 64:573–582
Bissery MC, Guenard D, Gueritte-Voegelein F, Lavelle F (1991) Experimental antitumour activity of Taxotere (RP 56976, NSC 628503), a taxol analogue. Cancer Res 51:4845–4852
Breedveld P, Beijnen JH, Schellens JH (2006) Use of P-glycoprotein and BCRP inhibitors to improve oral bioavailability and CNS penetration of anticancer drugs. Trends Pharmacol Sci 27:17–24
Fisher GA, Sikic BI (1995) Clinical studies with modulators of multidrug resistance. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 9:363–382
Fracasso PM, Goldstein LJ, de Alwis DP, Rader JS, Arquette MA, Goodner SA, Wright LP, Fears CL, Gazak RJ, Andre VA, Burgess MF, Slapak CA, Schellens JH (2004) Phase I study of docetaxel in combination with the P-glycoprotein inhibitor, zosuquidar, in resistant malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 10:7220–7228
Gelderblom H, Verweij J, Nooter K, Sparreboom A (2001) Cremophor EL: the drawbacks and advantages of vehicle selection for drug formulation. Eur J Cancer 37:1570–1598
Gershanik T, Benita S (2000) Self-dispersing lipid formulations for improving oral absorption of lipophilic drugs. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 50:179–188
Gottesman MM, Pastan I (1989) Clinical trials of agents that reverse multidrug resistance. J Clin Oncol 7:409–411
Gueritte-Voegelin F, Guenard D, Lavelle F, Legoff MT, Mangatal L, Poiter P (1991) Relationships between the structure of taxol analogues and their antimitotic activity. J Med Chem 34:992–998
Hanauske AR, Degen D, Hilsenbeck SG, Bissery MC, Von Hoff DD (1992) Effects of Taxotere and taxol on in vitro colony formation of freshly explanted human tumour cells. Anti-Cancer Drugs 3:121–124
Herwaarden AE, Wagenaar E, Kruijssen CMM, Waterschoot RAB, Smit JW, Song JY, Valk MA, Tellingen O, Hoorn JWA, Rosing H, Heijnen JH, Schinkel AH (2007) Knockout of cytochrome P450 3A yields new mouse models for understanding xenobiotic metabolism. J Clin Invest 117:3583–3592
Horwitz SB (1992) Mechanism of action of taxol. Trends Pharmacol Sci 13:134–136
Kemper EM, Verheij M, Boogerd W, Beijnen JH, van Tellingen O (2004) Improved penetration of docetaxel into the brain by co-administration of inhibitors of P-glycoprotein. Eur J Cancer 40:1269–1274
Lin YG, Kunnumakkara AB, Nair A, Merritt WM, Han LY, Armaiz-Pena GN, Kamat AA, Spannuth WA, Gershenson DM, Lutgendorf SK, Aggarwal BB, Sood AK (2007) Curcumin inhibits tumour growth and angiogenesis in ovarian carcinoma by targeting the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway. Clin Cancer Res 13:3423–3430
Lown KS, Kolars JC, Thummel KE, Barnett JL, Kunze KL, Wrighton SA, Watkins PB (1994) Interpatient heterogeneity in expression of CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 in small bowel. Lack of prediction by the erythromycin breath test. Drug Metab Dispos 22:947–955
Malingré MM, Richel DJ, Beijnen JH, Hilde R, Franciska J, Koopman WW, Ten BH, Margaret ES, Jan HMS (2001) Coadministration of cyclosporine strongly enhances the oral bioavailability of docetaxel. J Clin Oncol 19:1160–1166
Marre F, Sanderink GJ, de Sousa G, Gaillard C, Martinet M, Rahmani R (1996) Hepatic biotransformation of docetaxel (Taxotere) in vitro: involvement of the CYP3A subfamily in humans. Cancer Res 56:1296–1302
Oostendorp RL, Huitema A, Rosing H, Jansen RS, Ter Heine R, Keessen M, Beijnen JH, Schellens JH (2009) Coadministration of ritonavir strongly enhances the apparent oral bioavailability of docetaxel in patients with solid tumours. Clin Cancer Res 15:4228–4233
Ozols RF, Cunnion RE, Klecker W, Hamilton TC, Ostchega Y, Parrillo JE, Young RC (1987) Verapamil and adriamycin in the treatment of drug-resistant ovarian cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 5:641–647
Patel D, Sawant KK (2009) Self micro-emulsifying drug delivery system: formulation development and biopharmaceutical evaluation of lipophilic drugs. Curr Drug Deliv 6:419–424
Pouton CW (1997) Formulation of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 25:47–58
Ringel I, Horwitz SB (1991) Studies with RP56976 (taxotere): a semisynthetic analogue of taxol. J Natl Cancer Inst 83:288–291
Romiti N, Tongiani R, Cervelli F, Chieli E (1998) Effects of curcumin on P-glycoprotein in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Life Sci 62:2349–2358
Shou M, Martinet M, Korzekwa KR, Krausz KW, Gonzalez FJ, Gelboin HV (1998) Role of human cytochrome P450 3A4 and 3A5 in the metabolism of Taxotere and its derivatives: Enzyme specificity, interindividual distribution and metabolic contribution in human liver. Pharmacogenetics 8:391–401
Sinko PJ, Kunta JR, Usansky HH, Perry BA (2004) Differentiation of gut and hepatic first pass metabolism and secretion of saquinavir in ported rabbits. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 310:359–366
Society of Toxicology (SOT) (2009) Guiding principles in the use of animals in toxicology. http://www.toxicology.org/AI/FA/guidingprinciples.pdf
Songyot A, Pranee L, Melissa MS, Suresh VA, Porn-ngarm L (2002) Modulation of P-glycoprotein expression and function by curcumin in multidrug-resistant human KB cells. Biochem Pharmacol 64:573–582
Sparreboom A, van Asperen J, Mayer U, Schinkel AH, Smit JW, Meijer DK, Borst P, Nooijen WJ, Beijnen JH, van Tellingen O (1997) Limited oral bioavailability and active epithelial secretion of paclitaxel caused by P-glycoprotein in the intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:2031–2035
Valentine SP, LeNedelec MJ, Menzies AR, Scandlyn MJ, Goodin MG, Rosengren RJ (2006) Curcumin modulates drug metabolizing enzymes in the female Swiss Webster mouse. Life Sci 78:2391–2398
Wils P, Phung-Ba V, Warnery A, Lechardeur D, Raeissi S, Hidalgo IJ, Scherman D (1994) Polarized transport of docetaxel and vinblastine mediated by P-glycoprotein in human intestinal epithelial cell monolayers. Biochem Pharmacol 48:1528–1530
Woo JS, Lee CH, Shim CK, Hwang SJ (2003) Enhanced oral bioavailability of paclitaxel by coadministration of the P-glycoprotein inhibitor KR30031. Pharm Res 20:24–30
Yan YD, Kim DH, Sung JH, Yong CS, Choi HG (2010) Enhanced oral bioavailability of docetaxel in rats by four consecutive days of pre-treatment with curcumin. Int J Pharm 399:116–120
Yan YD, Kim JA, Kwak MK, Yoo BK, Yong CS, Choi HG (2011) Enhanced oral bioavailability of curcumin via a solid lipid-based self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) using a spray-drying technique. Biol Pharm Bull 34:1179–1186
Yasuda K, Lan LB, Sanglard D, Furuya K, Schuetz JD, Schuetz EG (2002) Interaction of cytochrome P450 3A inhibitors with P-glycoprotein. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303:323–332
Zhang W, Tan TMC, Lim LY (2007) Impact of curcumin-induced changed in P-glycoprotein and CYP3A expression on the phamacokinetics of peroral celiprolol and midazolam in rats. Drug Metab Dispos 35:110–115
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (No. 2010-0024185), and the Mid-career Researcher Program through the NRF grant funded by the MEST (No. 2010-0000363) in South Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, YD., Marasini, N., Choi, Y.K. et al. Effect of dose and dosage interval on the oral bioavailability of docetaxel in combination with a curcumin self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS). Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 37, 217–224 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-011-0078-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-011-0078-1