Abstract
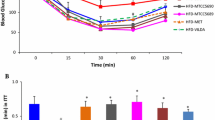
In recent studies we showed that gliclazide has no hypoglycemic effect on type 1 diabetic (T1D) rats while MKC does, and their combination exerted a better hypoglycemic effect than MKC alone. We also showed that the most hypoglycemic effect was noticed when T1D rats were treated with probiotics then gavaged with MKC + gliclazide (blood glucose decreased from 24 ± 3 to 10 ± 2 mmol/l). The aim of this study is to investigate the influence of probiotics on MKC pharmacokinetics when coadministered with gliclazide, in T1D rats. 80 male Wistar rats (weight 350 ± 50 g) were randomly allocated into 8 groups (10 rats/group), 4 of which were injected with alloxan (30 mg/kg) to induce T1D. Group 1 was healthy and group 2 was diabetic. Groups 3 (healthy) and 4 (diabetic) were gavaged with probiotics (75 mg/kg) every 12 h for 3 days and 12 h later all groups received a single oral dose of MKC + gliclazide (4 and 20 mg/kg respectively). The remaining 4 groups were treated in the same way but administered MKC + gliclazide via the i.v. route. Blood samples collected from T1D rats prior to MKC + gliclazide revealed that probiotic treatment alone reduced blood glucose levels twofold. When coadministered with gliclazide, the bioavailability of MKC was reduced in healthy rats treated with probiotics but remained the same in diabetic pretreated rats. The decrease in MKC bioavailability, when administered with gliclazide, caused by probiotic treatment in healthy but not diabetic rats suggests that probiotic treatment induced MKC metabolism or impaired its absorption, only in healthy animals. The different MKC bioavailability in healthy and diabetic rats could be explained by different induction of presystemic elimination of MKC in the gut by probiotic treatment.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam MJ, Rahman MA (1971) Changes in the saccharoid fraction in rats with alloxan-induced diabetes or injected with epinephrine. Clin Chem 17(9):915–920
Al-Salami H, Kansara H, King J, Morar B, Jayathilaka B, Fawcett PJ et al (2007) Bile acids: a bitter sweet remedy for diabetes. NZ Pharm J 27(10):17–20
Al-Salami H, Butt G, Tucker I, Mikov M (2008a) Influence of the semisynthetic bile acid (MKC) on the ileal permeation of gliclazide in healthy and diabetic rats. Pharmacol Reports 2008 60(4):532–541
Al-Salami H, Butt G, Tucker I, Mikov M (2008b) Probiotic treatment reduces blood glucose levels and increases systemic absorption of gliclazide in diabetic rats. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 33(2):101–106
Al-Salami H, Butt G, Tucker I, Mikov M (2008c) The influence of the symisynthetic bile acids, MKC on gliclazide PKs and glucose levels in healthy and diabetic rats after pre-treatment with probiotics. Med Hypothes and Res 4(2):1–9
Al-Salami H, Butt Grant, Tucker Ian, Mikov M (2008d) The influence of probiotics pre-treatment, on the ileal permeation of gliclazide, in healthy and diabetic rats. Archives Drug Inf 1(1):35–41
Al-Salami H, Butt G, Tucker I, Fawcett PJ, Golocorbin-Kon S, Mikov I et al (2009) Gliclazide reduces MKC intestinal transport in healthy but not diabetic rats. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 34(1):43–50
Bachmann K, Pardoe D, White D (1996) Scaling basic toxicokinetic parameters from rat to man. Environ Health Perspect 104(4):400–407
Ballatori N, Christian WV, Lee JY, Dawson PA, Soroka CJ, Boyer JL et al (2005) OSTalpha-OSTbeta: a major basolateral bile acid and steroid transporter in human intestinal, renal, and biliary epithelia. Hepatology 42(6):1270–1279
Bengmark S (1998) Ecological control of the gastrointestinal tract. The role of probiotic flora. Gut 42(1):2–7
Bezkorovainy A (2001) Probiotics: determinants of survival and growth in the gut. Am J Clin Nutr 73(2 Suppl):399S–405S
Bodo A, Bakos E, Szeri F, Varadi A, Sarkadi B (2003) Differential modulation of the human liver conjugate transporters MRP2 and MRP3 by bile acids and organic anions. J Biol Chem 278(26):23529–23537
Braaten JT, Faloona GR, Unger RH (1974) The effect of insulin on the alpha-cell response to hyperglycemia in long-standing alloxan diabetes. J Clin Invest 53(4):1017–1021
Brinton EA (2008) Novel pathways for glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes: focus on bile acid modulation. Diabetes Obes Metab 10(11):1004–1011
Campbell DB, Lavielle R, Nathan C (1991) The mode of action and clinical pharmacology of gliclazide: a review. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 14(Suppl 2):S21–S36
Cardin S, Walmsley K, Neal DW, Williams PE, Cherrington AD (2002) Involvement of the vagus nerves in the regulation of basal hepatic glucose production in conscious dogs. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 283(5):E958–E964
CarvalhoI ENd, CarvalhoII NASd, Ferreira. LM. Experimental model of induction of diabetes mellitus in rats. Acta Cirurgica Brasileira. 2003;18(3):120-67
Chen ZS, Guo Y, Belinsky MG, Kotova E, Kruh GD (2005) Transport of bile acids, sulfated steroids, estradiol 17-beta-d-glucuronide, and leukotriene C4 by human multidrug resistance protein 8 (ABCC11). Mol Pharmacol 67(2):545–557
Daugherty AL, Mrsny RJ (1999) Transcellular uptake mechanisms of the intestinal epithelial barrier Part one. Pharm Sci Technol Today 4(2):144–151
DeCarvalhoI E, CarvalhoII N, Ferreira L (2003) Experimental model of induction of diabetes mellitus in rats. Acta Cirurgica Brasileira 18(3):120–167
Delrat P, Paraire M, Jochemsen R (2002) Complete bioavailability and lack of food-effect on pharmacokinetics of gliclazide 30 mg modified release in healthy volunteers. Biopharm Drug Dispos 23(4):151–157
Devendra D, Liu E, Eisenbarth GS (2004) Type 1 diabetes: recent developments. BMJ 328(7442):750–4
Dow J, Lindsay G, Morrison J (1996) Biochemistry molecules, cells and the body. Addison-Wesley Publishing, Boston, pp 418–22
Esmaeili MA, Yazdanparast R (2004) Hypoglycaemic effect of teucrium polium: studies with rat pancreatic islets. J Ethnopharmacol 95(1):27–30
Fallucca F, Sciullo E, Maldonato A (1996) Combined therapy with insulin and sulfonylurea for the treatment of new-onset insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Horm Metab Res 28(2):86–88
FAO/WHO (2001) Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food 2002
Florkowski CM, Richardson MR, Le Guen C, Jennings PE, O’Donnell MJ, Jones AF et al (1988) Effect of gliclazide on thromboxane B2, parameters of haemostasis, fluorescent IgG and lipid peroxides in non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res 9(2):87–90
Goldfine AB (2008) Modulating LDL cholesterol and glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: targeting the bile acid pathway. Curr Opin Cardiol 23(5):502–511
Gonzalez J, Hidalgo F, Lopez MA, Esteller A (1983) Influence of bile salts on the endogenous excretion of bile pigments. Rev Esp Fisiol 39(1):69–75
Gonzalez-Alvarez I, Fernandez-Teruel C, Casabo-Alos VG, Garrigues TM, Polli JE, Ruiz-Garcia A et al (2007) In situ kinetic modelling of intestinal efflux in rats: functional characterization of segmental differences and correlation with in vitro results. Biopharm Drug Dispos 28(5):229–239
Hong SS, Lee SH, Lee YJ, Chung SJ, Lee MH, Shim CK (1998) Accelerated oral absorption of gliclazide in human subjects from a soft gelatin capsule containing a PEG 400 suspension of gliclazide. J Control Release 51(2–3):185–192
Houten S, Watanabe M, Auwerx J (2006) Endocrine functions of bile acids. EMBO J 25:1419–1425
Huang H, Shan J, Pan XH, Wang HP, Qian LB (2006) Carvedilol protected diabetic rat hearts via reducing oxidative stress. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 7(9):725–731
Jacobs DB, Hayes GR, Lockwood DH (1989) In vitro effects of sulfonylurea on glucose transport and translocation of glucose transporters in adipocytes from streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes 38(2):205–211
Karimi O, Pena AS (2003) Probiotics: Isolated bacteria strain or mixtures of different strains? Two different approaches in the use of probiotics as therapeutics. Drugs Today (Barc) 39(8):565–597
Khavinson VK (2005) Effect of tetrapeptide on insulin biosynthesis in rats with alloxan-induced diabetes. Bull Exp Biol Med 140(4):452–454
Korec R (1980) Treatment of alloxan and streptozotocin diabetes in rats by intrafamiliar homo (allo) transplantation of neonatal pancreases. Endocrinol Exp 14(3):191–198
Kramer W, Wess G, Neckermann G, Schubert G, F ink J, Girbig F et al (1994) Intestinal absorption of peptides by coupling to bile acids. J Biol Chem 269(14):10621–10627
Krittaphol W, Wescombe PA, Thomson CD, McDowell A, Tagg JR, Fawcett JP (2011a) Metabolism of l-Selenomethionine and Selenite by Probiotic Bacteria: in vitro and in vivo studies. Biol Trace Elem Res
Krittaphol W, McDowell A, Thomson CD, Mikov M, Fawcett JP (2011b) Biotransformation of l-selenomethionine and selenite in rat gut contents. Biol Trace Elem Res [Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t] 139(2):188–96
Kuhajda K, Kevresan S, Mikov M, Sabo A (1997) D. M. 3a, 7a-dihydroxy-12-keto-5β-cholanate as an enhancer of insluin nasal absorption in rats. Arch Toxicol Kinet Xenobiot 5:359–361
Levy P (2008) Bile acid sequestrants as a therapeutic option for glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocr Pract 14(5):644–647
Madsen D, Beaver M, Chang L, Bruckner-Kardoss E, Wostmann B (1976) Analysis of bile acids in conventional and germfree rats. J Lipid Res 17(2):107–111
Meinders AE, Van Berge Henegouwen GP, Willekens FL, Schwerzel AL, Ruben A, Huybregts AW (1981) Biliary lipid and bile acid composition in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Arguments for increased intestinal bacterial bile acid degradation. Dig Dis Sci 26(5):402–408
Merlob P, Levitt O, Stahl B (2002) Oral antihyperglycemic agents during pregnancy and lactation: a review. Paediatr Drugs 4(11):755–760
Mikov M, Fawcett JP (2006) Chemistry, biosynthesis, analysis, chemical & metabolic transformations and pharmacology. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 31(3):133–134
Mikov M, Fawcett JP, Kuhajda K, Kevresan S (2006) Pharmacology of bile acids and their derivatives: absorption promoters and therapeutic agents. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 31(3):237–251
Mikov M, Boni NS, Al-Salami H, Kuhajda K, Kevresan S, Golocorbin-Kon S et al (2007) Bioavailability and hypoglycemic activity of the semisynthetic bile acid salt, sodium 3alpha, 7alpha-dihydroxy-12-oxo-5beta-cholanate, in healthy and diabetic rats. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 32(1):7–12
Mikov M, Al-Salami H, Fawcett JP (2008) The influence of 3a, 7a-dihydroxy-12-keto-5β-cholanate on gliclazide pharmacokinetics and glucose levels in a rat model of diabetes. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 33(3):137–142
Miljkovic D, Kuhajda K, (1996) J. H. Selective C-12 oxidation of cholic acid. Chem Res 2(1):106–7
Mita S, Suzuki H, Akita H, Hayashi H, Onuki R, Hofmann AF et al (2006) Inhibition of bile acid transport across Na+/taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (SLC10A1) and bile salt export pump (ABCB 11)-coexpressing LLC-PK1 cells by cholestasis-inducing drugs. Drug Metab Dispos 34(9):1575–1581
Moursagaleeva G, Khafizianova RK, Kiyasov AP (1998) The elevating blood glucose levels as result of increasing of A-cell population in alloxan-induced diabetes in rats. Pathophysiology 5(Suppl 1):177
Noda Y, Mori A, Packer L (1997) Gliclazide scavenges hydroxyl, superoxide and nitric oxide radicals: an ESR study. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol 96(2):115–124
Palmer KJ, Brogden RN (1993) Gliclazide. An update of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Drugs 46(1):92–125
Pigeon RM, Cuesta EP, Gililliand SE (2002) Binding of free bile acids by cells of yogurt starter culture bacteria. J Dairy Sci 85(11):2705–2710
Ponz De Leon M, Ferenderes R, Carulli N (1976) Bile composition in patients with high risk of cholelithiasis. Minerva Med 67(53):3483–3490
Reasner CA (2008) Reducing cardiovascular complications of type 2 diabetes by targeting multiple risk factors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 52(2):136–144
Renier G, Desfaits AC, Serri O (2000) Effect of gliclazide on monocyte-endothelium interactions in diabetes. J Diabetes Complicat 14(4):215–223
Rieutord A, Stupans I, Shenfield GM, Gross AS (1995) Gliclazide hydroxylation by rat liver microsomes. Xenobiotica 25(12):1345–1354
Roberts MS, Magnusson BM, Burczynski FJ, Weiss M (2002) Enterohepatic circulation: physiological, pharmacokinetic and clinical implications. Clin Pharmacokinet 41(10):751–790
Rozanova GN, Voevodin DA, Stenina MA, Kushnareva MV (2002) Pathogenetic role of dysbacteriosis in the development of complications of type 1 diabetes mellitus in children. Bull Exp Biol Med 133(2):164–166
Rudman D, Kendall FE (1957a) Bile acid content of human serum. II. The binding of cholanic acids by human plasma proteins. J Clin Invest 36(4):538–542
Rudman D, Kendall FE (1957b) Bile acid content of human serum. I. Serum bile acids in patients with hepatic disease. J Clin Invest 36(4):530–537
Satoh J, Takahashi K, Takizawa Y, Ishihara H, Hirai M, Katagiri H et al (2005) Secondary sulfonylurea failure: comparison of period until insulin treatment between diabetic patients treated with gliclazide and glibenclamide. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 70(3):291–297
Setchell KD, Worthington J (1982) A rapid method for the quantitative extraction of bile acids and their conjugates from serum using commercially available reverse-phase octadecylsilane bonded silica cartridges. Clin Chim Acta 125(2):135–144
Shaham O, Wei R, Wang TJ, Ricciardi C, Lewis GD, Vasan RS et al (2008) Metabolic profiling of the human response to a glucose challenge reveals distinct axes of insulin sensitivity. Mol Syst Biol 4:214
Simoni P, Cerre C, Cipolla A, Polimeni C, Pistillo A, Ceschel G et al (1995) Bioavailability study of a new, sinking, enteric-coated ursodeoxycholic acid formulation. Pharmacol Res 31(2):115–119
Smith RJ (1990) Effects of the sulfonylureas on muscle glucose homeostasis. Am J Med 89(2A):38S–43S (discussion 51S-3S)
Stetinova V, Kvetina J, Pastera J, Polaskova A, Prazakova M (2007) Gliclazide: pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationships in rats. Biopharm Drug Dispos 28(5):241–248
Szkudelski T (2001) The mechanism of alloxan and streptozotocin action in B cells of the rat pancreas. Physiol Res 50(6):537–546
Uchida K, Makino S, Akiyoshi T (1985) Altered bile acid metabolism in nonobese, spontaneously diabetic (NOD) mice. Diabetes 34(1):79–83
Yang L, Zhang H, Mikov M, Tucker IG (2009) Physicochemical and biological characterization of monoketocholic acid, a novel permeability enhancer. Molecular Pharmaceutics [Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov’t] 6(2):448–56
Ziegler AG, Schmid S, Huber D, Hummel M, Bonifacio E (2003) Early infant feeding and risk of developing type 1 diabetes-associated autoantibodies. JAMA 290(13):1721–1728
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a University of Otago Research Grant. Probiotic bacteria were a kind gift of Professor John Tagg, Microbiology Department, University of Otago, Dunedin, New Zealand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Salami, H., Butt, G., Tucker, I. et al. Probiotics decreased the bioavailability of the bile acid analog, monoketocholic acid, when coadministered with gliclazide, in healthy but not diabetic rats. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 37, 99–108 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-011-0060-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-011-0060-y