Abstract
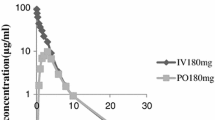
The pharmacokinetics of vertilmicin was investigated in rats and dogs following intramuscular or intravenous administration of vertilmicin. Following a single administration of an intramuscular dose, serum concentrations of vertilmicin peaked at 0.63 h in rats and 0.58 h in dogs. In rats, after intravenous administration of vertilmicin at dosages of 10, 20, and 40 mg/kg, the t 1/2 values for vertilmicin were 0.81, 0.76, and 0.86 h, respectively, while after intramuscular administration of vertilmicin at dose of 20 mg/kg, the t 1/2 value for vertilmicin was 0.79 h. In dogs, after intravenous or intramuscular administration of vertilmicin at a dose of 10 mg/kg, the t 1/2 values for vertilmicin were 0.83 and 0.85 h, respectively. After intravenous dosing to rats vertilmicin was distributed to most organs and tissues, and kidney tissue exhibited the highest exposure, while the tissue with the lowest exposure was the brain. Following single intravenous administration of vertilmicin at a dose of 20 mg/kg to rats, about 81.1% of the vertilmicin was excreted in urine, while only 3.12 and 1.44% of the administered dose was excreted in feces and bile within 48 h. The mean values for the plasma protein binding of vertilmicin were 22.7 and 20.4% in rats and dogs, respectively. These results indicate that vertilmicin was rapidly absorbed and widely distributed into various tissues in rats. The pharmacokinetic behavior of vertilmicin was dose-dependent when increasing doses of vertilmicin were administered intravenously to rats. Renal excretion was the primary elimination route of vertilmicin following intravenous administration to rats.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Q, Guo DW, Sun MQ, Li JT (1995) Comparison tissue distribution in rat and plasma protein binding between antibiotic 89-07 and gentamicin. Chin J Antibiot 20:439–441
Fujino A, Uda F, Nomonobu A, Tokiwa T (1982) Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of netilmicin in rats (IV). Distribution in kidney and transmigration to fetus or suckling. Jpn J Antibiot 35:979–986
Li CR, Yang XY, Lou RH, Zhang WX, Wang YM, Yuan M, Li Y, Chen HZ, Hong B, Sun CH, Zhao LX, Li ZR, Jiang JD (2008) In vitro antibacterial activity of vertilmicin and its susceptibility to modifications by the recombinant AAC6′-APH2″ enzyme. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52:3875–3882
Liu CX, Wei GL, Gu YB, Li QS, Xiao SH (2001) Balance dialyser. China Invention Patent Bulletin
Liu Z, Sha Y, Huang T, Yang B, Duan GL (2005) High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of vertilmicin in rat plasma using sensitive fluorometric derivatization. J Chromatogr B 828:2–8
Lu H, Zhang P, Li JT (1995) In vivo pharmacokinetic studies on antibiotic 89-07 and gentamicin in animals. Chin J Antibiot 20:434–438
Tokiwa T, Ohashi H (1982) Absorption, excretion and metabolism of netilmicin in beagle dogs. Jpn J Antibiot 35:987–992
Uda F, Ohashi H, Tokiwa T (1982a) Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of netilmicin in rats (I). Metabolic fate of netilmicin after a single dose. Jpn J Antibiot 35:950–959
Uda F, Fujino A, Tokiwa T (1982b) Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of netilmicin in rats (III). Metabolic fate of 14C-netilmicin after intramuscular administration. Jpn J Antibiot 35:967–978
Zhou MJ, Wei GL, Liu YP, Sun YM, Xiao SH, Lu R, Liu CX, Zhong DF (2003) Determination of vertilmicin in rat serum by high-performance liquid chromatography using 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene derivatization. J Chromatogr B 798:43–48
Acknowledgments
This paper was supported in part by the National Basic Research Project (973 Plan) of the Ministry of Science and Technology, China, No. 2007CB516807.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, MJ., Su, MY., Wan, RZ. et al. Pharmacokinetics of vertilmicin, a novel aminoglycoside antibiotic, in rats and dogs. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 35, 47–53 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-010-0007-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-010-0007-8