Abstract
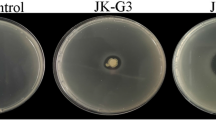
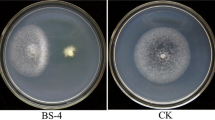
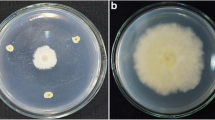
In recent years, crown gall of flowering cherry saplings, caused by Agrobacterium tumefaciens, become a serious disease in Xuzhou, China. In this study, the average disease incidence rate in the flowering cherry sapling was 76%, and the disease index was 38. Three-year-old flowering cherry saplings were the most susceptible, and the low-lying terrain was the most favorable condition for the disease. Two strains with distinct antagonistic effects against Agrobacterium tumefaciens were screened simultaneously from the rhizospheric soil of flowering cherry saplings and were named JK-XZ3 and JK-XZ8. The JK-XZ3 and JK-XZ8 strains were identified as Bacillus albus and B. velezensis, respectively, via morphological observation, physiological analysis, biochemical identification and multilocus sequence analysis. The strains JK-XZ3 and JK-XZ8 could effectively prevent the growth of A. tumefaciens. In a greenhouse experiment, the incidence of crown gall in flowering cherry seedlings without the JK-XZ3 and JK-XZ8 treatments was 100%, and the mean diameter of the root nodules was 18.8 mm. The disease incidence in seedlings treated with the JK-XZ3 and JK-XZ8 strains was 16.7% and 22.3%, respectively, and the mean diameter of the root nodules was 6.5 mm and 8.4 mm, respectively. In the field trials, the incidence of crown gall in untreated cherry saplings was 86%, while the incidence of crown gall in saplings treated with the JK-XZ3 and JK-XZ8 strains was 32% and 38%, respectively. These results indicate that the JK-XZ3 and JK-XZ8 strains have a high potential as biological control agents for crown gall of flowering cherry saplings.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandra K, Xiao H, Anke H et al (2004) Structural and functional characterization of gene clusters directing nonribosornal synthesis of bioactive cyclic lipopeptides in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strains FZB42. J Bacteriol 186:1084–1096
Aeini M, Mirzaee H, Taghavi SM et al (2014) Occurrence of crown gall disease on Ficus benjamina in Fars and Isfahan provinces of Iran. Arch Phytopathol Plant Protect 47:2257–2262
Abdallah DB, Frikha-Gargouri O, Tounsi S (2015) Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain 32a as a source of lipopeptides for biocontrol of Agrobacterium tumefaciens strains. Journal of Applied Microbiology 119(1):196–207
Cao FM, Yang XH, Ma MC et al (2014) Advances in identification methods of Bacillus subtilis closely related populations. Bulletin of Microbiology 5:968–974
Chen F, Guo YB, Wang JH, Li JY, Wang HM (2007) Biological control of grape crown gall by Rahnella aquatilis HX2. Plant Dis 91:957–963
Cheng HB, Liu XQ, Chen HM (2006) Research advance in controlling plant fungous diseases by Bacillus subtilis. Acta Agric Shanghai 22:109–112
Fei MJ, Chen JS, Wang XY (2006) Biochemical properties of phosphatase in the leaves of wheat. Acta Botan Boreali-Occiden Sin 26:110
Frikha-Gargouri O, Abdallah DB, Ghorbel I et al (2016) Lipopeptides from a novel Bacillus amethylotrophicus, 39b strain suppress Agrobacterium, crown gall tumours on tomato plants. Pest Manag Sci 73
Fan B, Borriss R, Bleiss W et al (2012) Gram-positive rhizobacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciensFZB42 colonizes three types of plants in different patterns. J Microbiol 50:38–44
Fan B, Chen XH, Budiharjo A, Bleiss W, Vater J, Borriss R (2011) Efficient colonization of plant roots by the plant growth promoting bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42, engineered to express green fluorescent protein[J]. J Biotechnol 151:303–311
Fan B, Li YL, Li L, Peng XJ, Bu C, Wu XQ, Borriss R (2017) Malonylome of the plant growth promoting rhizobacterium with potent biocontrol activity, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, FZB42. Data in Brief 10:548–550
Gao ZL, Qian L, Guo RJ et al (2015) Suppression effect of two peach rhizobacteria Alcaligenes faecalis on crown gall disease caused by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Journal of Fruit Science 32:267–273
Gupta AK, Kishore K, Bhardwaj SS et al (2010) Biological control of crown gall on peach and cherry rootstock colt by native Agrobacterium radiobacter isolates. Open Horticulture Journal 3:1–10
Huang LD, Chen YH (2006) Application of microorganism and related biotechnology to biological control of plant diseases. Journal of Southwest Forestry College 26:85–89
Huang L, Li QC, Hou Y et al (2017) Bacillus velezensis strain HYEB5-6 as a potential biocontrol agent against anthracnose on euonymus japonicus. Biocontrol Sci Tech 2017:1–18
Hu Zl, Zheng CY, Tian XY, et al. (2017) Determination of antibacterial Spectrum and stability of fermentation broth of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens HZM9 strain. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University, (3)
Tolba IH, Soliman MA (2013) Efficacy of native antagonistic bacterial isolates in biological control of crown gall disease in Egypt. Annals of Agricultural Sciences 58:43–49
Ji J, Wu XQ, He LX et al (2011) Occurrence of bamboo rust Brown spot in Nanjing. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University 35:123–126
Pascual J, Macián MC, Arahal DR et al (2010) Multilocus sequence analysis of the central clade of the genus Vibrio by using the 16S rRNA, recA, pyrH, rpoD, gyrB, rctB and toxR genes. International Journal of Systematic & Evolutionary Microbiology 60:154
Kerr A, Panagopoulo CG (1977) Biotype of Agrobaeterium radiobacter and their biological control. Photopathology 90:172–179
Kawaguchi A, Inoue K (2012) New antagonistic strains of non-pathogenic Agrobacterium vitis to control grapevine crown gall. J Phytopathol 160:509–518
Liang J (2007) Screening of antagonistic bacteria against poplar root cancer and preliminary study on its antagonistic activity MSc. Hebei Agricultural University
Li X (2005) The biocontrol progress on crown gall disease of fruit tree. Journal of Dalian Nationalities University 7:33–35
Li Z, Xiao Y, Wang R (2006) A preliminary study on screening antagonistic fungi against Agrobacterium tumefaciens and the antibacterial activity. Journal of Mountain Agriculture and Biology 25:229–232
Liu XY, Tian SZ, Qin GF et al (1997) An improved method for extracting DNA from plants and microorganisms using SDS-CTAB. Journal of Beijing Forestry University 19:101–104
Liu Y, Du J, Lai Q et al (2017) Proposal of nine novel species of the bacillus cereus group. International Journal of Systematic & Evolutionary Microbiology 67:2499
Oliwa-Stasiak K, Molnar CI, Arshak K, Bartoszcze M, Adley CC (2010) Development of a PCR assay for identification of the Bacillus cereus group species. J Appl Microbiol 108:266–273
Ren LL, Wang Y, Ma FL et al (2007) Relationship between soil environment and occurrence of crown gall disease in Shanghai. Ecol Environ 16:498–502
Shu QL, Feng Y, Zuo AR et al (2015) Application of gradient dilution and simple drop plate method in isolation of environmental γ-proteobacteria. Development and Application 25:281–300
Tzifira T, Citovsky V (2008) Agrobacterium: from biology to biotechnology. Springer New York
Wang S, Ji J, Ma H et al (2014a) A novel antibacterial peptide active against peach crown gall (Agrobacterium tumefaciens) isolated from cyanide-tolerant actinomycetes G19. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 31:69–74
Wang ZL, Jin YT, Tan ZW et al (2014b) Identification of the pathogen from Cerasus crown gall in Ningbo. Plant Prot 40:147–150
Wang LT, Lee FL, Tai CJ, Kuo HP (2008) Bacillus velezensis is a later heterotypic synonym of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:671–675
Wu JP, Song ZH et al (2009) Resistance mechanism of antagonistic bacterium in plant disease biocontrol. Hubei Agricultural Sciences 48:2286–2288
Wan QL (2016) Isolation of pathogens of peach root cancer and screening of antagonistic bacteria. (doctoral dissertation)
Yu XM, Zheng FC, Lin C et al (2009) Isolation and identification of siderphore producing bacteria CAS15 from the soil. Journal of Plant Protection 36:129–135
Zhao YJ, Zhang HL (2009) Isolation, purification and molecular weight determination of Agrobacterium mutant MI15. Hubei Agricultural Sciences 48:2451–2455
Zhang YZ, Chen GH (2007) Study on the relationship between the incidence of rice leafhopper and disease index[J]. Journal of Biological Disaster Sciences 30:117–118
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFD0600104) and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD). We are grateful to Dr. De-Wei Li, The Connecticut Agricultural Experiment Station, USA for reviewing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, P., Zhang, XT., Hu, LJ. et al. Two novel strains, Bacillus albus JK-XZ3 and B. velezensis JK-XZ8, with activity against Cerasus crown gall disease in Xuzhou, China. Australasian Plant Pathol. 49, 127–136 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-020-00682-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-020-00682-z