Abstract
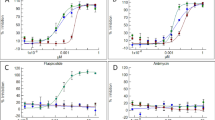
Rice sheath blight is one of the most important rice diseases in the world and the succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor fungicide flutolanil has potential for its control. In this study, a total of 112 Rhizoctonia solani isolates from Jiangsu province in China were characterized for their baseline sensitivity to flutolanil. The baseline sensitivity curve was unimodal with an average EC50 value of 0.0736 ± 0.0331 μg mL−1 for inhibition of mycelial growth. Flutolanil exhibited excellent acropetal movement in rice, and better protective and curative activity than validamycin against rice sheath blight. In field trials in 2011 and 2012, flutolanil used at a concentration of 150 g a.i. ha−1 provided control efficacy ranging from 63.7 to 88.9 %, and its control efficacy could reach 83.9 % ~ 96.5 % at a concentration of 300 g a.i. ha−1. These results suggested that flutolanil will be a good alternative fungicide to validamycin for control of rice sheath blight.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson NA (1982) The genetics and pathology of Rhizoctonia solani. Ann Rev Phytopathol 20:329–347
Araki F, Ysbutanik (1981) a, a, a-trifluoto-3′-ispropoxy-o-toluanilide (NNF-136), a new fungicide for the control of disease caused by basidiomycetes. Proc Br Crop Conf Pests Dis 1:3–9
Araki F (1985) Monct (flutolanil), a new systemic fungicide. Jpn Pestic Inf 7:23–25
Avenot H, Morgan DP, Michailides TJ (2008) Resistance to pyraclostrobin, boscalid and multiple resistance to Pristine (pyraclostrobin + boscalid) fungicide in Alternaria alternate causing alternaria late blight of pistachios in California. Plant Pathol 57:135–140
Baker KF (1970) Types of Rhizoctonia diseases and their occurrence. In: Parmeter JR Jr (ed) Rhizoctonia solani: biology and pathology. California University Press, Berkeley, pp 124–148
Blazier SR, Conway KE (2004) Characterization of Rhizoctonia solani isolates associated with patch diseases on turf grass. Proc Okla Acad Sci 84:41–51
Brent KJ (1992) Monitoring fungicide resistance: purpose, procedures and progress. In: Denholm I, Devonshire AL, Hollomon DW (eds) Resistance 91: achievements and developments in combating pesticide resistance. Elsevier, London and New York, pp 1–18
Brent KJ, Hollomon DW (1998) Fungicide resistance: the assessment of risk. In: FRAC Monograph, 2. GCPF (Now Crop Life International), Brussels. Available from: www.frac.info
CAMA (The Institute for the Control of Agrochemicals, Ministry of Agriculture, China) (2006) Rules for pesticide field experiments (2): part 20–control strawberry grey mould disease by fungicides (GB/T 17980.20-2000). Chinese Standard Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Chen Y, Zhang AF, Wang WX, Zhang Y, Gao TC (2012) Baseline sensitivity and efficacy of thifluzamide in Rhizoctonia solani. Ann Appl Biol 161:247–254
Groth D, Lee F (2003) Rice diseases. In: Smith CW, Dilday RH (eds) Rice origin, history, technology, and production. Wiley Hoboken NJ, 413–436
Groth DE, Bond JA (2006) Initiation of rice sheath blight epidemics and effects of application timing of azoxystrobin on disease incidence, severity, yield and milling yields. Plant Dis 90:1073–1078
Groth DE (2008) Effects of cultivar resistance and single fungicide application on rice sheath blight, yield, and quality. Crop Prot 27:1125–1130
Hirooka T, Miyagi Y, Araki F, Kunoh H (1989) Biological mode of action of flutolanil in its systemic control of rice sheath blight. Dis Control Pest Manag 79:1091–1094
Hu XR, Xu WY, Lv WC, Li L (2006) Monitor of resistance to validamycin in Rhizoctonia solani from Fujian province. Chin Agric Sci Bull 22:160–162
Keinath AP, DuBose V, Walters E (2009) First report from South Carolina of boscalid-insensitive isolates of Didymella bryoniae on field-grown watermelon treated with boscalidpyraclostrobin. Phytopathology 99:S62
Kim YK, Xiao CL (2009) Resistance to pyraclostrobin and boscalid in Botrytis cinerea populations from apple in Washington State. Phytopathology 99:S63
Li SZ, Zhang SH (1987) Studies on the properties on action of three fungicides against rice sheath blight. J Plant Prot 17:277–281 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lu CT, Zhang GF, Wang KR (1995) The experiment report on effect of fungicide Basitic and Moncut on control of rice sheath blight in field. Henan Agric Sci 7:18–20 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Marchetti MA (1983) Potential impact of sheath blight on yield and milling quality of short statured rice lines in the southern United States. Plant Dis 67:162–165
Marchetti MA, Bollich CN (1991) Quantification of the relationship between sheath blight severity and yield loss in rice. Plant Dis 75:773–775
Miazzi M, McGrath MT (2008) Sensitivity of Podosphaera xanthii to registered fungicides and experimentals in GA and NY, USA, in 2007. J Plant Pathol 90(2, Suppl):S2.90
Mitkowski N (2010) Turfgrass program: SDHI fungicides. The University of Rhode Island. 6(3)
Miyamoto T, Ishii H, Seko T, Kobori S, Tomita Y (2009) Occurrence of Corynespora cassiicola isolates resistant to boscalid on cucumber in Ibaraki Prefecture, Japan. Plant Pathol 58:1144–1151
Mochizuki H, Araki F, Yabutani K (1987) Rice sheath blight control with flutolanil. J Pestic Sci 12:29–33
Ou SH (1985) Rice diseases. Common Wealth Agricultural Bureau, Great Britain (UK)
Prasad B, Eizenga GC (2008) Rice sheath blight disease resistance identified in Oryza spp. accessions. Plant Dis 92:1503–1509
Ren CM, Gao BD, He YC (2001) Advance in rice resistance to rice sheath blight. Plant Prot 27:32–36 (in Chinese with English Abstract)
Rush MC, Lee FN (1983) Rice sheath blight: a major rice disease. Plant Dis 7:829–832
Rush MC, Lee FN (1992) Sheath blight. In: Webster RK, Gunnell PS (eds) Compendium of rice diseases. APS Press, St. Paul, pp 22–23
Russell PE (2004) Sensitivity baselines in fungicide resistance research and management. FRAC Monograph No. 3. FRAC, Brussels, Belgium
Stammler G, Brix HD, Glättli A, Semar M, Schoefl U (2007) Biological properties of the carboxamide boscalid including recent studies on its mode of action. In: Proceedings of the BCPC XVI International Plant Protection Congress. British Crop Protection Council Publications, Alton. 16–21
Stevenson KL, Langston DB, Sanders F (2008) Baseline sensitivity and evidence of resistance to boscalid in Didymella bryoniae. Phytopathology 98:S151
Zhang CQ, Liu YH, Ma XY, Feng Z, Ma ZH (2009) Characterization of sensitivity of Rhizoctonia solani, causing rice sheath blight, to mepronil and boscalid. Crop Prot 28:381–386
Zhang HY, Zhao SR, Xu YQ, Feng ZT, Zhang XH (2007) Synergistic effect of the complex between Shenqinmycin and synergistic on rice sheath blight (Rhizoctonia solani) disease. J Shanghai Jiao-tong Univ (Agric Sci) 6:556–560 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhou MG, Liu JF, Ye ZY (1991) Detection and induction of resistance of Rhizoctonia solani from rice to validamycin. Chin J Rice Sci 5:73–78 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Science Foundation of China (31171880, 31201543, 30971891, and 31272065); National Science and Technology Support Program (2012BAD19B01); Commonweal Specialized Research Fund of China Agriculture (201303023, 201103016 and 200903052). Thanks for Suli Chemical Limited Company of Jiangyin, China for providing the technical grade flutolanil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Hou, Y., Peng, D. et al. Baseline sensitivity and control efficacy of flutolanil in Rhizoctonia solani . Australasian Plant Pathol. 43, 313–320 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-014-0272-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-014-0272-0