Abstract
Objective
To determine the diagnostic accuracy of Pediatric Appendicitis Score (PAS) in predicting appendicitis in children presenting with acute abdominal pain to the Emergency Department (ED) of a private hospital in Pakistan.
Methods
This validation study was through retrospective chart review of children between 4–18 years of age with clinical suspicion of acute appendicitis, presenting to the pediatric ED. Diagnostic accuracy was determined using sensitivity, specificity, predictive values, and area under the curve (AUC).
Results
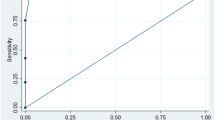
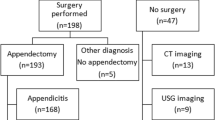
104 children (76% boys) with mean (SD) age of 10.9 (3.5) years met the eligibility criteria. 91% (n=95) patients had moderate to high PAS (score ≥4), and 95% (n=99) had biopsy-proven appendicitis. The likelihood ratio calculated for low, equivocal and high-risk PAS was 0.10, 2.17 and 2.53, respectively. An equivocal PAS (score 4–6) showed a sensitivity of 96.8%, specificity of 80%, positive predictive value of 98.9% and AUC of 0.84 for predicting acute appendicitis.
Conclusion
PAS showed good diagnostic accuracy in predicting acute appendicitis in children presenting to the ED.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pogorelic Z, Rak S, Mrklic I, Juric I. Prospective validation of Alvarado score and Pediatric appendicitis score for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis in children. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2015;31:164–68.
Rothrock SG, Pagane J. Acute appendicitis in children: emergency department diagnosis and management. Ann Emerg Med. 2000;36:39–51.
Alvarado A. A practical score for the early diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Pediatr Emerg Care. 1986;2:206–207.
Brenner D, Elliston C, Hall E, Berdon W. Estimated risks of radiation-induced fatal cancer from pediatric CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;176:289–96.
Shah NB, Platt SL. ALARA: is there a cause for alarm? Reducing radiation risks from computed tomography scanning in children. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2008;20:243–47.
Doria AS, Moineddin R, Kellenberger CJ, et al. US or CT for diagnosis of appendicitis in children and adults? A meta-analysis. Radiology. 2006;241:83–94.
Samuel M. Pediatric appendicitis score. J Pediatr Surg. 2002;37:877–81.
Kulik DM, Uleryk EM, Maguire JL. Does this child have appendicitis? A systematic review of clinical prediction rules for children with acute abdominal pain. J Clin Epidemiol. 2013;66:95–104.
Goldman RD, Carter S, Stephens D, et al. Prospective validation of the pediatric appendicitis score. J Pediatr. 2008;153:278–82
Rehman S, Afzal M, Butt MQ. Validity of Samuel’s paediatric appedicitis score (PAS) in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis in children. Pakistan Armed Forces Medical Journal. 2014; 64:172–77.
Bhatt M, Joseph L, Ducharme FM, et al. Prospective validation of the pediatric appendicitis score in a Canadian pediatric emergency department. Acad Emerg Med. 2009; 16:591–96.
Kim DY, Shim DH, Cho KY. Use of the pediatric appendicitis score in a community hospital. Indian Pediatr. 2016;53:217–20
Sayed A, Zeidan N, Fahmy D, Ibrahim H. Diagnostic reliability of pediatric appendicitis score, ultrasound and low-dose computed tomography scan in children with suspected acute appendicitis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017; 13:847–54.
Ebell MH, Shinholser J. What are the most clinically useful cutoffs for the Alvarado and Pediatric appendicitis scores? A systematic review. Ann Emerg Med. 2014;64:365–372.e2.
Funding
Funding: None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Contributors: MS, AIM: helped in conceptualization of the study, devised methodology, developed tool for the study, contributed in training the research assistant for data collection, gave supervision in data collection, input in data analysis, manuscript writing and critically reviewed the manuscript as submitted. OA: data collection and manuscript writing; MJ: data collection; RN: arranging data collection logistics, maintained data folders, manuscript reviewed by all co-authors, drafting the manuscript; SST: cleaned and performed statistical analysis of the data and provided technical input in the data interpretation. All authors have contributed, designed and approved the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics clearance IEC, Aga Khan University; No.: 4433-EM ERC-16 dated Sept 9, 2016.
Competing interests: None stated.
Additional information
Note: Additional matter related to this article is available with the web version at "https://www.indianpediatrics.net
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salahuddin, S.M., Ayaz, O., Jaffer, M. et al. Pediatric Appendicitis Score for Identifying Acute Appendicitis in Children Presenting With Acute Abdominal Pain to the Emergency Department. Indian Pediatr 59, 774–777 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-022-2620-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-022-2620-4