Abstract
Background
There are limited data on congenital lung malformations (CLM) and their clinical course from developing countries.
Methods
A 10-year retrospective chart review of records of children with CLM attending pediatric chest clinic at an Indian tertiary care center was conducted.
Results
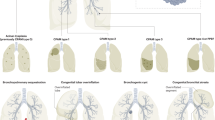
Among the 48 children (24 boys) included in the review, the malformations included congenital lung hypoplasia/agenesis in 24 (50%), cystic pulmonary airway malformation in 9 (19%), bronchogenic/foregut cyst in 8 (18%), and congenital lobar emphysema in 4 (9%). Median (IQR) age at symptom onset and diagnosis were 1.5 (0.4,9.5) and 24 (3,62) months, respectively. Median (IQR) weight for age for age z-score at presentation was −2.4 (−1.4,− 3.4). More than a third (37.5%) children underwent surgical removal of resectable lesions at median (IQR) age of 14 (6,42) months. 14 (27%) children had associated congenital heart disease. Median duration of follow-up was 13 months. In children with lung hypoplasia, median (IQR) number of hospitalizations in follow-up were significantly less than that prior to diagnosis 0 (0,0) vs 1(0,2) (P=0.001). Median (IQR) numbers of hospitalizations in follow up were significantly less than that of prior to surgical resection 0 (0,0) vs 1(1,1) (P=0.016) in children with CPAM.
Conclusion
Lung hypoplasia was the most common congenital lung malformation in our setup. Detection of malformation during antenatal period was poor. Age of diagnosis and surgical intervention is often delayed. Regular follow up and definitive and/or supportive management decreased the morbidity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annunziata F, Bush A, Borgia F, et al. Congenital lung malformations: Unresolved issues and unanswered questions. Front Pediatr.2019;7:239.
Andrade CF, Ferreira HP da C, Fischer GB. Malformac oespulmonares congênitas. J Bras Pneumol. 2011;37: 259–71.
Meenu S, Sudeshna M, Anil N, Rao KLN, Nandita K. Congenital cystadenomatoid malformation of lung. Indian Pediatrics. 2003;37:1269–74.
Chikkannaiah P, Kangle R, Hawal M. Congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation of lung: Report of two cases with review of literature. Lung India. 2013;30:215–18.
Dewan RK, Kesieme EB, Sisodia A, Ramchandani R, Kesieme CN. Congenital malformation of lung parenchyma: 15 years experience in a thoracic surgical unit. Indian J Chest Dis. 2012;54:105–9.
Sadiqi J, Hamidi H. CT features of lung agenesis — A case series (6 cases). BMC Med Imaging. 2018;18:37.
Seear M, Townsend J, Hoepker A, et al. A review of congenital lung malformations with a simplified classification system for clinical and research use. Pediatr Surg Int. 2017;33:657–64.
Zhang L, Ai T, Wang L, Zhang L, Zhang Y. Hypoplasia of the left lung presenting as hemoptysis: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019; 98:e14077.
Ayed AK, Owayed A. Pulmonary resection in infants for congenital pulmonary malformation. Chest. 2003;24: 98–101.
Delestrain C, Khen-Dunlop N, Hadchouel A, et al. Respiratory morbidity in infants born with a congenital lung malformation. Pediatrics. 2017;139:e20162988.
Maneenil G, Ruangnapa K, Thatrimontrichai A, et al. Clinical presentation and outcome in congenital pulmonary malformation: 25 year retrospective study in Thailand. Pediatr Int. 2019;61:812–16.
Schwartz MZ, Ramachandran P. Congenital malformations of the lung and mediastinum — A quarter century of experience from a single institution. J Pediatr Surg. 1997;32:44–7.
Ortac R, Diniz G, Yildirim HT, Aktas S, Karaca I. Retrospective evaluation of children with congenital pulmonary airway malformation: A single center experience of 20 years. Fetal Pediatr Pathol. 2016;35:143–8.
Calzolari F, Braguglia A, Valfrè L, Dotta A, Bagolan P, Morini F. Outcome of infants operated on for congenital pulmonary malformations: Outcome of congenital pulmonary malformations. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2016;51:1367–72.
Funding
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors were involved in patient management, reviewed the manuscript, and approved the final version of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics clearance: Institute Ethics Committee; Ref No. IEC-770/08.11.2019; RP- 10/2019, dated 27 November, 2019
Competing interest: None stated.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gulla, K.M., Parihar, M.S., Jat, K.R. et al. Congenital Lung Malformations: Experience From a Tertiary Care Center in India. Indian Pediatr 58, 129–133 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-021-2127-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-021-2127-4