Abstract
Background
Published Indian studies on the economic burden of juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) are lacking.
Methods
A prospective observational study recruited pediatric patients aged from 1 to 12 years with JIA in the pediatric rheumatology clinic of a public sector tertiary care hospital. Direct healthcare costs and indirect costs for transportation, accommodation of the caregivers, and productivity loss for work absenteeism were assessed.
Results
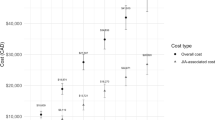
The proportions of direct annualized cost assessed in 60 patients (mean (SD) age 8.46 (2.24) year) spent on outpatient visits, blood tests, imaging investigations, other tests, medications and hospitalization were 0.85%, 12.8%, 9.0%, 2.9%, 41.7% and 32.7%, respectively. Direct healthcare costs for blood tests and medicine were lowest in oligoarticular JIA and highest in systemic onset JIA and (P=0.043 and 0.001 respectively). The direct and indirect costs were higher with the use of biologic agents (n=9) than in those without (n=51).
Conclusions
JIA imposes considerable economic burden with the largest share attributable to medicines, and maximum in those with systemic onset JIA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shenoi S, Horneff G, Cidon M, et al. The burden of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis for patients and caregivers: An international survey and retrospective chart review. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018;36:920–28.
Moorthy LN, Peterson MG, Hassett AL, Lehman TJ. Burden of childhood-onset arthritis. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2010;8:20.
Minden K, Niewerth M, Listing J, Biedermann T, Schontube M, Zink A. Burden and cost of illness in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004;63:836–42.
Bernatsky S, Duffy C, Malleson P, Feldman DE, St Pierre Y, Clarke AE. Economic impact of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;57:44–8.
Minden K, Niewerth M, Listing J, et al. The economic burden of juvenileidiopathic arthritis-Results from the German paediatric rheumatologic database. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2009;27:863–9.
Angelis A, Kanavos P, Lopez-Bastida J, Linertova R, Serrano-Aguilar P for BURQOL-RD Research Network. Socioeconomic costs and health-related quality of life in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: A cost-of-illness study in the United Kingdom. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17: 321.
Allaire SH, DeNardo BS, Szer IS, Meenan RF, Schaller JG. The economic impacts of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1992;19:952–5.
Mondal R, Sarkar S, Das NK, et al. Growth of children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Indian Pediatr. 2014;51:199–202.
Hogan ME, Shah V, Katz J, Krahn MD, Taddio A. Cost-of-illness studies for juvenile idiopathic arthritis: A systematic review. Value Health. 2014;17:A45.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Contributors
MK: primary investigator, data collection, draft preparation; DD: patient management, literature search; AH: literature search, draft review, statistical analysis; PG: study design, patient management, draft review and interpretation; MBS: technical inputs, data collection and interpretation; RM: conception of study, draft review, study design and literature search. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Ethical clearance
Institutional Ethics committee of Medical College Kolkata; No. 368/11-2016 dated November 19, 2016.
Funding
None
Competing interest
None stated.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khatun, M., Datta, D., Hazra, A. et al. Economic Burden of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis in India. Indian Pediatr 58, 38–40 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-021-2094-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-021-2094-9