Abstract
Objective
To examine the common and specific clinical features, mutation spectrum and genotype-phenotype correlation in Noonan syndrome and related RASopathies.
Participants
Records of 30 patients with clinical diagnosis of Noonan syndrome and related RASopathies presenting over a six-year period at a tertiary care medical genetics centre were reviewed. Detailed clinical phenotype evaluation and genetic testing (PTPN11 sequencing or next generation sequencing) was done. The genetic results were used to classify the patients.
Results
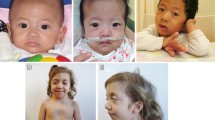
Noonan syndrome was confirmed in 22 patients, 5 had cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome and 3 had Noonan syndrome like disorder with loose anagen hair. The molecular diagnosis was confirmed in 27 patients. Mutations in PTPN11 gene were confirmed in 57.8 % patients. Developmental delay, cardiac defects, ectodermal abnormalities and coarse face was the predominant phenotype. Noonan syndrome like disorder with loose anagen hair was clinically identifiable by the sparse, slow growing hair and caused by one recurrent SHOC2, c.4A>G mutation.
Conclusions
Noonan syndrome and other RASopathies should be suspected in patients with short stature, cardiac defects, typical facial dysmorphism with or without ectodermal involvement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tajan M, Paccoud R, Branka S, Edouard T, Yart A. The Rasopathy family: Consequences of germline activation of the RAS/MAPK pathway. Endocr Rev. 2018;39:676–700.
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, et al. ACMG Laboratory Quality Assurance Committee. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015;17:405–24.
Schulz AL, Albrecht B, Arici C, et al. Mutation and pheno-typic spectrum in patients with cardio-facio-cutaneous and Costello syndrome. Clin Genet. 2008;73:62–7
Cordeddu V, Di Schiavi E, Pennacchio LA, et al. Mutation of SHOC2 promotes aberrant protein N-myristoylation and causes Noonan-like syndrome with loose anagen hair. Nat Genet. 2009;41:1022–6.
Kruszka P, Porras AR, Addissie YA, et al. Noonan syndrome in diverse populations. Am J Med Genet A. 2017; 173:2323–34.
Allanson JE, Bohring A, Dörr HG, et al. The face of Noonan syndrome: Does phenotype predict genotype. Am J Med Genet A. 2010;152A:1960–6.
Chen H, Li X, Liu X, et al. Clinical and mutation profile of pediatric patients with RASopathy-associated hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: Results from a Chinese cohort. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2019;14:29.
Seo GH, Yoo HW. Growth hormone therapy in patients with Noonan syndrome. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2018;23:176–81.
George CD, Patton MA, el Sawi M, Sharland M, Adam EJ. Abdominal ultrasound in Noonan syndrome: A study of 44 patients. Pediatr Radiol. 1993;23:316–8.
Golay V, Pandey R, Roychowdhary A. Chronic tubulo-interstitial nephritis in a solitary kidney of a child with Noonan syndrome. Indian J Nephrol. 2012;22:304–6.
Cizmeci MN, Lequin M, Lichtenbelt KD, et al. Characteristic MR imaging findings of the neonatal brain in RASopathies. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2018;39:1146–52.
Allanson JE, Roberts AE. Noonan Syndrome. 2001 Nov 15 [Updated 2019 Aug 8]. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al. editors. GeneReviews. University of Washington, 1993–2020.
Nugent DJ, Romano AA, Sabharwal S, Cooper DL. Evaluation of bleeding disorders in patients with Noonan syndrome: A systematic review. J Blood Med. 2018;9:185–92.
Kratz CP, Niemeyer CM, Castleberry RP, et al. The mutational spectrum of PTPN11 in juvenile myelomono-cytic leukemia and Noonan syndrome/myeloproliferative disease. Blood. 2005;106:2183–5.
Jenkins C, Luty SB, Maxson JE, et al. Synthetic lethality of TNK2 inhibition in PTPN11-mutant leukemia. Sci Signal. 2018;11(539).
Narayanan DL, Pandey H, Moirangthem A, et al. Hotspots in PTPN11 gene among indian children with Noonan syndrome. Indian Pediatr. 2017;54:638–43.
Athota JP, Bhat M, Nampoothiri S, et al. Molecular and clinical studies in 107 Noonan syndrome affected individuals with PTPN11 mutations. BMC Med Genet. 2020;21:50.
Yamamoto GL, Aguena M, Gos M, et al. Rare variants in SOS2 and LZTR1 are associated with Noonan syndrome. J Med Genet. 2015;52:413–21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Contributors
ML: study design, article writing, data collection; ICV: article review, critical input, study design, data collection; RDP: article critical review and writing, data collection, study design; SBM: article critical review, data collection; KM: article critical review, data collection, PTPN11 test. All authors approved the final version of manuscript.
Funding
None
Competing interest
None stated.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lallar, M., Bijarnia-Mahay, S., Verma, I.C. et al. Mutation and Phenotypic Spectrum of Patients With RASopathies. Indian Pediatr 58, 30–33 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-021-2092-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-021-2092-y