Abstract
Background
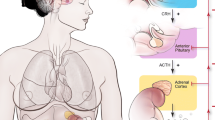
The most common cause of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis suppression is systemic glucocorticoids administration.
Case characteristics
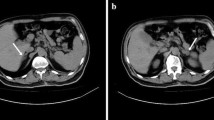
A 14- year-old boy with juvenile idiopathic arthritis receiving repeated intra-articular steroids for last 3 years developed fever, fatigue, nausea and abdominal pain. Stimulation with lowdose Synathen revealed low adrenal reserve, suggesting secondary adrenal insufficiency.
Outcome
Temporary hydrocortisone substitution therapy improved condition.
Message
Intra-articular steroids may cause potentially life-threatening suppression of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Charmandari E, Nicolaides NC, Chrousos GP, Adrenal insufficiency. The Lancet. 2014;383:2152–67.
Weitoft T, Ronnblom I. Glucocorticoid resorption and influence on the hypothalamicpituitary–adrenal axis after intra–articular treatment of the knee in resting and mobile patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65:955–7.
Lazarevic MB, Skosey JL, Djordjevic–Denic G, Swedler WI, Zgardic I, Myones BA. Reduction of cortisol levels after single intra–articular and intramuscular steroid injection. Am J Med. 1955;99:370–3.
Mader R, Lavi I, Luboshitzky R. Evaluation of the pituitary–adrenal axis function following single intraarticular injection of methylprednisolone. Arthritis Rhematism. 2005;52:924–8.
Lipworth BJ. Systemic adverse effect of inhaled corticosteroid therapy: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Arch Intern Med. 1999;159:941–55.
Smith RW, Downey K, Gordon M, Hudak A, Meder R, Barker S, et al. Prevalence of hypothalamic–pituitaryadrenal axis suppression in children treated for asthma with inhaled corticosteroid. Paediatr Child Health. 2012;17:34–9.
Armstrong RD, English J, Gibsn T, Marks V. Serum methyloprednisolone levels following intra–articular injection of methyloprednisolone acetate. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981;40:571–4.
Derendorf H, Mollman H, Vortman G, van der Ouweland FA, van de Putte LB, Gevers G, et al. Pharmacokinetics of rimexolone after intra–articular administration. J Clin Pharmacol. 1990;30:476–9.
Kazlauskeite R, Evans AT, Villabona CV, Abdu TA, Ambrosi B, Atkinson AB, et al. For the Consortium for Evaluation of Corticotropin Test in Hypothalamic–Pituitary Adrenal Insufficiency: A meta–analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:4245–53.
Habib G, Jabbour A, Artul S Hakim G. Intra–articular methylprednisolone acetate injection at the knee joint and the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis: A randomized controlled study. Clin Rheumatol. 2014;33:99–103.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wojcik, M., Ruszala, A., Janus, D. et al. Secondary Adrenal Insufficiency due to Intra-articular Glucocorticoid Injections. Indian Pediatr 56, 242–243 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-019-1507-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-019-1507-5