Abstract
Objective
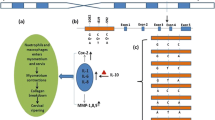
To assess the association of TLR4 (rs4986790 and rs4986791) and TNF-α (rs1800629) genes polymorphisms and TLR4mRNA levels with preterm birth.
Methods
Hospital-based case-control study on women of Caucasoid morphological subtype ethnicity in Northern India. Inclusion criteria for cases: women aged between 18–40 years with preterm birth (<37 weeks gestation), and for controls: women who delivered a term neonate consecutive to an enrolled case. Three polymorphisms TLR4 (Asp299 Gly, Thr399 Ill) and TNF-á (-308G/A) and TLR4 mRNA levels were compared between cases and controls.
Results
From 2012–2015, 559 cases and 559 controls were recruited. TLR4 mRNA levels were found to be higher (P<0.001) in cases [(0.7 (0.04)] than in controls [(0.5 (0.04)]. No association was found between TLR4 Asp299 Gly, TLR4 Thr399 Ill and TNF-α (-308G/A) with preterm birth.
Conclusion
Increased TLR4 mRNA levels seem to be associated with preterm birth, and can be investigated further as a potential biomarker for identifying women at risk.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pandey M, Awasthi S. Prognostic role of interluekin–1 α and β gene polymorphisms in preterm birth. Gene Rep. 2016;4:112–7.
Pandey M, Chauhan M, Awasthi S. Interplay of cytokines in preterm birth. Ind J Med Res. 2017;146:316–27.
Pfaffl MW. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real–time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29:e45.
Pawelczyk E, Nowicki BJ, Izban MG, Pratap S, Sashti NA, Sanderson M, et al. Spontaneous preterm labor is associated with an increase in the proinflammatory signal transducer TLR4 receptor on maternal blood monocytes. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2010;10:66.
Robertson SA, Wahid H, Chin P, Hutchinson M, Moldenhauer L, Keelan J. Toll–like Receptor–4: A New Target for Preterm Labour Pharmacotherapies? Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24:960–73.
Li L, Kang J, Lei W. Role of Toll–like receptor 4 in inflammation–induced preterm delivery. Mol Hum Reprod. 2010;16:267–72.
Noguchi T, Sado T, Naruse K, Shigetomi H, Onogi A, Haruta S, Kawaguchi R, et al. Evidence for activation of Toll–like receptor and receptor for advanced glycation end products in preterm birth. Mediators Inflamm. 2010:2010:490–506.
Chin YP, Dorian CL, Hutchinson MR, Olson DM, Rice KC, Moldenhauer LM, et al. Novel Toll–like receptor–4 antagonist (+)–naloxone protects mice from inflammationinduced preterm birth. Sci Rep. 2016:6:1–13.
Patni S, Aled H. Bryant A, Louise P. Wynen b, Anna L, et al. Functional activity but not gene expression of toll–like receptors is decreased in the preterm versus term human placenta. Placenta. 2015:36:1031–8.
Krediet TG, Wiertsema SP, Vossers MJ, Hoeks SB, Fleer A, Ruven HJ, et al. Toll–likereceptor 2 polymorphism is associated with preterm birth. Pediatr Res. 2007;62:474–6.
Lorenz E, Hallman M, Marttila R, Haataja R, Schwartz DA. Association between the Asp299Gly polymorphisms in the Toll–like receptor 4 and premature births in the Finnish population. Pediatr Res. 2002;52:373–6.
Elovitz MA, Wang Z, Chien EK, Rychlik DF, Phillippe M. A new model for inflammation–induced preterm birth: the role of platelet–activating factor and Toll–like receptor–4. Am J Pathol. 2003;163:2103–11.
Kalinka J, Bitner A. Selected cytokine gene polymorphisms and the risk of preterm delivery in the population of Polish women. Ginekol Pol. 2009;80:111–7.
Jafarzadeh L, Danesh A, Sadeghi M, Heybati F, Hashemzadeh M. Analysis of relationship between tumor necrosis factor alpha gene (G308A Polymorphism) with preterm labor. Int J Prev Med. 2013;4:896–901.
Andalas M, Hakimi M, Nurdiati DS, Astuti I, Imran I, Harapan H. Association of 308G/A TNF–α gene polymorphism and spontaneous preterm birth in Acehnese Ethnic Group, Indonesia: This polymorphism is not associated with preterm birth. Egypt J Med Hum Genet. 2016;17:33–40.
Yilmaz Y, Verdi H, Taneri A, Yazici AC, Ecevit AN, Karakas NM, et al. Maternal fetal proinflammatory cytokine gene polymorphism and preterm birth. DNA Cell Biol. 2012;31:92–7.
Speer EM, Gentile DA, Zeevi A, Pillage G, Huo D, Skoner DP. Role of single nucleotide polymorphisms of cytokine genes in spontaneous preterm delivery. Hum Immunol. 2006;67:915–23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Awasthi, S., Pandey, M. Association of TLR4 and TNF-α Gene Polymorphisms and TLR4 mRNA Levels in Preterm Birth in a Northern Indian Population. Indian Pediatr 56, 202–204 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-019-1500-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-019-1500-z