Abstract
Objective
The primary objective was to evaluate the postnatal maturation pattern on aEEG during first two weeks of life in clinically stable and neurologically normal preterm small for gestational age (PSGA) and gestation matched (1 week) preterm appropriate for gestational age (PAGA) neonates born between 300/7 and 346/7 weeks of gestation.
Methods
Serial aEEG tracings were recorded on 3rd, 7th and 14th day of life. The primary outcome was total aEEG maturation score. Three blinded assessors assigned the scores.
Results
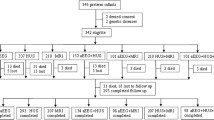
We analyzed a total of 117 aEEG recordings in 40 (19 PSGA and 21 PAGA) neonates. The baseline characteristics were comparable except for birthweight [1186 (263) vs 1666 (230) g]. There was no difference in the mean (SD) total scores on day 3 (9.0 (1.8) vs. 9.5 (1.1), P=0.32) and day 14 of life, but was lower in PSGA infants on day 7 (8.6 (2.4) vs. 10.1 (1.1), P=0.02). On multivariate analysis, maturation of PSGA neonates was found to be significantly delayed at any point of life from day 3 to day 14 (mean difference, -0.8, 95 % CI: -1.6 to -0.02, P=0.04).
Conclusion
Lower aEEG maturation score on day 7 possibly indicates delayed maturation in PSGA neonates in the first week of life.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ward RM, Beachy JC. Neonatal complications following preterm birth. BJOG. 2003;110S:8–16.
Vanderveen JA, Bassler D, Robertson CMT, Kirpalani H. Early interventions involving parents to improve neurodevelopmental outcomes of premature infants: a meta-analysis. J Perinatol. 2009;29:343–51.
Ozdemir OMA, Ergin H, Sahiner, T. Electrophysiological assessment of the brain function in term SGA infants. Brain Res. 2009;1270:33–8.
Morgane PJ, Austin K, Siok C, LaFrance R, Bronzino JD. Power spectral analysis of hippocampal and cortical EEG activity following severe prenatal protein malnutrition in the rat. Brain Res. 1985;354:211–8.
Toet MC,van der Meij W, de Vries LS, Uiterwaal CS, van Huffelen KC. Comparison between simultaneously recorded amplitude integrated electroencephalogram (cerebral function monitor) and standard electroencephalogram in neonates. Pediatrics. 2002;109:772–9.
Clancy RR, Dicker L, Cho S, Cook N, Nicolson SC, Wernovsky G, et al. Agreement between long-term neonatal background classification by conventional and amplitude-integrated EEG. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2011;28:1–9.
Burdjalov VF, Baumgart S, Spitzer AR. Cerebral function monitoring: A new scoring system for the evaluation of brain maturation in neonates. Pediatrics. 2003;112:855–61.
Thornberg E, Thiringer K. Normal pattern of the cerebral function monitor trace in term and preterm neonates. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1990;79:20–5.
Olischar M, Klebermass K, Kuhle S, Hulek M, Kohlhauser C, Rücklinger E, et al. Reference values for amplitude-integrated electroencephalographic activity in preterm neonates younger than 30 weeks’ gestational age. Pediatrics. 2004;113:e61–6.
Soubasi V, Mitsakis K, Nakas CT, Petridou S, Sarafidis K, Griva M, et al. The influence of extrauterine life on the aEEG maturation in normal preterm neonates. Early Hum Dev. 2009;85:761–5.
Toet MC, Hellström-Westas L, Groenendaal F, Eken P, de Vries LS. Amplitude integrated EEG 3 and 6 hours after birth in full term neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1999;81:F19–23.
Griesmaier E, Burger C, Ralser E, Neubauer V, Kiechl-Kohlendorfer U. Amplitude-integrated electroencephalography shows mild delays in electrocortical activity in preterm neonates born small for gestational age. Acta Paediatr. 2015;104:e283–8.
Yerushalmy-Feler A, Marom R, Peylan T, Korn A, Haham A, Mandel D, et al. Electroencephalographic characteristics in preterm infants born with intrauterine growth restriction. J Pediatr. 2014;164:756–61.
Schwindt E, Thaller C, Czaba-Hnizdo C, Giordano V, Olischar M, Waldhoer T, et al. Being born small for gestational age influences Amplitude-integrated electroencephalography and later outcome in preterm infants. Neonatology. 2015;108:81–7.
Sommers R, Tucker R, Harini C, Laptook AR. Neurological maturation of late preterm infants at 34 week assessed by amplitude integrated electroencephalogram. Pediatr Res. 2013;74:705–11.
Ballard JL. Khoury JC, Wedig K, Wang L, Eilers-Walsman BL, Lipp R. New Ballard Score: Expanded to include extremely premature infants J Pediatr. 1991;119:417–23.
Singh M, Giri SK, Ramachandran K. Intrauterine growth curves of live born single babies. Indian Pediatr. 1974;11:475–9.
Kidokoro H, Inder T, Okumura A, Watanabe K. What does cyclicity on amplitude-integrated EEG mean? J Perinatol. 2012;32:565–9.
Lena Hellström-Westas. An Atlas of Amplitude-Integrated EEGs in the Newborn, Second Edition: Informa healthcare; 2008.
Kidokoro H, Kubota T, Hayashi N, Hayakawa M, Takemoto K, Kato Y, et al. Absent cyclicity on aEEG within the first 24 h is associated with brain damage in preterm infants. Neuropediatrics. 2010;41:241–5.
Hellström-Westas L, Rosén I, Svenningsen NW. Predictive value of early continuous amplitude integrated EEG recordings on outcome after severe birth asphyxia in full term infants. Arch Dis Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1995;72:F34–8.
Van Leuven K, Groenendaal F, Toet MC, Schobben AF, Bos SA, de Vries LS, et al. Midazolam and amplitude-integrated EEG in asphyxiated full-term neonates. Acta Paediatr. 2004;93:1221–7.
Shany E. The influence of phenobarbital overdose on aEEG recording. Eur J Paediatr. Neurol. 2004;8:323–5.
Tas JD, Mathur AM. Using amplitude-integrated EEG in neonatal intensive care. J Perinatol. 2010;30(Suppl): S73–81.
Ter Horst HJ, Brouwer OF, Bos AF. Burst suppression on amplitude-integrated electroencephalogram may be induced by midazolam: A report on three cases. Acta Paediatr. 2004;93:559–63.
Foreman SW, Thorngate L, Burr RL, Thomas KA. Electrode challenges in amplitude-integrated electroencephalography (aEEG): Research application of a novel noninvasive measure of brain function in preterm infants. Biol Res Nurs. 2011;13:251–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arora, K., Thukral, A., Sankar, M.J. et al. Postnatal Maturation of Amplitude Integrated Electroencephalography (aEEG) in Preterm Small for Gestational Age Neonates. Indian Pediatr 55, 865–870 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-018-1396-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-018-1396-z