Abstract
Background
Maternal electrolyte imbalance is rarely reported as causative factor of severe perinatal brain injury.
Case characteristics
This case outlines a unique maternal and neonatal pseudo-Bartter syndrome presented with metabolic alkalosis and hypochloremia due to maternal severe vomiting.
Observation
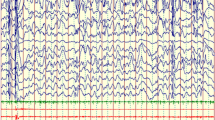
Neonatal MRI brain revealed extensive brain hemorrhages with porencephalic cysts. Subsequent investigation workup points towards maternal severe metabolic alkalosis as its cause.
Message
Careful medical attention should be paid to pregnant women with excessive vomiting to ensure a healthy outcome for both the mother and the baby.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calisici E, Eras Z, Oncel MY, Oguz SS, Gokce ÝK, Dilmen U. Neurodevelopmental outcomes of premature infants with severe intraventricular hemorrhage. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015;28:2115–20.
Lee NM, Saha S. Nausea and vomiting of pregnancy. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2011;40:309.
Mathot M, Maton P, Henrion E, Francosis-Adant A, Murguglio A, Gaillez S, et al. Pseudo-Bartter syndrome in a pregnant mother and her fetus. Pediatr Nephrol. 2006;21:1037–40.
Nakagawa A, Furuhashi M, Kidokoro K, Yoshida K, Kuno N, Ishikawa K. Maternal excessive vomiting: Association with periventricular leukomalacia. J Maternal-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2006;19:675–7.
Amirlak I, Dawson KP. Bartter syndrome: an overview. Q J Med. 2000;93:207–15.
Amorim JBO, Bailey MA, Musa-Aziz R, Giebisch G, Malnic G. Role of luminal anion and pH in distal tubule potassium secretion. Am J Physiol. 2003;284:F381–8.
Seed AE. Maternal-fetal acid-base relationships and fetal scalp-blood analysis. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 1978;21:579–91.
Yoon SH, Zuccarello M, Rapoport RM. pCO2 and pH regulation of cerebral blood flow. Front Physiol. 2012;3:365.
Watanabe K, Hayakawa F, Okumura A. Neonatal EEG: A powerful tool in the assessment of brain damage in preterm infants. Brain Dev. 1999;21:361–72.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vora, S., Ibrahim, T. & Rajadurai, V.S. Maternal pseudo-Bartter syndrome associated with severe perinatal brain injury. Indian Pediatr 54, 771–773 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-017-1173-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-017-1173-4