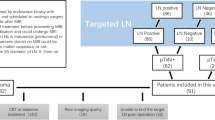
Abstract
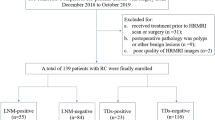
This study aimed to develop a radiomics model for predicting lateral lymph node (LLN) metastasis in rectal cancer patients using MR-T2WI and CT images, and assess its clinical value. This prospective study included rectal cancer patients with complete MR-T2WI and portal enhanced CT images who underwent LLN dissection at Tianjin Union Medical Center between June 2017 and November 2022. Primary lesions and LLN were segmented using 3D slicer. Radiomics features were extracted from the region of interest using pyradiomics in Python. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator algorithm and backward stepwise regression were employed for feature selection. Three LLN metastasis radiomics prediction models were established via multivariable logistic regression analysis. The performance of the model was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, and the area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity were calculated for the training, validation, and test sets. A nomogram was constructed for visualization, and decision curve analysis (DCA) was performed to evaluate clinical value. We included 94 eligible patients in the analysis. For each patient, we extracted a total of 1344 radiomics features. The CT combined with MR-T2WI model had the highest AUC for all sets compared to CT and MR-T2WI models. AUC values for the CT combined with MR-T2WI model in the training, validation, and test sets were 0.957, 0.901, and 0.936, respectively. DCA revealed high prediction value for the combined MR-T2WI and CT model. A radiomics model based on CT and MR-T2WI data effectively predicted LLN metastasis in rectal cancer patients preoperatively.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- LLN:
-
Lateral lymph node
- LLND:
-
Lateral lymph node dissection
- MLN:
-
Mesenteric lymph nodes
- TME:
-
Total mesorectal excision
- nCRT:
-
Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
- MAX:
-
Maximum
- MIN:
-
Minimum
- STD:
-
Standard deviation
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- DCA:
-
Decision curve analysis
- LASSO:
-
Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- PPV:
-
Positive predictive value
- NPV:
-
Negative predictive value
References
Kim TG, Park W, Choi DH, Park HC, Kim SH, Cho YB et al (2014) Factors associated with lateral pelvic recurrence after curative resection following neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer patients. Int J Colorectal Dis 29(2):193–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-013-1797-3
Chen JN, Liu Z, Wang ZJ, Mei SW, Shen HY, Li J et al (2020) Selective lateral lymph node dissection after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 26(21):2877–2888. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i21.2877
Hazen SJA, Sluckin TC, Konishi T, Kusters M (2021) Lateral lymph node dissection in rectal cancer: state of the art review. Eur J Surg Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2021.11.003
Yang X, Gu C, Hu T, Bi L, Wei M, Deng X et al (2019) Is laparoscopic selective lateral lymph node dissection for locally advanced rectal cancer after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy safe? ANZ J Surg 89(11):E492-e7. https://doi.org/10.1111/ans.15449
Sun Y, Lian L, Zhang H, Bai X, Xie Z, Ouyang J et al (2021) The feasibility and technical strategy of a fascia space priority approach in laparoscopic lateral lymph node dissection for advanced middle and low rectal cancer: a retrospective multicentre study. Wideochirurgia i inne techniki maloinwazyjne 16(2):312–320. https://doi.org/10.5114/wiitm.2021.105143
Tang J, Li H, Liu T, Zhang J (2021) Thirty years’ changes of the strategy of lateral lymph node dissection in low rectal cancer: treatment experience and prognostic analysis of 289 cases in one single center. Chin J Gastrointest Surg 24(10):889–896
Rogers W, Thulasi Seetha S, Refaee TAG, Lieverse RIY, Granzier RWY, Ibrahim A et al (2020) Radiomics: from qualitative to quantitative imaging. Br J Radiol 93(1108):20190948. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20190948
Guiot J, Vaidyanathan A, Deprez L, Zerka F, Danthine D, Frix AN et al (2022) A review in radiomics: making personalized medicine a reality via routine imaging. Med Res Rev 42(1):426–440. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.21846
Chen LD, Liang JY, Wu H, Wang Z, Li SR, Li W et al (2018) Multiparametric radiomics improve prediction of lymph node metastasis of rectal cancer compared with conventional radiomics. Life Sci 208:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2018.07.007
Meng X, Xia W, Xie P, Zhang R, Li W, Wang M et al (2019) Preoperative radiomic signature based on multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for noninvasive evaluation of biological characteristics in rectal cancer. Eur Radiol 29(6):3200–3209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5763-x
Hui C, Baclay R, Liu K, Sandhu N, Loo P, von Eyben R et al (2022) Rectosigmoid cancer-rectal cancer or sigmoid cancer? Am J Clin Oncol 45(8):333–337. https://doi.org/10.1097/coc.0000000000000931
van Griethuysen JJM, Fedorov A, Parmar C, Hosny A, Aucoin N, Narayan V et al (2017) Computational radiomics system to decode the radiographic phenotype. Cancer Res 77(21):e104–e107. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-17-0339
Zhu H, Zhang X, Li X, Shi Y, Zhu H, Sun Y (2019) Prediction of pathological nodal stage of locally advanced rectal cancer by collective features of multiple lymph nodes in magnetic resonance images before and after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. Chin J Cancer Res 31(6):984–992. https://doi.org/10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2019.06.14
Han EC, Kwon YH, Park KJ, Jeong SY, Kang SB, Oh JH et al (2018) Significance of lymph node metastasis in the survival of stage IV colorectal cancer by hematogenous metastasis. Ann Surg Treat Res 95(4):201–212. https://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2018.95.4.201
Li XT, Sun YS, Tang L, Cao K, Zhang XY (2015) Evaluating local lymph node metastasis with magnetic resonance imaging, endoluminal ultrasound and computed tomography in rectal cancer: a meta-analysis. Colorectal Dis 17(6):129–135. https://doi.org/10.1111/codi.12909
Tsunoda Y, Ito M, Fujii H, Kuwano H, Saito N (2008) Preoperative diagnosis of lymph node metastases of colorectal cancer by FDG-PET/CT. Jpn J Clin Oncol 38(5):347–353. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyn032
Bae SU, Won KS, Song BI, Jeong WK, Baek SK, Kim HW (2018) Accuracy of F-18 FDG PET/CT with optimal cut-offs of maximum standardized uptake value according to size for diagnosis of regional lymph node metastasis in patients with rectal cancer. Cancer Imaging 18(1):32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40644-018-0165-5
Ogawa S, Itabashi M, Hirosawa T, Hashimoto T, Bamba Y, Kameoka S (2015) A logistic model including risk factors for lymph node metastasis can improve the accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis of rectal cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 16(2):707–712. https://doi.org/10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.2.707
Liu Y, Wang R, Ding Y, Tu S, Liu Y, Qian Y et al (2016) A predictive nomogram improved diagnostic accuracy and interobserver agreement of perirectal lymph nodes metastases in rectal cancer. Oncotarget 7(12):14755–14764. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.7548
Kumar V, Gu Y, Basu S, Berglund A, Eschrich SA, Schabath MB et al (2012) Radiomics: the process and the challenges. Magn Reson Imaging 30(9):1234–1248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2012.06.010
Bedrikovetski S, Dudi-Venkata NN, Kroon HM, Seow W, Vather R, Carneiro G et al (2021) Artificial intelligence for pre-operative lymph node staging in colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 21(1):1058. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-021-08773-w
Yang YS, Feng F, Qiu YJ, Zheng GH, Ge YQ, Wang YT (2021) High-resolution MRI-based radiomics analysis to predict lymph node metastasis and tumor deposits respectively in rectal cancer. Abdom Radiol (NY) 46(3):873–884. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-020-02733-x
Xian MF, Zheng X, Xu JB, Li X, Chen LD, Wang W (2021) Prediction of lymph node metastasis in rectal cancer: comparison between shear-wave elastography based ultrasomics and MRI. Diagn Interv Radiol 27(3):424–431. https://doi.org/10.5152/dir.2021.20031
He J, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Wu H, Zhou Y, Zhao S (2021) Preoperative prediction of regional lymph node metastasis of colorectal cancer based on 18F-FDG PET/CT and machine learning. Ann Nucl Med 35(5):617–627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-021-01605-8
Nakanishi R, Akiyoshi T, Toda S, Murakami Y, Taguchi S, Oba K et al (2020) Radiomics approach outperforms diameter criteria for predicting pathological lateral lymph node metastasis after neoadjuvant (chemo)radiotherapy in advanced low rectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 27(11):4273–4283. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-020-08974-w
Funding
This study has received funding by Science and Technology Project of Tianjin municipal health and Health Committee (ZC20081); Tianjin Key Medical Discipline (Specialty) Construction Project (TJYXZDXK-044A); Project supported by the hospital level scientific research fund of Tianjin Union Medical Center (2022GCXK001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Research involving human participants and/or animals and Informed consent
This study is retrospective, using anonymized existing data. Therefore, it did not involve new research with human participants or animals, and specific informed consent was not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., Jiang, P., Dong, L. et al. Diagnostic value of a radiomics model based on CT and MRI for prediction of lateral lymph node metastasis of rectal cancer. Updates Surg 75, 2225–2234 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-023-01618-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-023-01618-0