Abstract
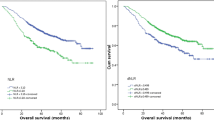
Inflammation plays a key role in malignant tumor progression. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is a marker of systemic inflammation and, as such, high isolated pretreatment NLR has been shown to be associated with worse long-term outcomes. The aim of the present study is to evaluate the prognostic value of pre- and post-operative NLR in relation to mortality and recurrence rates in patients undergoing lung lobectomy for NSCLC. A single-center retrospective analysis of 534 lobectomies was performed between 2009 and 2018. NLR was measured in two opportunities: 1 month prior to surgery and 1–4 months after. Primary outcomes were overall survival (OS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS). Secondary outcomes were variables associated with mortality and recurrence. The study sample included 264 lobectomies. Independent predictors of OS were ASA 3/4 (p = 0.041) and open surgical approach (p = 0.042). Adjuvant chemotherapy (p = 0.002) and pathological N 1/2-stage (p = 0.0015) were associated with RFS. Delta NLR correlated with OS (p = 0.042) and RFS (p < 0.001). Patients were divided into three delta NLR categories: delta NLR < 0, delta NLR 0–0.5 and delta NLR > 0.5. Increasing delta NLR was significantly associated with worse OS (p < 0.001) and RFS (p < 0.001). Dynamic behaviour of NLR assessed through delta NLR is a useful tool that potentially allows predicting mortality and recurrence outcomes in patients undergoing lung lobectomy for NSCLC and may be more informative than static baseline values.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NLR:
-
Neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- RFS:
-
Recurrence-free survival
References
Paramanathan A, Saxena A, Morris DL (2014) A systematic review and meta-analysis on the impact of pre-operative neutrophil lymphocyte ratio on long term outcomes after curative intent resection of solid tumours. Surg Oncol 23(1):31–39
Petrova MP, Eneva MI, Arabadjiev JI et al (2020) Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as a potential predictive marker for treatment with pembrolizumab as a second line treatment in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Biosci Trends 14(1):48–55
Mizuguchi S, Izumi N, Tsukioka T, Komatsu H, Nishiyama N (2018) Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio predicts recurrence in patients with resected stage 1 non-small cell lung cancer. J Cardiothorac Surg 13(1):78
Lugg S, Theofano T, Kerr A et al (2015) Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic marker for curative-intent surgery in non-small cell lung cancer. 81 Thorac Surg. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.congress-2015.pa2509
National Cancer Institute (2020) AJCC cancer staging manual 8th edition. Definitions. https://doi.org/10.32388/b30ldk
Sonoda D, Matsuura Y, Ichinose J et al (2019) Ultra-late recurrence of non-small cell lung cancer over 10 years after curative resection. Cancer Manag Res 11:6765–6774
Guthrie GJK, Charles KA, Roxburgh CSD, Horgan PG, McMillan DC, Clarke SJ (2013) The systemic inflammation-based neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: experience in patients with cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 88(1):218–230
Zhan H, Ma J-Y, Jian Q-C (2018) Prognostic significance of pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in melanoma patients: a meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta 484:136–140
Choi N, Kim JH, Chie EK, Gim J, Kang H-C (2019) A meta-analysis of the impact of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio on treatment outcomes after radiotherapy for solid tumors. Medicine 98(18):e15369
Yu Y, Wang H, Yan A et al (2018) Pretreatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in determining the prognosis of head and neck cancer: a meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 18(1):383
Suh J, Jung JH, Jeong CW, Kwak C, Kim HH, Ku JH (2019) Clinical significance of pre-treated neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in the management of urothelial carcinoma: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol 9:1365
Wang Z, Zhan P, Lv Y et al (2019) Prognostic role of pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with systemic therapy: a meta-analysis. Transl Lung Cancer Res 8(3):214–226
Yuan D, Zhu K, Li K, Yan R, Jia Y, Dang C (2014) The preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio predicts recurrence and survival among patients undergoing R0 resections of adenocarcinomas of the esophagogastric junction. J Surg Oncol 110(3):333–340
Howard R, Kanetsky PA, Egan KM (2019) Exploring the prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in cancer. Sci Rep 9(1):19673
Koo CY, Hyder JA, Wanderer JP, Eikermann M, Ramachandran SK (2015) A meta-analysis of the predictive accuracy of postoperative mortality using the American Society of Anesthesiologists’ physical status classification system. World J Surg 39(1):88–103
Pisters KMW, Evans WK, Azzoli CG et al (2007) Cancer Care ontario and American society of clinical oncology adjuvant chemotherapy and adjuvant radiation therapy for stages I–IIIA resectable non-small-cell lung cancer guideline. J Clin Oncol 25(34):5506–5518. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2007.14.1226
Qiang G, Liang C, Yu Q et al (2015) Risk factors for recurrence after complete resection of pathological stage N2 non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac Cancer 6(2):166–171
Dunn GP, Old LJ, Schreiber RD (2004) The immunobiology of cancer immunosurveillance and immunoediting. Immunity 21(2):137–148
Liu J, Lin PC, Zhou BP (2015) Inflammation fuels tumor progress and metastasis. Curr Pharm Des 21(21):3032–3040
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RM: conceptualization, formal analysis, writing-original draft, writing-review and editing, visualization. CL: formal analysis, writing-review and editing, visualization. CF: formal analysis, writing-review and editing, visualization. CF: resources. DA: conceptualization, methodology, supervision. SD: project administration, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Micaela, R., Lucas, C., Franco, C. et al. Dynamic perioperative variation of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as an independent prognosis factor following lobectomy for NSCLC. Updates Surg 73, 1567–1574 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-020-00936-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-020-00936-x