Abstract
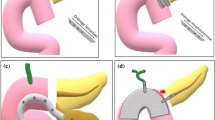
The authors describe the technique to perform a mechanical biliodigestive anastomosis after pancreatoduodenectomy that could be able to reduce the time of surgical intervention and the major systemic postoperative complication especially in elderly patients. Pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD) is considered to be the most effective procedure for the treatment of tumors of the pancreatic head and periampullary tumors. Postoperative morbidity remains high, reaching 40–50% in some series. Leakage and stricture of hepaticojejunal anastomosis have a special significance and occur in 2.5–5% of cases. The usefulness of mechanical staplers is well established in gastric and colorectal surgery, but their use in creating biliodigestive anastomosis is still a very controversial application. In the last 2 years (Nov 2008–Nov 2010), seven patients who underwent PD and presented at the time of operation, a main bile duct (MBD) greater of 20 mm, received a mechanical biliodigestive anastomosis with surgical stapler. All the patients were postoperatively controlled with an ultrasonography at 3 and 6 months, and a cholangio MRI at 1 year from operation. The follow up of the seven patients ranged from 3 to 18 months. Six patients are still alive and free of oncologic disease. One patient presented a single episode of cholangitis with a significant reduction of caliber of the biliodigestive anastomosis. The remaining five patients showed a good caliber of hepaticojejunal anastomosis. The authors suggest this procedure as a safe, feasible, more rapid and easier technique than traditional suture for bilioenteric anastomosis, when a suitable caliber of MBD allows to perform it.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balcom JH IV, Rattner DW, Warshaw AL, Chang Y, Fernandez del Castillo C (2001) Ten-year experience with 733 pancreatic resections: changing indications, older patients, and decreasing length of hospitalization. Arch Surg 136:391–398
Kazanjian KK, Hines OJ, Eibl G, Reber HA (2005) Management of pancreatic fistulas after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Arch Surg 140:849–855
Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Sohn TA (1997) Six hundred fifty consecutive pancreaticoduodenectomies in the 1990s: pathology, complications, and outcomes. Ann Surg 226:248–257
House MG, Cameron JL, Shulick RD, Campbell KA, Sauter PK, Coleman JA, Lillemoe KD, Yeo CJ (2006) Incidence and outcome of biliary strictures after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Ann Surg 243:571–577
Reddy DM, Townsend CM Jr, Kuo YF, Freeman JL, Goodwin JS, Riall TS (2009) Readmission after pancreatectomy for pancreatic cancer in medicare patients. J Gastrointest Surg 13:1963–1975
Gusarev VF, Iareshko VG, Egorov AM, Tabakov AI, Sitsinskii SA (1991) Biliodigestive anastomoses using mechanical sutures. Khirurgiia 2:134–138
Mullin TJ, Damazo F, Dawe EJ (1983) Cholecystoenteric anastomosis with EEA stapler for cancer of the pancreas. Am J Surg 145:338–342
Thompson E, Nagorney DM (1986) Stapled cholecystojejunostomy and gastrojejunostomy for the palliation of unresectable pancreatic carcinoma. Am J Surg 151:509–511
Vallasciani S, Pintus C, Grottesi A, Riccioni M (2003) Choledochal cyst in a pediatric patient: creation of a bilijejunal anastomosis with surgical staples. A case report. Pediatr Med Chir 25:281–284
Cirocchi R, Covarelli P, Mazieri M, Fabbri B, Bisacci C, Fabbri C, Bisacci R (1999) Choledochojejunostomy using a mechanical stapler. Chir Ital 51:177–179
Winter JM, Cameron JL, Campbell KA (2006) 1423 pancreatoduodenectomies for pancreatic cancer: a single institution experience. J Gastrointest Surg 10:1199–1210
Yeo CJ, Barry MK, Sauter PK (1993) Erythromycin accelerates gastric emptying after pancreaticoduodenectomy. A prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Surg 218:229–237
Benzoni E, Zompicchiatti A, Saccomanno E, Lorenzin D, Baccarani U, Adani G, Noce L, Uzzau A, Cedolini C, Bresadola F, Intini S (2008) Postoperative complications linked to pancreaticoduodenectomy. An analysis of pancreatic stump management. J Gastrointest Liver Dis 17:43–47
Kuhlmann KF, de Castro SM, Wesseling JG (2004) Surgical treatment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma; actual survival and prognostic factors in 343 patients. Eur J Cancer 40:549–558
Reid-Lombardo KM, Ramos-De la Medina A, Thomsen K, Harmsen WS, Farnell MB (2007) Long-term anastomotic complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy for benign diseases. J Gastrointest Surg 11:1704–1711
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tersigni, R., Capaldi, M. & Cortese, A. Biliodigestive anastomosis with circular mechanical device after pancreatoduodenectomy: our experience. Updates Surg 63, 253–257 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-011-0102-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-011-0102-7