Abstract
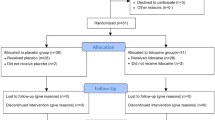
Laparoscopic floppy Nissen fundoplication (LFNF) is an effective treatment for gastroesophageal reflux disease. The duration of convalescence, after noncomplicated LFNF, may depend on several factors of which pain, fatigue and sociocultural factors are the most important. Nausea and vomiting occur mainly on the day of operation. Glucocorticoids are well known for their analgesic, anti-inflammatory, immune-modulating and antiemetic effects. We therefore undertook the present study to investigate whether preoperative dexamethasone could improve surgical outcome in patients undergoing uncomplicated laparoscopic floppy Nissen fundoplication. From March 2005 to April 2008, 82 patients were randomized to receive dexamethasone (8 mg) intravenously, 90 min before skin incision or saline (placebo). Patients received a similar standardized anesthetic, surgical and multimodal analgesic treatment. The primary end points were pain and fatigue. Preoperatively and at several times during the first 24 postoperative hours, we measured C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 and 1 (IL-6, IL-1), pain scores and nausea, and the number of vomiting episodes were registered. Dexamethasone significantly reduced postoperative levels of CRP (p = 0.01), IL-6 and IL-1 (p < 0.05), fatigue (p = 0.01) and overall pain during the first 24 postoperative hours (p < 0.05) and the total requirement of analgesic (ketorolac) (p < 0.05). Dexamethasone also reduced nausea and vomiting on the day of operation (p < 0.05). Preoperative dexamethasone (8 mg) reduced pain, fatigue, nausea and vomiting in patients undergoing uncomplicated LNF when compared with placebo.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rimkus C, Martignoni M (2008) Therapy of the gastroesophageal reflux disease: laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Chirurg 79:261–262
Attwood SE, Lundell L, Ell C, Galmiche JP, Hatlebakk J, Fiocca R, Lind T, Eklund S, Junghard O, The LOTUS Trial Group (2008) Standardization of surgical technique in antireflux surgery: the LOTUS Trial Experience. World J Surg 27
Antoniu SA, Delivorias P, Antoniou GA, Natsiopoulos I, Kalambakas A, Dalenbäck J, Makridis C (2008) Symptom-focused results after laparoscopic fundoplication for refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease-a prospective study. Langenbecks Arch Surg 20
Sapolsky RM, Romero LM, Munck AU (2000) How do glucocorticoids influence stress responses? Integrating permissive, suppressive, stimulatory, and preparative actions. Endocr Rev 21:55–89
Holte K, Kehlet H (2002) Perioperative single dose glucocorticoid administration—pathophysiological effects and clinical implication. J Am Coll Surg 195:694–712
Henzi I, Walder B, Tramèr MR (2000) Dexamethasone for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting: a quantitative systematic review. Anesth Analg 90:186–194
Fujii Y, Saitoh Y, Tanaka H, Toyooka H (2000) Granisetron/dexamethasone combination for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Eur J Anaesthesiol 17:64–68
Meneghetti AT, Tedesco P, Galvani C, Gorodner MV, Patti MG (2008) Outcomes after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication are not influenced by the pattern of reflux. Dis Esophagus 21:165–169
Christensen T, Stage JG, Galbo H, Christensen NJ, Kehlet H (1989) Fatigue and cardiac and endocrine metabolic response to exercise after abdominal surgery. Surgery 105:46–50
Greif R, Laciny S, Rapf B, Hickle RS, Sessler DI (1999) Supplemental oxygen reduces the incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Anesthesiology 91:1246–1252
Vittimberga FJ Jr, Foley DP, Meyers WC, Callery MP (1998) Laparoscopic surgery and the systemic immune response. Ann Surg 227:326–334
Bisgaard T, Klarskov B, Kehlet H, Rosenberg J (2003) Preoperative dexamethasone improves surgical outcome after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Ann Surg 238:651–660
Fraser CG, Preuss FS, Bigford WD (1952) Adrenal atrophy and irreversible shock associated with cortisone therapy. J Am Med Assoc 149:1542–1543
Chernow B, Alexander HR, Smallridge RC, Thompson WR, Cook D, Beardsley D, Fink MP, Lake CR, Fletcher JR (1987) Hormonal responses to graded surgical stress. Arch Intern Med 147:1273–1278
Jakeways MS, Mitchell V, Hashim IA, Chadwick SJ, Shenkin A, Green CJ, Carli F (1994) Metabolic and inflammatory responses after open or laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Br J Surg 81:127–131
Kristiansson M, Saraste L, Soop M, Sundqvist KG, Thörne A (1999) Diminished interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein responses to laparoscopic versus open cholecystectomy. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 43:146–152
Troidl H, Spangenberger W, Langen R, al-Jaziri A, Eypasch E, Neugebauer E, Dietrich J (1992) Laparoscopic cholecystectomy: technical performance, safety and patient’s benefit. Endoscopy 24:252–261
Bisgaard T, Kehlet H, Rosenberg J (2001) Pain and convalescence after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Eur J Surg 167:84–96
Späth-Schwalbe E, Hansen K, Schmidt F, Schrezenmeier H, Marshall L, Burger K, Fehm HL, Born J (1998) Acute effects of recombinant human interleukin-6 on endocrine and central nervous sleep functions in healthy men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:1573–1579
Nagelschmidt M, Fu ZX, Saad S, Dimmeler S, Neugebauer E (1999) Preoperative high dose methylprednisolone improves patients outcome after abdominal surgery. Eur J Surg 165:971–978
Schulze S, Andersen J, Overgaard H, Nørgard P, Nielsen HJ, Aasen A, Gottrup F, Kehlet H (1997) Effect of prednisolone on the systemic response and wound healing after colonic surgery. Arch Surg 132:129–135
Yared JP, Starr NJ, Torres FK, Bashour CA, Bourdakos G, Piedmonte M, Michener JADavis JA, Rosenberger TE (2000) Effects of single dose, postinduction dexamethasone in recovery after cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg 69:1420–1424
Bigler D, Jonsson T, Osen J, Brenoe J, Sander-Jensen K (1996) The effect of preoperative methylprednisolone on pulmonary function and pain after lung operations. J Thoracic Cardiovasc Surg 112:142–145
Sauerland S, Nagelschmidt M, Mallmann P, Neugebauer EA (2000) Risks and benefits of preoperative high dose methylprednisolone in surgical patients: a systematic review. Drug Saf 23:449–461
Hargreaves KM, Costello A (1990) Glucocorticoids suppress levels of immunoreactive bradykinin in inflamed tissue as evaluated by microdialysis probes. Clin Pharmacol Ther 48:168–178
Hong D, Byers MR, Oswald RJ (1993) Dexamethasone treatment reduces sensory neuropeptides and nerve sprouting reactions in injured teeth. Pain 55:171–181
McKenzie R, Tantisira B, Karambelkar DJ, Riley TJ, Abdelhady H (1994) Comparison of ondansetron with ondansetron plus dexamethasone in the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Anesth Analg 79:961–964
Baxendale BR, Vater M, Lavery KM (1993) Dexamethasone reduces pain and swelling following extraction of third molar teeth. Anaesthesia 48:961–964
Coloma M, White PF, Markowitz SD, Whitten CW, Macaluso AR, Berrisford SB, Thornton KC (2002) Dexamethasone in combination with dolasetron for prophylaxis in the ambulatory setting: effect on outcome after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Anesthesiology 96:1346–1350
Wang JJ, Ho ST, Liu YH, Lee SC, Liu YC, Liao YC, Ho CM (1999) Dexamethasone reduces nausea and vomiting after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Br J Anaesth 83:772–775
Wang JJ, Ho ST, Uen YH, Lin MT, Chen KT, Huang JC, Tzeng JI (2002) Small-dose dexamethasone reduces nausea and vomiting after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a comparison of tropisetron with saline. Anesth Analg 95:229–232
Donnelly LE, Newton R, Kennedy GE, Fenwick PS, Leung RH, Ito K, Russell RE, Barnes PJ (2004) Anti-inflammatory effects of resveratrol in lung epithelial cells: molecular mechanisms. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 287:774–783
Wang JJ, Ho ST, Tzeng JI, Tang CS (2000) The effect of timing of dexamethasone administration on its efficacy as a prophylactic for postoperative nausea and vomiting. Anesth Analg 91:136–139
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13304-010-0021-z
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schietroma, M., Giuliani, M., Zoccali, G. et al. How does dexamethasone influence surgical outcome after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication? A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Updates Surg 62, 47–54 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-010-0009-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-010-0009-8