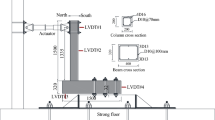
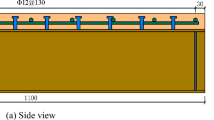
Abstract
Steel Circular Hollow Section (CHS) joints have been extensively utilized in construction. Current research mainly focuses on joints reinforced in unloaded states, reinforcement under load less commonly addressed. This study examines the mechanical behavior of CHS T-joints through an experimental analysis of six specimens, each featuring varying brace-to-chord diameter ratios (β), welded under different load factors. Identified primary failure modes of the joints are local buckling and out-of-plane inclination. Furthermore, a thermo-mechanical coupling finite element model, considering the material addition during the welding process, was developed to investigate the influence of the welding under load. The results indicate that welding under axial load has little effect on the ultimate loading capacity of the CHS T-joints. Notably, welding-induced residual deformation on the chord surpasses that on the brace, particularly when welding passes are proximal to the brace-chord intersection. Residual stress in welds is not significantly affected by the stress in the tubular; only the stiffeners near the welds are affected. Despite some joints exhibiting out-of-plane inclination, the enhancement in ultimate bearing capacity exceeds 24%.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- d 0 :
-
Chord diameter
- d 1 :
-
Brace diameter
- t 0 :
-
Chord thickness
- t 1 :
-
Brace thickness
- t s :
-
Stiffener thickness
- l 0 :
-
Chord length
- l 1 :
-
Brace length
- l s :
-
Stiffener side length
- α :
-
Coefficient of thermal expansion
- β :
-
Brace to chord diameter ratio (d1/d0)
- γ :
-
Chord radius-to thickness ratio(d0/(2t0))
- μ :
-
Load factor
- τ :
-
Brace-to-chord thickness ratio(t1/t0)
- E 0 :
-
Chord Young 's modulus
- E 1 :
-
Brace Young's modulus
- E 2 :
-
Stiffener Young's modulus
- f y0 :
-
Chord yield stress
- f y1 :
-
Brace yield stress
- f y2 :
-
Stiffener yield stress
- N i :
-
Brace axial force
- σ 0 :
-
Chord compressive stress
- \({\psi}_{n}^{c}\) :
-
Brace inclination influence coefficient
- P u, FEA :
-
Ultimate load of joint welded under load obtained by FE analysis
- P u, FEA0 :
-
Ultimate load of unreinforced joint obtained by FE analysis
- P u, EXP :
-
Experimental ultimate load
References
Chen, C., Shao, Y. B., & Yang, J. (2011). Study on static strength of circular hollow section (CHS) T-joint reinforced with FRP. Applied Mechanics & Materials, 99–100, 72–75. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.99-100.72
Chen, Y., Hu, Z. Z., Guo, Y., Wang, J. Y., & Tong, G. S. (2019). Effects of chord pre-load on strength of CHS X-joints stiffened with external ring stiffeners and gusset plates. Engineering Structures, 195, 125–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2019.05.076
Chinese standard GB50017-2017. (2017). Standard for design of steel structures (in Chinese).
Choo, Y. S., Liang, J. X., van der Vegte, G. J., & Liew, J. Y. R. (2004). Static strength of collar plate reinforced CHS X-joints loaded by in-plane bending. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 60(12), 1745–1760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2004.05.005
CIDECT Design Guide No.1. (2008). Design guide for circular hollow section (CHS) joints under predominantly static loading [S]. 2nd edn. LSS Verlag.
Ding, Y., Zhu, L., Zhang, K., Yu, B., & Sun, H. L. (2018). CHS X-joints strengthened by external stiffeners under brace axial tension. Engineering Structures, 171, 445–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.05.101
Erfani, S., Naseri, M., & Akrami, V. (2017). Effect of in-service strengthening on the axial load carrying capacity of steel box columns. International Journal of Steel Structures, 17(1), 231–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-015-0178-x
Fu, G. M., Lourenço, M. I., Duan, M. L., & Estefen, S. F. (2016). Influence of the welding sequence on residual stress and distortion of fillet welded structures. Marine Structures, 46, 30–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marstruc.2015.12.001
Goldak, J., Chakravarti, A., & Bibby, M. (1984). A new finite element model for welding heat source. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions b: Process Metallurgy and Materials Processing Science, 15, 299–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02667333
Hu, S. L., Wang, W., & Lin, X. G. (2022). Two-stage machine learning framework for developing probabilistic strength prediction models of structural components: An application for RHS-CHS T-joint. Engineering Structures, 266, 114548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2022.114548
Huang, J. M., Wang, Y. Q., Zong, L., Zhang, Y. W., & Zhang, Y. W. (2021). Experimental study on the influence of welding processes on the residual distortion of reinforcing I-section steel beams under load. Engineering Mechanics, 38(S1), 243–250. https://doi.org/10.26914/c.cnkihy.2020.012438. in Chinese.
Huang, S., Zhu, L., Sun, H. L., Wang, M., & Chen, X. (2020). Studies on axial tensile loading capacity of CHS T-joints reinforced with external stiffening rings. International Journal of Steel Structures, 20(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-020-00319-3
Jiang, L., Wang, Y. Q., Dai, G. X., Zhang, T. S., & Shi, Y. J. (2016). Analysis of welding heat effect on load carrying behavior of I-section steel beam-columns strengthened by welding. J. Civ. Environ. Eng., 38(4), 96–107. in Chinese.
Kim, S. H., Song, X., Cho, C. H., & Lee, C. H. (2021). Strength prediction of steel CHS X-joints via leveraging finite element method and machine learning solutions. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 176, 106394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2020.106394
Kou, S. (2002). Welding metallurgy. Wiley-Interscience.
Li, C., Zhang, D. C., & Li, B. H. (2018a). Experimental research and simulation analysis on in-plane flexural bearing capacity of circular steel tubular T-joint with stiffening ribs. Ind. Constr., 48(07), 135–139. https://doi.org/10.13204/j.gyjz201807025. in Chinese.
Li, W., Zhang, S., Huo, W., Yu, B., & Zhu, L. (2018b). Axial compression capacity of steel CHS X-joints strengthened with external stiffeners. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 141, 156–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2017.11.009
Li, P. Y., & Zhu, L. (2020). Experimental research on axial bearing capacity of circular hollow section steel K-joints reinforced with collar plates. Industrial Construction, 50(06), 144–149. https://doi.org/10.13204/j.gyjz202006023. in Chinese.
Liu, H. B., Zhao, Y. L., Chen, Z. H., & Dong, X. T. (2021). Axial-compression mechanical properties of square steel columns strengthened by welding under high load. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 176, 106390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2020.106390
Liu, H. B., Hu, J., Chen, Z. H., Wang, L. X., & Mashrah, W. A. H. (2022a). Reinforcement of circular steel tubes using welded casings under axial compression loading. International Journal of Steel Structures, 22(3), 894–912. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13296-022-00613-2
Liu, H. B., Lan, J., Chen, Z. H., Zhao, Y. L., & Jia, L. (2022b). Study on the seismic behavior of connection via welding strengthening under load. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 196, 107387. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCSR.2022.107387
Liu, Y., & Gannon, L. (2009). Finite element study of steel beams reinforced while under load. Engineering Structures, 31, 2630–2642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2009.06.011
Nagaraj Rao, N. R., & Tall, L. (1963) Columns reinforced under load. Weld. J. 42.
NF EN 1993-1-2-Eurocode 3. (2005). Design of steel structures-Part 1–2: General Rules-Structural fire design.
Park, J.-U., An, G., & Lee, H.-W. (2012). Effect of external load on angular distortion in fillet welding. Materials and Design, 42, 403–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2012.06.006
Samoilovich, AYu. (2011). Stress reduction in quenched steel under low tempering. Steel in Translation, 41(7), 565–569. https://doi.org/10.3103/S0967091211070114
Tang, Y. C., Chen, M. Y., Lin, Y. F., Huang, X. Y., Huang, K. Y., He, Y. X., & Li, L. J. (2020). Vision-based three-dimensional reconstruction and monitoring of large-scale steel tubular structures. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2020, 1236021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1236021
Van der Vegte, G. J., Lera, D. H., Owo, Y. S., & Owo, S. (1997). Axial strength of uniplanar X-joints reinforced by T-shaped ring-stiffeners. Proceedings of the International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference, 4, 65–69.
Wang, G., & Zhang, J. C. (2007). Study on application of IGP-stiffen CHS joints in Guangdong science center. Industrial Construction, 10, 93–97. in Chinese.
Wang, Y. Q., Zong, L., Zhu, R. X., Liu, X. Y., & Shi, Y. J. (2015). Behavior of I-section steel beam welding reinforced while under load. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 106, 278–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2014.12.020
Wardenier, J. (2001). Hollow sections in structural applications (pp. 10–15). Wiley.
Zhao, Y., Li, S. W., Huang, Y. X., Ban, L. R., & Zhu, L. (2014). Experimental study on strength of CHS T-joints strengthened by external stiffeners. China Civ. Eng. J., 47(9), 70–75. https://doi.org/10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2014.09.034. in Chinese.
Zhu, L., Song, Q. M., Bai, Y., Wei, Y., & Ma, L. M. (2017). Capacity of steel CHS T-joints strengthened with external stiffeners under axial compression. Thin-Walled Structures, 113, 39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2017.01.007
Zhu, L., Zhao, Y., Li, S., Li, S. W., Huang, Y. X., & Ban, L. R. (2014). Numerical analysis of the axial strength of CHS T-joints reinforced with external stiffeners. Thin-Walled Structures, 85, 481–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2014.09.018
Acknowledgements
Support from Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Future Urban Design (Grant No. UDC2016030200), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51778035), Research Center for Energy Saving and Emission Reduction is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Wang, Z., Sun, H. et al. Axial Capacity of CHS T-Joints Reinforced with Welded External Stiffeners Under Load. Int J Steel Struct (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-024-00827-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-024-00827-6