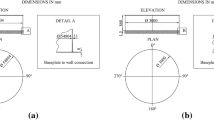
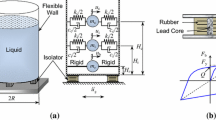
Abstract
In this research, seismic fragility analysis of storage tanks is carried out with a large damage database from past earthquakes and analytical studies. At the fragility analysis, a new damage state has been defined. Peak ground acceleration is employed as an intensity measure. Epistemic and aleatory uncertainties are considered. At the observational fragility analysis, logit, probit and cumulative lognormal model and maximum likelihood method are utilized. In this research, Finite Element Analysis is also performed. As a result, new seismic fragility curves for storage tanks obtained and compared with the existing tank fragility curves in the literature.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
22 January 2023
Corresponding author's email address is corrected in this version.
References
Fire and Disaster Management Agency. 2011. Report on countermeasures against the liquid sloshing of inner float tanks. FDMA. http://www.fdma.go.jp/html/data/tuchi2305/pdf/230512-index.pdf.
Agresti, A. (2002). Introduction to generalized linear models. in categorical data analysis. Wiley.
Aldrich, J. H. and F. D. Nelson. 1984. Linear Probability, Logit, and Probit Models. Quantitative Application in the Social Science-Sera Miller McCun, University of Minnesota and Iola, 95 pp. London: Sage Publications Inc.
Almutfi, I., A. Barbosa., J. Bray., T. Dawson., J. Marrow., and M. Mieler., 2014. M 6.0 South Napa Earthquake of August 24, 2014. p. 1–27. Earthquake Engineering Research Institute, Special Earthquake Report EERI. Oakland, CA.
American Lifelines Alliance (ALA). 2001. Seismic Fragility Formulations for Water Systems, Part 2: Appendices, American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) and Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA)
API Standard, 650. 2001. Welded Steel Tanks for Oil Storage, 12th Edition, American Petroleum Institute, Washington, DC/USA.
Arthur, D. L. and R. Levine. 1988. Guidelines for Safe Storage and Handling of High Toxic Hazard Materials. American Institute of Chemical Engineers - Center for Chemical Process Safety. New York/USA.
Baker, J. W. (2015). Efficient analytical fragility function fitting using dynamic structural analysis. Earthquake Spectra, 31(1), 579–599.
Ballantyne, P. E. and C. B. Crouse. 1997. Reliability and Restoration of Water Supply Systems for Fire Suppression and Drinking Following Earthquakes, U. S. Department of Commerce, National Institute of Standards and Technology. Gaithersburg, MD.
Belanger, D. P. 1973. Port of Whittier. In The Great Alaska Earthquake of 1964. Washington, DC. p. 1074–1107.
Berahman, F., & Behnamfar, F. (2007). Seismic fragility curves for un-anchored on-grade steel storage tanks: Bayesian approach. Journal of Earthquake Engineering, 11(2), 166–192.
Booth, E. D., and C. A. Taylor. 1988. The Chilean Earthquake of 3 March 1985: A Field Report by EEFIT, Earthquake Engineering Field Investigation Team. 86 pp. Earthquake Engineering Research Centre, Bristol University. Bristol/UK.
CCPS, and John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2012. Guidelines for Engineering Design for Process Safety. 2 Edition. Reviewed by Stanley S. Grossel. Hoboken, 31(3): 320–321. NJ/USA: Wiley Online Library
Connor, I. N. (1985). The san antonio, Chile, earthquake of 3 march 1985. Bulletin of the New Zealand National Society for Earthquake Engineering, 18(2), 128–138.
Cooper, T., and T. Wachholz. 1994. The effects of the 1994 Northridge Earthquake on storage tanks. Proceeding of the NEHRP Conference and Workshop on Research on the Northridge, California Earthquake of January 17, 1994. 751–764.
Cooper, T. W. 1997. A study of the performance of petroleum storage tanks during earthquakes, 1933–1995, USA. Gaithersburg, MD/USA: US National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Cozzani, V., Gubinelli, G., Antonioni, G., Spadoni, G., & Zanelli, S. (2005). 2005. The assessment of risk caused by domino effect in quantitative area risk analysis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 127(1–3), 14–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.07.003
D’Amico, M. (2018). Seismic fragility and dynamic behavior of atmospheric cylindrical steel tanks. Università di Bologna.
D’Amico, M., and N. Buratti. 2018. Seismic Fragility Curves for Atmospheric On-Grade Steel Storage Tanks Based on Damage States in Terms of Structural Performance and Release of Content. 16th European Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Thessaloniki, 18–21 June 2018.
Davey, R. A. (2010). Damage to potable water reservoirs in the darfield earthquake. Bulletin of the New Zealand Society for Earthquake Engineering, 43(4), 429–431. https://doi.org/10.5459/bnzsee.43.4.429-431
Edwards, C. L. 2012. Haiti Mw 7.0 Earthquake of January 12, 2010 Lifeline Performance. Reston, Virginia/USA: American Society of Civil Engineers.
EEFIT. 1993. The Loma Prieta Earthquake of 17 October 1989, A Field Report by EEFIT. 184 p. London/England: Earthquake Engineering Field Investigation Team
EERI. (1986). The Chile Earthquake of March 3, 1985 - Industrial Facilities. Earthquake Spectra., 2(2), 373–409. https://doi.org/10.1193/1.1585388
EERI. 2001. Preliminary Observations on the Origin and Effects of the January 26, 2001 Bhuj (Gujarat, India) Earthquake. 16pp. EERI Special Earthquake Report
EERI, and National Research Council. 1989. Loma Prieta Earthquake October 17, 1989. Preliminary Reconnaissance Report. 56 p. Oakland, CA/USA: Earthquake Engineering Research Institute.
Eidinger, J. M., E. A. Avila., D. Ballantyne., L. Cheng., A. der Kiureghian., B. F. Maison., T. D. O’Rourke., and M. Power., 2001. Seismic Fragility Formulations for Water Systems Part 1 – Guideline. American Lifelines Alliance, 96 p. Reston, VA.
EQE Engineering and Consulting, Inc. 1993. The June 28, 1992, Landers and Big Bear Earthquakes: Effects on Power and Industrial Facilities, Electric Power Research Institute. 131 p. San Francisco, CA/USA.
Eshghi, S. and M. S. Razzaghi. 2004. The behavior of special structures during the Bam earthquake of 26 December 2003, Structural Engineering Research Center, Journal of Seismology and Earthquake Engineering. International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and Seismology, Tehran/Iran.
Eshghi, S., & Razzaghi, M. S. (2005). Performance of industrial facilities in the 2003 bam, Iran earthquake. Earthquake Spectra, 21(1), 395–410. https://doi.org/10.1193/1.2098810
FEMA. (1999). Earthquake loss estimation methodology—HAZUS 99 (p. 325). Washington DC/USA: Federal emergency management agency and national institute of buildings sciences.
Fire department dangerous goods security room. 2011. examination of safety measures for outdoor storage tanks with internal floating lids. fire and disaster management agency dangerous goods security office. http://202.229.132.195/pdf/guide/magazine/137/contents/137_8.pdf.
Fire department fire research centre. 2011. report on the 2011 tohoku-pacific ocean earthquake damage and fire fighting activities, Fire Defence Research Technical Document. FDFRC. Japan, 489 pp.
Fischer, E. C. (2014a). Learning from earthquakes: 2014 napa valley earthquake reconnaissance report, Purdue University Report (p. 83). West Lafayette.
Fischer, E. C. 2014. Learning from Earthquakes: 2014 Napa Valley Earthquake Reconnaissance Report. Lyles School of Civil Engineering Graduate Student Reports. Paper 1. https://docs.lib.purdue.edu/civlgradreports/1
Girgin, S. (2011). The NATECH events during the 17 august 1999 kocaeli earthquake: Aftermath and lessons learned. Natural Hazards and Earth System, 11(4), 1129–1140. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-11-1129-2011
Gujarati, D. N. (1988). Basic econometrics (2nd ed., p. 705). McGraw-Hill.
Hall, J. F., Holmes, W. T., & Somers, P. (1995). Northridge earthquake of january 17, 1994: Reconnaissance report (p. 104). Earthquake Engineering Research Institute. Oakland.
Hanson, R. D. 1973. Behavior of liquid-storage tanks, The Great Alaska Earthquake of 1964. National Academy of Science WA/USA: 331–339.
Haroun, M. A. (1983). Behavior of unanchored oil storage tanks: imperial valley earthquake. Journal of Technical Topics in Civil Engineering, 109(1), 23–40.
Hashimoto, P. S., & Tiong, L. W. (1989). Earthquake experience data on anchored, ground-mounted vertical storage tanks. EPRI-NP-6276 (p. 130). Electric Power Research Inst. Palo Alto.
Hatayama, K. (2008). Lessons from The 2003 Tokachi-Oki, Japan, earthquake for prediction of long-period strong ground motions and sloshing damage to oil storage tanks. Journal of Seismology., 12(2), 255–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-007-9066-y
Hatayama, K. 2015. Damage to Oil Storage Tanks from the 2011 Mw 9.0 Tohoku-Oki Tsunami. Earthquake Spectra. 31(2):1103–1124. doi: https://doi.org/10.1193/050713EQS120M.
Herrera, R., and J. F. Beltran. 2012. Performance of steel structures during the February 27, 2010, Chile earthquake. In 15th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering (WCEE), 23816–23825. LX/Portugal. September 24–28.
Hopkins, D., Bell, D., Benites, R., Burr, J., Hamilton, C., & Kotze, R. (2008). The pisco (Peru) earthquake of 15 August 2007. Bulletin of the New Zealand Society for Earthquake Engineering, 41(3), 109–192. https://doi.org/10.5459/bnzsee.41.3.109-192
JMP, Version 15. 2019. SAS Institute Inc. Cary, NC/USA: 1989–2019.
Johnson, G. (2002). Refinery damage and emergency response in the 1999 Izmit, Turkey earthquake (p. 10). In CA State Land Commission. Oakland.
Kawano, K., T. Oda., K. Yoshida., S. Yamamoto., T. Shibuva., and S. Yamada. 1978. Damage of Oil Storage Tanks for Off Miyagi Prefecture Earthquake of June 12, 1978, Preliminary Report. United States Geological Survey. Menlo Park, CA/USA: 507–510.
Kiremidjian, A., K. Ortiz., R. Nielsen., and B. Safavi. 1985. Seismic Risk to Major Industrial Facilities. Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Stanford University. Stanford, CA/USA: 108 p.
Korkmaz, K. A., Sari, A., & Carhoglu, A. I. (2011). Seismic risk assessment of storage tanks in Turkish industrial facilities. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 24(4), 314–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlp.2011.01.003
Lindell, M. K., & Perry, R. W. (1997). Hazardous materials releases in the Northridge earthquake: Implications for seismic risk assessment. Risk Analysis, 17(2), 147–156. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1539-6924.1997.tb00854.x
LS-DYNA R11.0. 2017. Keyword User's Manual Volume I-II. Livermore Software Technology Corporation. Livermore, CA/USA.
Madabhushi, S. P. G., and S. K. Haigh. 2005. The Bhuj, India Earthquake of 26th January 2001, A Field Report by EEFIT. Earthquake Engineering Field Investigation Team. LDN/England: 120 p.
The MathWorks, Inc. 2016. MATLAB Release 2016b. Natick, MA/USA.
Mavko, G. M., Schulz, S., & Brown, B. D. (1985). Effects of the 1983 Coalinga, California, earthquake on creep along the san andreas fault. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 75(2), 475–489.
Merriman, P. A., & Williams, M. S. (1994). The magnitude 6.7 northridge California earthquake of 17 january 1994. Science, 266, 389–397. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.266.5184.389
Mitchell, D., & Tinawi, R. (1992). Structural damage due to the April 22, 1991, costa rican earthquake. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering, 19(4), 586–605. https://doi.org/10.1139/l92-069
Moehle, J., R. Riddell., and R. Boroschek. 2010. The Mw 8.8 Chile Earthquake of February 27, 2010. EERI Special Earthquake Report. 20 pp.
Myers, P. E. 1997. Above Ground Storage Tanks. 1st ed. NY/USA: McGraw-Hill Education. 690 pp.
O’Reilly, G. J., Monteiro, R., Nafeh, A. M. B., Sullivan, T. J., & Calvi, G. M. (2020). Displacement-based framework for simplified seismic loss assessment. Journal of Earthquake Engineering, 24(1), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/13632469.2020.1730272
O’Rourke, M. J., & So, P. (2000). Seismic fragility curves for on-grade steel tanks. Earthquake Spectra., 16(4), 801–815. https://doi.org/10.1193/1.1586140
Ozbey, C., and A. Sari. 2007. Damage to Petrochemical Facilities during Earthquakes. In AIChE Spring Meeting and Global Congress on Process Safety. Houston, TX/USA: April 22–27.
Ozdemir, Z. (2012). Nonlinear fluid-structure interaction for multi-dimensional seismic analyses of liquid storage tanks. Bogazici University.
Ozturk, S., F. Bezir., and A. Sari. 2019. Atmosferik Depolama Tankların Deprem Riski ve Kırılganlık Eğrileri. In 5. International Conference on Earthquake Engineering and Seismology (5ICEES). Ankara/Turkey: October. 9 pp.
Pineda, P., G. R. Saragoni., and E. Arze. 2012. Performance of Steel Tanks in Chile 2010 and 1985 Earthquakes. In Behavior of Steel Structures in Seismic Areas. ed. F. M. Mazzolani and R. Herrera, 337–342. 1st ed. LDN/UK: CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/b11396.
National Fire Protection Association: NFPA 59A. 1996. Standard for the Production, Storage, and Handling of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG). National Fire Protection Association. Houston, TX/USA.
Razzaghi, M. S., & Eshghi, S. (2015). Probabilistic seismic safety evaluation of precode cylindrical oil tanks. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities., 29(6), 04014170. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CF.1943-5509.0000669
Salzano, E., Iervolino, I., & Fabbrocino, G. (2003). Seismic risk of atmospheric storage tanks in the framework of quantitative risk analysis. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries., 16(5), 403–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0950-4230(03)00052-4
Santana, G. 1992. The April 22, 1991 Limon (Costa Rica) Earthquake. In Earthquake Engineering Tenth World Conference. Madrid/Spain: July 19–24. 7033–7038.
Sari, A., and A. Korkmaz. 2007. Petrokimyasal Tesislerindeki Depolama Tanklarının Sismik Davranışın Değerlendirilmesi. In Istanbul Sixth National Conference on Earthquake Engineering. Istanbul/Turkey: October 16–20. 53–61.
Sari, A. 2019. Depolama Tanklarının Risk Analizi. Kontrol Medya, Monthly Process Automation Magazine. Istanbul/Turkey
SAS Institute Inc. 2013. SAS Enterprise Miner 13.1. Cary, NC/USA.
Scawthorn, C., & Johnson, G. S. (2000). preliminary report: Kocaeli (Izmit) earthquake of 17 August 1999. Engineering Structures, 22(7), 727–745. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0296(99)00106-6
Schiff, A. J., and T. L. Holzer. 1998. The Lorna Prieta, California, Earthquake of October 17, 1989-Lifelines. U.S. Geological Survey. WA/USA:133 pp.
Schneider, J. 2006. Introduction to safety and reliability of structures Vol. 5. IABSE.
Scholl, R. E., and J. L. Stratta. 1984. Coalinga, California, earthquake of May 2, 1983: Reconnaissance Report. Earthquake Engineering Research Institute with support from the National Science Foundation. USA: 299 pp.
Sezen, H., & Whittaker, A. S. (2006). Seismic performance of industrial facilities affected by the 1999 Turkey earthquake. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities., 20(1), 28–36. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0887-3828(2006)20:1(28)
Sezen, H., K. J. Elwood., A. S. Whittaker., K. M. Mosalam., J. W. Wallace., and J. F. Stanton. 2000. Structural Engineering Reconnaissance of the August 17, 1999, Kocaeli (Izmit), Turkey. Earthquake, Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center Report. Berkeley, CA/USA: University of California, 120 pp.
Shea, G. H. (1991). Costa rica earthquake of April 22, 1991: reconnaissance report (p. 127). Earthquake Engineering Research Institute. Oakland.
Steinberg, L. J., A. M. Cruz., F. Vardar-Sukar., and Y. Ersoz. 2001. Hazardous Materials Releases During the August 17, 1999 Earthquake in Turkey. In Bridging the Gap: Meeting the World's Water and Environmental Resources Challenges. Orlando, Florida/USA: May 20–24 https://doi.org/10.1061/40569(2001)445.
Steinbrugge, K. V., & Moran, D. F. (1954). An engineering study of the southern California earthquake of July 21, 1952 and its aftershocks. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America., 44(2B), 201–462.
Stratta, J. L. 1980. Reconnaissance Report Greenville (Diablo/Livermore). California Earthquake Sequence January 1980. CA/USA: 35 pp.
Suzuki, K. (2002). Report on damage to industrial facilities in the 1999 Kocaeli earthquake Turkey. Journal of Earthquake Engineering, 6(2), 275–296. https://doi.org/10.1080/13632460209350417
Taucer, F., Alarcon, J. E., & So, E. (2009). 2007 August 15 magnitude 7.9 earthquake near the coast of central Peru: Analysis and field mission report. Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering., 7(1), 1–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-008-9092-3
Watanabe, T. (1966). Damage to oil refinery plants and a building on compacted ground by the niigata earthquake and their restoration. Soils and Foundations., 6(2), 86–99. https://doi.org/10.3208/sandf1960.6.2_86
Yazdanian, M., Ingham, J. M., Kahanek, C., & Dizhur, D. (2020). Damage to flat-based wine storage tanks in the 2013 and 2016 New Zealand earthquakes. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 168, 105983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2020.105983
Yochida, S., Zama, S., Yamada, M., Ishida, K., & Tahara, T. (2000). Report on damage and failure of oil storage tanks due to the 1999 Chi-Chi earthquake in Taiwan. Journal of High Institute of Japan., 38(6), 363–374. https://doi.org/10.11181/hpi1972.38.363
Zama, S. (2003). Damage and failure of oil storage tanks due to the 1999 Kocaeli earthquake in Turkey and Chi-Chi earthquake in Taiwan. Journal of High Institute of Japan, 41(2), 79–86. https://doi.org/10.11181/hpi.41.79.S
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bezir, F., Öztürk, S., Sarı, A. et al. Fragility Analysis of Atmospheric Storage Tanks by Observational and Analytical Data. Int J Steel Struct 22, 192–205 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-021-00567-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-021-00567-x