Abstract
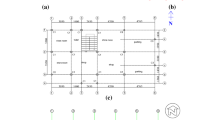
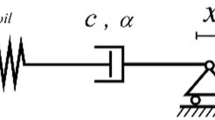
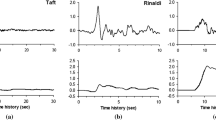
Retrofitting buildings in densely populated areas with a soft story configuration on the first floor can pose a daunting challenge to the community. Against this backdrop, this study set out to evaluate the seismic retrofit strategy's adequacy in enhancing the seismic performance of buildings with a soft story. The proposed strategy utilizes an earthquake energy dissipation device consisting of a combination of a diagonal brace and a metallic-yielding damper at the ground story level. Two prototype buildings, one with five and the other with ten floors, were chosen to assess the proposed retrofit strategy's seismic response through nonlinear static and dynamic analyses. The seismic capacity, lateral displacement response, maximum inter-story drift ratio, energy dissipation, and collapse fragility are the major response parameters used to compare original and retrofitted buildings. The nonlinear static analysis results revealed that the seismic capacity for buildings equipped with a yielding damper was higher than that of the original buildings. It was also found that retrofitted frame buildings had a desirable structural behavior with a higher value of dissipated energy and a lower value of residual displacements and inter-story drift ratio, in turn reducing the likelihood of soft-story failure.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data, models, and code generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
References
Agha Beigi, H., Christopoulos, C., Sullivan, T., & Calvi, M. (2015). Seismic response of a case study soft-story frame retrofitted using a GIB system. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 44(7), 997–1014.
Ahmadi, M. (2012). Developing empirical approaches for determining the axial compressive capacity and compressive strength of confined concrete in circular concrete-filled steel tube columns (in Persian). M.S. thesis, Semnan University.
ANSI/AISC360–10 (2010). Specification for Structural Steel Buildings (ANSI/AISC 360–10). American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC), Chicago-Illinois.
ASCE/SEI 41 (2006). Seismic rehabilitation of existing buildings: American Society of Civil Engineers, Virginia, USA.
ASCE/SEI 7 (2010). Minimum design loads for buildings and other structures. American Society of Civil Engineers, Virginia, USA.
Bagheri, S., Barghian, M., Saieri, F., & Farzinfar, A. (2015). U-shaped metallic-yielding damper in building structures: Seismic behavior and comparison with a friction damper. Structures, 3, 163–171.
Bahmani, P., van de Lindt, J. W., Mochizuki, G. L., Gershfeld, M., & Pryor, S. E. (2015). Experimental seismic collapse study of a full-scale, 4-story, soft-story, wood-frame building. Journal of Architectural Engineering, 21(2), B4014009.
Benavent-Climent, A., & Mota-Páez, S. (2017). Earthquake retrofitting of R/C frames with soft first story using hysteretic dampers: Energy-based design method and evaluation. Engineering Structures, 137, 19–32.
Di Sarno, L., & Wu, J. R. (2020). Seismic assessment of existing steel frames with masonry infills. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 169, 106040.
Ebadi Jamkhaneh, M., Ebrahimi, A. H., & Amiri, M. S. (2019). Experimental and numerical investigation of steel moment resisting frame with U-shaped metallic yielding damper. International Journal of Steel Structures, 19(3), 806–818.
IIEES. (2017). Report on November 12, 2017, Sarpol-e-Zahab earthquake, Kermanshah Province, 5th edition. In International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and Seismology.
Javidan, M. M., & Kim, J. (2019). Seismic Retrofit of Soft-First-Story Structures Using Rotational Friction Dampers. Journal of Structural Engineering, 145(12), 4019162.
Jamkhaneh, M. E., Ahmadi, M., & Sadeghian, P. (2020a). Simplified relations for confinement factors of partially and highly confined areas of concrete in partially encased composite columns. Engineering Structures, 208, 110303.
Jamkhaneh, M. E., Ebrahimi, A. H., & Amiri, M. S. (2020b). Numerical Investigation of the Behavior of MERO Joint System Under Combined Loading Regarding Helical Threads of Elements. International Journal of Steel Structures, 20(3), 897–909.
McKenna, F., Fenves, G. L., & Scott, M. H. (2015). Open system for earthquake engineering simulation. University of California, Berkeley, CA. http://OpenSees.berkeley.edu.
Misir, I. S. (2015). Potential use of locked brick infill walls to decrease soft-story formation in frame buildings. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities, 29(5), 4014133.
Noorifard, A., Tabeshpour, M. R., & Saradj, F. M. (2020). New approximate method to identify soft story caused by infill walls. Structures, 24, 922–939.
Oinam, R. M., & Sahoo, D. R. (2019). Using metallic dampers to improve seismic performance of soft-story RC frames: Experimental and numerical study. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities, 33(1), 4018108.
PEER. (2013). PEER NGA-West2 Database. Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center. Retrieved March 3, 2015, from http://peer.berkeley.edu/ngawest2/databases/.
Sahoo, D. R., & Rai, D. C. (2013). Design and evaluation of seismic strengthening techniques for reinforced concrete frames with soft ground story. Engineering Structures, 56, 1933–1944.
Salmon, J., Agha Beigi, H., & Christopoulos, C. (2019). Full-scale tests of gapped-inclined bracing system: seismic retrofit for soft-story buildings. Journal of Structural Engineering, 145(10), 4019095.
SAP2000. (2010). Integrated structural analysis and design software. Berkeley, CA: Computers and Structures Inc.
Scott, M. H. (2011). Numerical integration options for the force-based beam-column element in OpenSees. Force-Based Element Integration Options in OpenSees, pp. 1–7.
Scott, M. H., & Fenves, G. L. (2006). Plastic hinge integration methods for force-based beam-column elements. Journal of Structural Engineering, 132(2), 244–252.
Shen, H., Zhang, R., Weng, D., Gao, C., Luo, H., & Pan, C. (2017). Simple design method of structure with metallic yielding dampers based on elastic–plastic response reduction curve. Engineering Structures, 150, 98–114.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadi, M., Ebadi Jamkhaneh, M. Numerical Investigation of Energy Dissipation Device to Improve Seismic Response of Existing Steel Buildings with Soft-First-Story. Int J Steel Struct 21, 691–702 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-021-00466-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-021-00466-1