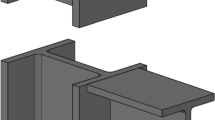
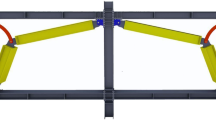
Abstract
After the Northridge and Kobe earthquakes, several destruction of the structural beams were occurred. The difficulty and cost-effectiveness of beam replacement after earthquakes is a major problem on steel structures. For this purpose, the idea of using replaceable connection is suggested. A slit steel damper (SSD) is introduced that leads to the further energy damping and the ability to move the plastic joint outside of structural elements. The stiffness and damping characteristics of SSD is related to the thickness, height and number of sheets of the damper. The usage of SSD is more progressive and at the same time, the optimal design of SSDs should be proposed to meet the economical criterion and the reduction of the stress and deflection. In this study, an optimal SSD connection is proposed to enhance the performance of the classical SSD connection to meet the criterion of AISC to utilize in special moment frames. The results demonstrated that increasing the thickness and reduction of the steel sheets in the damper had a greater effect on the performance of the SSD connection, in comparison with the increase in the number of sheets. Therefore, the Cuckoo Search (CS) was utilized to optimize the several SSD parameters. Furthermore, a comparison between the CS-SSD and Reduced Beam Section (RBS) which is known as a common moment steel fixed-connection was accomplished. Results indicate that CS-SSD connection can reach the same function as the RBS connections under cycling loadings, in addition to the easy replacement capability after seismic excitations. The performance of the proposed CS optimization algorithm in designing of the optimal SSD was compared with the traditional Genetic Algorithm and the particle swarm optimization (PSO) with considering several designing constraints. High capabilities of the proposed CS optimization algorithm in terms of weight, energy absorption, stiffness and bearing capacity of SSD connections are simultaneously clarified by the results.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghajanian, S., Baghi, H., Amini, F., & Samani, M. Z. (2014). Optimal control of steel structures by improved particle swarm. International Journal of Steel Structures, 14(2), 223–230.
AISC 358. (2016). Prequalified connections for special & intermediate steel moment frams for seismic applications. Chicago, USA.
Amadeo, B. C., Oh, S.-H., & Akiyama, H. (1998). Ultimate energy absorption capacity of slit-type steel plates subjected to shear deformations. Journal of Structural and Construction Engineering (Transactions of AIJ), 63(503), 139–147.
Amini, F., & Zabihi-Samani, M. (2014). A wavelet-based adaptive pole assignment method for structural control. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 29(6), 464–477.
Chan, R. W. K., & Albermani, F. (2008). Experimental study of steel slit damper for passive energy dissipation. Engineering Structures, 30(4), 1058–1066.
Chen, C.-C., & Lin, C.-C. (2013). Seismic performance of steel beam-to-column moment connections with tapered beam flanges. Engineering Structures, 48, 588–601.
FEMA 350. (2000). Recommended seismic design criteria for new steel moment frame buildings. USA: SAC Joint Venture.
Gandomi, A., Yang, X.-S., & Alavi, A. (2013). Cuckoo search algorithm: A metaheuristic approach to solve structural optimization problems. Engineering with Computers, 29(1), 17–35.
Ghabraie, K., Chan, R., Huang, X., & Xie, Y. M. (2010). Shape optimization of metallic yielding devices for passive mitigation of seismic energy. Engineering Structures, 32(8), 2258–2267.
Ghanooni-Bagha, M., Ali Shayanfar, M., Reza-Zadeh, O., & Zabihi-Samani, M. (2017). The effect of materials on the reliability of reinforced concrete beams in normal and intense corrosions. Eksploatacja i Niezawodnosc—Maintenance and Reliability, 19(3), 393–402.
Hedayat, A. A. (2015). Prediction of the force displacement capacity boundary of an unbuckled steel slit damper. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 114, 30–50.
Karavasilis, T. L., Kerawala, S., & Hale, E. (2012). Hysteretic model for steel energy dissipation devices and evaluation of a minimal-damage seismic design approach for steel buildings. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 70, 358–367.
Kaveh, A., & Bakhshpoori, T. (2013). Optimum design of steel frames using Cuckoo search algorithm with Lévy flights. The Structural Design of Tall and Special Buildings, 22(13), 1023–1036.
Köken, A., & Köroğlu, M. A. (2012). Waste rubber damper using on steel beam to column connection. International Journal of Arts & Sciences, 5(4), 217–222.
Lee, C.-H., Kim, J., Kim, D. H., Ryu, J., & Ju, Y.-K. (2016). Numerical and experimental analysis of combined behavior of shear-type friction damper and non-uniform strip damper for multi-level seismic protection. Engineering Structures, 114, 75–92.
Moshtagh, A., Sheydaei, M. R., & Tohidi Moghadam, V. (2012). Usage of CSSD on the failure behavior of spatial double-layer smooth and evaluation of progressive failure. In Third national conference on earthquake and structures. Kerman, Iran.
Oh, S.-H., Kim, Y.-J., & Ryu, H.-S. (2009). Seismic performance of steel structures with slit dampers. Engineering Structures, 31(9), 1997–2008.
Ostadali-Makhmalbaf, M., Tutunchian, M., & Zabihi-Samani, M. (2011). Optimized fuzzy logic controller for semi-active control of buildings using particle swarm optimization. Advanced Material Research, 2505(9), 255–260.
Saffari, H., Hedayat, A. A., & Nejad, M. P. (2013). Post-Northridge connections with slit dampers to enhance strength and ductility. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 80, 138–152.
Saleh, A., Mirghaderi, S. R., & Zahrai, S. M. (2016a). Cyclic testing of tubular web RBS connections in deep beams. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 117, 214–226.
Saleh, A., Zahrai, S. M., & Mirghaderi, S. R. (2016b). Experimental study on innovative tubular web RBS connections in steel MRFs with typical shallow beams. Structural Engineering & Mechanics, 57(5), 785–808.
Shahri, S., & Mosavi, S. R. (2016). Development of slit dampers at the junction to the column by creating oval gaps. Modares Civil Engineering Journal, 16(1), 93–104.
Swati, A. K., & Gaurang, V. (2014). Study of steel moment connection with and without reduced beam section. Case Studies in Structural Engineering, 1, 26–31.
Systemes, D. (2010). ABAQUS. USA.
Tagawa, H., Yamanishi, T., Takaki, A., & Chan, R. W. K. (2016). Cyclic behavior of seesaw energy dissipation system with steel slit dampers. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 117, 24–34.
Teruna, D. R., Majid, T. A., & Budiono, B. (2015). Experimental study of hysteretic steel damper for energy dissipation capacity. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2015, 12.
Xin-She, Y., & Deb, S. (2009). Cuckoo search via Lévy flights. In Nature & biologically inspired computing, 2009. NaBIC 2009. World congress on. 2009.
Zabihi-Samani, M., & Amini, F. (2015). A Cuckoo search controller for seismic control of a benchmark tall building. Journal of Vibroengineering, 17(3), 1382–1400.
Zabihi-Samani, M., & Ghanooni-Bagha, M. (2017). A fuzzy logic controller for optimal structural control using MR dampers and particle swarm optimization. Journal of Vibroengineering, 19(3), 1901–1914.
Zabihi-Samani, M., & Ghanooni-Bagha, M. (2018a). An optimal cuckoo search-fuzzy logic controller for optimal structural control. International Journal of Optimization in Civil Engineering, 8(1), 117–135.
Zabihi-Samani, M., & Ghanooni-Bagha, M. (2018). Optimal semi-active structural control with a wavelet-based Cuckoo-search fuzzy logic controller. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transactions of Civil Engineering.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zabihi-Samani, M. Design of Optimal Slit Steel Damper Under Cyclic Loading for Special Moment Frame by Cuckoo Search. Int J Steel Struct 19, 1260–1271 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-019-00206-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-019-00206-6