Abstract
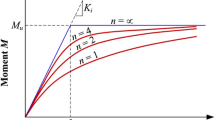
This paper presents an exact way for computation prying action forces in bolted rigid connections with circular end plate by studying the behavior of this type of connections. Besides, finite element models of bolted connections with circular end plate is made in various geometry. Prying action effect in these models is regarded and collapse mechanism of T connections is used to computation stiffness. Also, deformation and distribution of surface press which result from prying action phenomena is used. With using the result from parametric analyses of connections, an improved method is presented to computation prying action. Then, an improved method is proposed to design bolted rigid connections with circular end plate in regard with prying action effect. Accuracy assessment of proposed method, will display efficiency and favor accuracy in designing bolted connections with circular end plate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abaqus Element Reference. (2016). “Abaqus documentation.” Online help.
American institute of steel construction, ANSI/AISC. (2010). “Specification for structural steel building.”
American Institute of Steel Construction. (2005). “Manual of steel construction, Load and resistance factor design.” connections, Chicago.
Bahaari, M.R. Sherburne, Archibald, N. (2000). “Behavior of eight-bolt large capacity end-plate connections.” Journal of Computers & Structures, 77, pp. 315–325.
Cavdar, O., Bayraktar, A. Cavdar, A. and Kartal, M. E. (2009). “Stochastic finite element analysis of structural systems with partially restrained connections subjected to seismic loads.” Steel and Composite Structures, 9(2), pp. 123–135.
Chakhari and Zghal, A. (2007). “Numerical model for bolted T-stubs with two bolt rows.” Journal of Structural Engineering and Mechanics, 26(3).
Crocetti, R. Gustafsson P. J. Girhammar, U. A., Costa, L. and Asimakidis, A. (2016). “Nailed Steel Plate Connections: Strength and Ductile Failure Modes.” Journal of Structures, 8(1), pp. 44–52.
Da-Silva, L., Lima, L., Vellasco, P., De Andrade, S., De Castro R.A. (2008). “Nonlinear dynamic analysis of steel portal frames with semi-rigid connections.” Journal of Engineering Structures, 30, pp. 2566–2579.
Da-Silva, L., Lima, L., Vellasco, P. and De Andrade, S. (2001). “Experimental behavior of end-plate beam to column joints under bending and axial force.” Eccs technical committee 10, twg 10.2, Department of civil engineering, University of Coimbra.
Dubina, D., Stratan, A. (2002). “Behavior of welded connections of moment resisting frames beam-to-column joints.” Journal of Engineering Structures, 24, pp. 1431–1440.
Farajpour, M. R. (2013). “Effect of beam to column connections on static and seismic response of steel frames.” M.Sc. thesis, Azad university, Maraghe branch, Iran.
Farajpour, M. R., Hosseinzadeh, Y. and Lotfollahiyaghin, M. A. (2013). “Effect of prying action forces on rigid end plate connections.” Journal of Sharif, 4, pp. 3–13.
Huihuan Ma, Shan Ren and Feng Fan, A. (2016). “Experimental and numerical research on a new semirigid joint for single-layer reticulated structures.” Journal of Engineering Structures, 126, pp. 725–738.
Huu-Tai Thai and Brian Uy. (2016). “Rotational stiffness and moment resistance of bolted endplate joints with hollow or CFST columns.” Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 126, pp. 139–152.
Irtem, E. (2001). “Investigation of semi-rigid bolted beam connections on prefabricated frame joints.” Journal of Structural Engineering and Mechanics, 12(4).
Krishnamurthy, N. (1980). “Modeling and prediction of steel bolted connection behavior.” Journal of Computers & Structures, 11(2), pp. 75–82.
Mirghaderi1, S.R., Dehghani Renani, M. (2009). “The rigid seismic connection of continuous beams to column.” Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 64, pp. 1516–1529.
Smith, J.C. (1991). “Structural steel design LRFD approach.” North Carolina State University, Wiley Inc.
Smitha, M. S. and Satish Kumar S. R. (2013). “Steelconcrete composite flange plate connections, finite element modeling and parametric studies.” Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 82, pp. 164–176.
Urbonas, K., Daniunas, A. (2006). “Behavior of semi-rigid steel beam-to-beam joints under bending and axial forces.” Journal of construction steel research, 62, pp. 1244–1249.
Wheeler, A. T., Clarke, M. J. and Hancock, G. J. (2000). “FE Modeling of four-bolt, tubular moment end-plate connections.” Journal of Structural Engineering, ASCE, 126(7), pp. 816–822.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farajpour, M.R., Sabouri, J. Effect of Prying Action Forces on Design Method of Rigid Bolted Connections with Circular End Plate. Int J Steel Struct 18, 127–137 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-018-0310-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-018-0310-9