Abstract
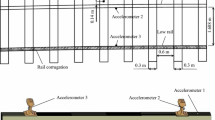
In recent years, a number of researches into dynamic characteristics of the noise and vibration in the railway have been performed. Since the high frequency vibration, which occurs in the irregularity(roughness) of the wheel and rail running surfaces, causes the track noise in railway system, analytic study with measurement of the vibration for the wheel and rail is needed. So, the algorithm and program for the vibration analysis in the track system were developed as a part of the analytic study. In this study, evaluation for the effect of the linearized contact spring in track dynamic system was studied with the developed program. In addition, analytical study for the comparison between hysteretic and viscous damping in this system was performed. The result shows that both the linearized contact spring stiffness and damping of track system are important factors in track dynamic analysis model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Esveld C. (2001). Modern Railway Track, Second Edition, MRT-productions.
Kim JH, Won DH, Kim DH and Kang YJ. (2012). A Study about Vibration Analysis of Track System. The International Symposium on Speed-up, Safety and Service Technology for Railway and Maglev Systems.
Kim JH. (2012). Noise and vibration Analysis for Wheel/Rail Interaction. Ph.D. Dissertation, Korea University.
Remington P.J. (1987). Wheel/rail rolling noise, I: Theoretical analysis. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 81(6), pp. 1805–1823.
Sato Y. (1976). Railway Technical Research Report-Study on High Frequency Vibrations in Track. The Railway Technical Research Institute.
Thompson D.J. (1993). Wheel-rail noise generation. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 161(3), pp. 387–400.
Thompson D.J., Fodiman P., and Mahe H. (1996). Experimental validation of the TWINS prediction program for rolling noise. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 193(1), pp. 137–147.
Thompson D.J. and Jones C.J.C. (2000). A review of the modeling of wheel/rail noise generation. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 231(3), pp. 519–536.
Yang SC. (1995). Evaluation of Running Train Loads Transmitting to Sub-structure. Korea Rail Network Authority Report.
Yang SC. (2002). Development of Numerical Analysis Method of Train/Track Interaction for Evaluation of Dynamic Track Design Load. Proceedings of Korean Society for Railway.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J., Jang, J., Han, S. et al. Effect of linearized contact spring in track dynamic system. Int J Steel Struct 16, 1365–1371 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-016-0077-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-016-0077-9