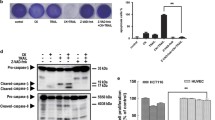
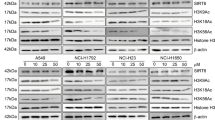
Abstract
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is an ideal apoptosis inducer and believed to have promise in cancer therapy, yet part of cancer cells exhibit resistance to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. This necessitates the exploration of agents that resensitizes cancer cells to TRAIL. In our study, we found that Trichostatin A (TSA), an histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, augmented TRAIL-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells in a caspase-dependent manner. Besides, upregulation of DR5 and downregulation of anti-apoptotic proteins including XIAP, Mcl-1, Bcl-2 and Survivin also contributed to this synergism. Noticeably, TSA treatment inhibited Forkhead boxM1 (FOXM1), which expression level showed negative correlation with TRAIL sensitivity. Similarly, silencing of FOXM1 by small interfering RNA (siRNA) resensitized cancer cells to TRAIL and strengthened the TRAIL-augmenting effect of TSA. In addition, we demonstrated the depletion of FOXM1 was a consequence of the inactivation of ERK mediated by TSA. Collectively, it was first shown that TSA potentiated TRAIL sensitivity via ERK/FOXM1 pathway in gastric cancer cells. FOXM1 might serve as a biomarker for predicting sensitivity to TRAIL.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108.
Marrelli D, Polom K, de Manzoni G, Morgagni P, Baiocchi GL, Roviello F. Multimodal treatment of gastric cancer in the west: where are we going? World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(26):7954–69.
Gonzalvez F, Ashkenazi A. New insights into apoptosis signaling by Apo2L/TRAIL. Oncogene. 2010;29(34):4752–65.
Kischkel FC, Lawrence DA, Chuntharapai A, Schow P, Kim KJ, Ashkenazi A. Apo2L/TRAIL-dependent recruitment of endogenous FADD and caspase-8 to death receptors 4 and 5. Immunity. 2000;12(6):611–20.
Bellail AC, Tse MC, Song JH, Phuphanich S, Olson JJ, Sun SY, et al. DR5-mediated DISC controls caspase-8 cleavage and initiation of apoptosis in human glioblastomas. J Cell Mol Med. 2010;14(6A):1303–17.
Stuckey DW, Shah K. TRAIL on trial: preclinical advances in cancer therapy. Trends Mol Med. 2013;19(11):685–94.
den Hollander MW, Gietema JA, de Jong S, Walenkamp AM, Reyners AK, Oldenhuis CN, et al. Translating TRAIL-receptor targeting agents to the clinic. Cancer Lett. 2013;332(2):194–201.
Dimberg LY, Anderson CK, Camidge R, Behbakht K, Thorburn A, Ford HL. On the TRAIL to successful cancer therapy? Predicting and counteracting resistance against TRAIL-based therapeutics. Oncogene. 2013;32(11):1341–50.
Maksimovic-Ivanic D, Stosic-Grujicic S, Nicoletti F, Mijatovic S. Resistance to TRAIL and how to surmount it. Immunol Res. 2012;52(1–2):157–68.
Bin L, Thorburn J, Thomas LR, Clark PE, Humphreys R, Thorburn A. Tumor-derived mutations in the TRAIL receptor DR5 inhibit TRAIL signaling through the DR4 receptor by competing for ligand binding. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(38):28189–94.
Zhang YQ, Zhang BL. TRAIL resistance of breast cancer cells is associated with constitutive endocytosis of death receptors 4 and 5. Mol Cancer Res. 2008;6(12):1861–71.
Grotzer MA, Eggert A, Zuzak TJ, Janss AJ, Marwaha S, Wiewrodt BR, et al. Resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in primitive neuroectodermal brain tumor cells correlates with a loss of caspase-8 expression. Oncogene. 2000;19(40):4604–10.
Ricci MS, Kim SH, Ogi K, Plastaras JP, Ling J, Wang W, et al. Reduction of TRAIL-induced Mcl-1 and cIAP2 by c-Myc or sorafenib sensitizes resistant human cancer cells to TRAIL-induced death. Cancer Cell. 2007;12(1):66–80.
Kocab AJ, Veloso A, Paulsen MT, Ljungman M, Duckett CS. Effects of physiological and synthetic IAP antagonism on c-IAP-dependent signaling. Oncogene. 2015. doi:10.1038/onc.2015.3.
Hellwig CT, Rehm M. TRAIL signaling and synergy mechanisms used in TRAIL-based combination therapies. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11(1):3–13.
Hwang JS, Lee HC, Oh SC, Lee DH, Kwon KH. Shogaol overcomes TRAIL resistance in colon cancer cells via inhibiting of survivin. Tumour Biol. 2015. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-3629-2.
Chen J, Sun X, Yang W, Jiang G, Li X. Cisplatin-enhanced sensitivity of glioblastoma multiforme U251 cells to adenovirus-delivered TRAIL in vitro. Tumour Biol. 2010;31(6):613–22.
Khan O, La Thangue NB. HDAC inhibitors in cancer biology: emerging mechanisms and clinical applications. Immunol Cell Biol. 2012;90(1):85–94.
Sun S, Han Y, Liu J, Fang Y, Tian Y, Zhou J, et al. Trichostatin A targets the mitochondrial respiratory chain, increasing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production to trigger apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e91610.
De Souza C, Chatterji BP. HDAC inhibitors as novel anti-cancer therapeutics. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2015;10(2):145–62.
Morales JC, Ruiz-Magana MJ, Carranza D, Ortiz-Ferron G, Ruiz-Ruiz C. HDAC inhibitors with different gene regulation activities depend on the mitochondrial pathway for the sensitization of leukemic T cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2010;297(1):91–100.
Bangert A, Cristofanon S, Eckhardt I, Abhari BA, Kolodziej S, Hacker S, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors sensitize glioblastoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by c-myc-mediated downregulation of cFLIP. Oncogene. 2012;31(44):4677–88.
Nakata S, Yoshida T, Horinaka M, Shiraishi T, Wakada M, Sakai T. Histone deacetylase inhibitors upregulate death receptor 5/TRAIL-R2 and sensitize apoptosis induced by TRAIL/APO2-L in human malignant tumor cells. Oncogene. 2004;23(37):6261–71.
Halasi M, Gartel AL. FOX(M1) news—it is cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013;12(3):245–54.
Song JG, Xie HH, Li N, Wu K, Qiu JG, Shen DM, et al. SUMO-specific protease 6 promotes gastric cancer cell growth via deSUMOylation of FoxM1. Tumour Biol. 2015. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-3737-z.
Shao DF, Wang XH, Li ZY, Xing XF, Cheng XJ, Guo T, et al. High-level SAE2 promotes malignant phenotype and predicts outcome in gastric cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;5(2):589–602.
Li X, Yao R, Yue L, Qiu W, Qi W, Liu S, et al. FOXM1 mediates resistance to docetaxel in gastric cancer via up-regulating Stathmin. J Cell Mol Med. 2014;18(5):811–23.
Hu CJ, Wang B, Tang B, Chen BJ, Xiao YF, Qin Y, et al. The FOXM1-induced resistance to oxaliplatin is partially mediated by its novel target gene Mcl-1 in gastric cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1849(3):290–9.
Pandit B, Gartel AL. FoxM1 knockdown sensitizes human cancer cells to proteasome inhibitor-induced apoptosis but not to autophagy. Cell Cycle. 2011;10(19):3269–73.
Prasad S, Kim JH, Gupta SC, Aggarwal BB. Targeting death receptors for TRAIL by agents designed by Mother Nature. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2014;35(10):520–36.
Jiang L, Wang P, Chen L, Chen H. Down-regulation of FoxM1 by thiostrepton or small interfering RNA inhibits proliferation, transformation ability and angiogenesis, and induces apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(9):5450–60.
Zhang JR, Lu F, Lu T, Dong WH, Li P, Liu N, et al. Inactivation of FoxM1 transcription factor contributes to curcumin-induced inhibition of survival, angiogenesis, and chemosensitivity in acute myeloid leukemia cells. J Mol Med. 2014;92(12):1319–30.
Gayle SS, Castellino RC, Buss MC, Nahta R. MEK inhibition increases lapatinib sensitivity via modulation of FOXM1. Curr Med Chem. 2013;20(19):2486–99.
Chan DW, Hui WW, Cai PC, Liu MX, Yung MM, Mak CS, et al. Targeting GRB7/ERK/FOXM1 signaling pathway impairs aggressiveness of ovarian cancer cells. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52578.
Wang IC, Chen YJ, Hughes DE, Ackerson T, Major ML, Kalinichenko VV, et al. FoxM1 regulates transcription of JNK1 to promote the G1/S transition and tumor cell invasiveness. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(30):20770–8.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646–74.
Han MH, Park C, Kwon TK, Kim GY, Kim WJ, Hong SH, et al. The histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A sensitizes human renal carcinoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through down-regulation of c-FLIPL. Biomol Ther. 2015;23(1):31–8.
Finlay D, Vamos M, Gonzalez-Lopez M, Ardecky RJ, Ganji SR, Yuan H, et al. Small-molecule IAP antagonists sensitize cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis: roles of XIAP and cIAPs. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13(1):5–15.
Beyer U, Kronung SK, Leha A, Walter L, Dobbelstein M. Comprehensive identification of genes driven by ERV9-LTRs reveals TNFRSF10B as a re-activatable mediator of testicular cancer cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2015. doi:10.1038/cdd.2015.68.
Hisanaga A, Ishida H, Sakao K, Sogo T, Kumamoto T, Hashimoto F, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity and molecular mechanism of Oolong tea theasinensin. Food Funct. 2014;5(8):1891–7.
Okada K, Fujiwara Y, Takahashi T, Nakamura Y, Takiguchi S, Nakajima K, et al. Overexpression of forkhead box M1 transcription factor (FOXM1) is a potential prognostic marker and enhances chemoresistance for docetaxel in gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(3):1035–43.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 81402308, No.81301874), the Natural Science Foundation of Beijing (No.7132051), 985 special project sponsored by Peking University Health Science Center (No.2013-5-09), and the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (No. 2014AA020603).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Fan, B., Zhang, LH. et al. Trichostatin A potentiates TRAIL-induced antitumor effects via inhibition of ERK/FOXM1 pathway in gastric cancer. Tumor Biol. 37, 10269–10278 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-4816-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-4816-5