Abstract
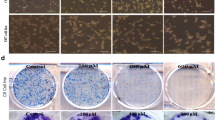
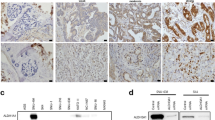
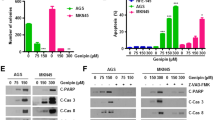
Gastric cancer is a big threat to human health. Effective therapeutic cancer target remains to be discovered. Aquaporin 3 (AQP3) belongs to a family of transmembrane channels that are important in transporting water, glycerol, and other small molecules across the cell membrane. Glycerol that is transported by AQP3 is necessary for cell energy generation and lipid synthesis which fulfill the cell biological processes. Previous studies have shown that AQP3 is implicated in disease progression in several cancer types. However, whether AQP3-regulated glycerol uptake and metabolism were involved in cancer progression remains to be further studied. Our study demonstrated that the expression of AQP3 was positively correlated with glycerol level in human gastric cancer tissues. AQP3 inhibition induced proliferation impairment in gastric cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. AQP3 inhibition that induced glycerol uptake reduction and glycerol administration would rehabilitate the cell proliferation. The energy and lipid production decreased when AQP3 was knocked down since the cellular glycerol level and several lipogenesis enzymes were downregulated. PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, which was involved in the impaired lipid and ATP production, was also inhibited after AQP3 knockdown. Our study indicated that the energy and lipid production inhibition, which were responsible for gastric cancer cell proliferation impairment, were induced by glycerol uptake reduction after AQP3 knockdown.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AQP3:
-
Aquaporin 3
- GYK:
-
Glycerol kinase
- G3P:
-
Glycerol-3-phosphate
- MAG:
-
Monoglyceride
- DAG:
-
Dialyceride
- TAG:
-
Triglyceride
- PA:
-
Phosphatidic acid
- LPA:
-
Lysophosphatidic acid
- AGPAT1, 2, and 3:
-
1-Acylglycerol-3-phosphate O-acyltransferase 1, 2, and 3
- GPAT1 and 2:
-
Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 1 and 2
- MOGAT1 and 2:
-
Monoacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1 and 2
- DGAT1 and 2:
-
Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1 and 2
- FFA:
-
Free fatty acid
- FAO:
-
Fatty acid oxidation
- FA:
-
Fatty acid
- RT:
-
Room temperature
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108.
Agre P, Kozono D. Aquaporin water channels: molecular mechanisms for human diseases. FEBS Letters. 2003;555:72–8.
Verkman AS, Mitra AK. Structure and function of aquaporin water channels. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2000;278:F13–28.
Fujiyoshi Y, Mitsuoka K, de Groot BL, Philippsen A, Grubmuller H, Agre P, et al. Structure and function of water channels. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2002;12:509–15.
Matsuzaki T, Tajika Y, Ablimit A, Aoki T, Hagiwara H, Takata K. Aquaporins in the digestive system. Medical Electron Microscopy. 2004;37:71–80.
Zhi X, Tao J, Li Z, Jiang B, Feng J, Yang L, et al. Mir-874 promotes intestinal barrier dysfunction through targeting aqp3 following intestinal ischemic injury. FEBS Letters. 2014;588:757–63.
Wang G, Gao F, Zhang W, Chen J, Wang T, Zhang G, et al. Involvement of aquaporin 3 in helicobacter pylori-related gastric diseases. PloS one. 2012;7, e49104.
Verkman AS, Hara-Chikuma M, Papadopoulos MC. Aquaporins—new players in cancer biology. Journal of Molecular Medicine. 2008;86:523–9.
Wang J, Feng L, Zhu Z, Zheng M, Wang D, Chen Z, et al. Aquaporins as diagnostic and therapeutic targets in cancer: how far we are? J Transl Med. 2015;13:96.
Huang YH, Zhou XY, Wang HM, Xu H, Chen J, Lv NH. Aquaporin 5 promotes the proliferation and migration of human gastric carcinoma cells. Tumour Biology. 2013;34:1743–51.
Shi X, Wu S, Yang Y, Tang L, Wang Y, Dong J, et al. Aqp5 silencing suppresses p38 mapk signaling and improves drug resistance in colon cancer cells. Tumour Biology. 2014;35:7035–45.
Wei M, Shi R, Zeng J, Wang N, Zhou J, Ma W. The over-expression of aquaporin-1 alters erythroid gene expression in human erythroleukemia k562 cells. Tumour Biology. 2015;36:291–302.
Zhao H, Yang X, Zhou Y, Zhang W, Wang Y, Wen J, et al. Potential role of aquaporin 3 in gastric intestinal metaplasia. Oncotarget. 2015.
Swinnen JV, Van Veldhoven PP, Timmermans L, De Schrijver E, Brusselmans K, Vanderhoydonc F, et al. Fatty acid synthase drives the synthesis of phospholipids partitioning into detergent-resistant membrane microdomains. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2003;302:898–903.
Zheng H, Liu W, Anderson LY, Jiang QX. Lipid-dependent gating of a voltage-gated potassium channel. Nature Communications. 2011;2:250.
Moreno-Sanchez R, Rodriguez-Enriquez S, Marin-Hernandez A, Saavedra E. Energy metabolism in tumor cells. FEBS J. 2007;274:1393–418.
Mazurek S, Boschek CB, Eigenbrodt E. The role of phosphometabolites in cell proliferation, energy metabolism, and tumor therapy. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1997;29:315–30.
Brisson D, Vohl MC, St-Pierre J, Hudson TJ, Gaudet D. Glycerol: a neglected variable in metabolic processes? Bioessays. 2001;23:534–42.
Baba H, Zhang XJ, Wolfe RR. Glycerol gluconeogenesis in fasting humans. Nutrition. 1995;11:149–53.
Lass A, Zimmermann R, Oberer M, Zechner R. Lipolysis—a highly regulated multi-enzyme complex mediates the catabolism of cellular fat stores. Prog Lipid Res. 2011;50:14–27.
Cui G, Staron MM, Gray SM, Ho PC, Amezquita RA, Wu J, et al. Il-7-induced glycerol transport and TAG synthesis promotes memory CD8+ T cell longevity. Cell. 2015;161:750–61.
Naidoo K, Coetzer TL. Reduced glycerol incorporation into phospholipids contributes to impaired intra-erythrocytic growth of glycerol kinase knockout plasmodium falciparum parasites. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1830;2013:5326–34.
Wang C, Chi Y, Li J, Miao Y, Li S, Su W, et al. Fam3a activates pi3k p110alpha/akt signaling to ameliorate hepatic gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis. Hepatology. 2014;59:1779–90.
Lee N, Kim I, Park S, Han D, Ha S, Kwon M, et al. Creatine inhibits adipogenesis by downregulating insulin-induced activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathway. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24:983–94.
Shaik ZP, Fifer EK, Nowak G. Akt activation improves oxidative phosphorylation in renal proximal tubular cells following nephrotoxicant injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008;294:F423–432.
Davila D, Fernandez S, Torres-Aleman I. Astrocyte resilience to oxidative stress induced by insulin like growth factor I (IGF-I) involves preserved AKT (protein kinase B) activity. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2015.
Mata R, Palladino C, Nicolosi ML, Presti AR, Malaguarnera R, Ragusa M, et al. IGF-I induces upregulation of DDR1 collagen receptor in breast cancer cells by suppressing MIR-199a-5p through the PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget. 2015.
Rodriguez A, Catalan V, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Fruhbeck G. Aquaglyceroporins serve as metabolic gateways in adiposity and insulin resistance control. Cell Cycle. 2011;10:1548–56.
Hara-Chikuma M, Verkman AS. Prevention of skin tumorigenesis and impairment of epidermal cell proliferation by targeted aquaporin-3 gene disruption. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2008;28:326–32.
Chen J, Wang T, Zhou YC, Gao F, Zhang ZH, Xu H, et al. Aquaporin 3 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2014;33:38.
Xu H, Xu Y, Zhang W, Shen L, Yang L, Xu Z. Aquaporin-3 positively regulates matrix metalloproteinases via PI3K/AKT signal pathway in human gastric carcinoma SGC7901 cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2011;30:86.
Medes G, Thomas A, Weinhouse S. Metabolism of neoplastic tissue. IV. A study of lipid synthesis in neoplastic tissue slices in vitro. Cancer Research. 1953;13:27–9.
Abramson HN. The lipogenesis pathway as a cancer target. J Med Chem. 2011;54:5615–38.
Cantor JR, Sabatini DM. Cancer cell metabolism: one hallmark, many faces. Cancer Discov. 2012;2:881–98.
Boroughs LK, DeBerardinis RJ. Metabolic pathways promoting cancer cell survival and growth. Nat Cell Biol. 2015;17:351–9.
Rojek AM, Skowronski MT, Fuchtbauer EM, Fuchtbauer AC, Fenton RA, Agre P, et al. Defective glycerol metabolism in aquaporin 9 (aqp9) knockout mice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2007;104:3609–14.
Oronsky BT, Oronsky N, Fanger GR, Parker CW, Caroen SZ, Lybeck M, et al. Follow the atp: tumor energy production: a perspective. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2014;14:1187–98.
Shi Y, Cheng D. Beyond triglyceride synthesis: the dynamic functional roles of MGAT and DGAT enzymes in energy metabolism. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009;297:E10–18.
Athenstaedt K, Daum G. The life cycle of neutral lipids: synthesis, storage and degradation. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006;63:1355–69.
Watt MJ, Steinberg GR. Regulation and function of triacylglycerol lipases in cellular metabolism. The Biochemical Journal. 2008;414:313–25.
Acknowledgements
Our work was sponsored by the Natural Science Foundation of China (30901421), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China (BK20141493), and the Program for Development of Innovative Research Team in the First Affiliated Hospital of NJMU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Ethics approval
The Institutional Ethical Board of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University approved of our study. Human samples were taken after informed contents be signed. For animal experiments, our designs were in line with the institutional animal care and use committee guidelines.
Additional information
Zheng Li, Bowen Li and Lei Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Li, B., Zhang, L. et al. The proliferation impairment induced by AQP3 deficiency is the result of glycerol uptake and metabolism inhibition in gastric cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 37, 9169–9179 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4753-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4753-8