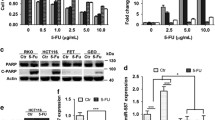
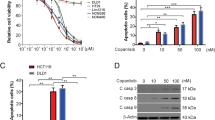
Abstract
Colorectal carcinoma (CRC) is the second most common and frequent cause of cancer-related deaths for men and women in the world. PIK3CA and PIK3CB that reverse multidrug resistance (MDR) can serve as predictive and prognostic markers as well as therapeutic targets for CRC treatment. In the present study, we showed that PIK3CA and PIK3CB are upregulated in CRCs and positively correlated with MDR-1, LRP, and GST-π. Long-term monitoring of 316 CRC patients showed that PIK3CA and PIK3CB were associated with poor survival time as shown by Kaplan-Meier analysis. Furthermore, we found that the downregulation of PIK3CA and PIK3CB reversed MDR; inhibited the capability of proliferation, migration, and invasion of CRC cells; and slowed down the CRC tumor growth in nude mice. Consistent with clinical observations, PIK3CA and PIK3CB significantly increase multidrug resistance of CRC cells in vivo. Together, these results suggest that PIK3CA and PIK3CB may be used as potential therapeutic drug targets for colorectal cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yokota J. Tumor progression and metastasis. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21:497–503.
Quail DF, Joyce JA. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med. 2013;19:1423–37.
Siegel R et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:220–41.
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29.
Fearon ER, Vogelstein B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1990;61:759–67.
Valastyan S, Weinberg RA. Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell. 2011;147:275–92.
Szakacs G, Paterson JK, Ludwig JA, Booth-Genthe C, Gottesman MM. Targeting multidrug resistance in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:219–34.
Rodriguez-Nieto S, Zhivotovsky B. Role of alterations in the apoptotic machinery in sensitivity of cancer cells to treatment. Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12:4411–25.
Xia L, Zhang D, Du R, Pan Y, Zhao L, Sun S, et al. miR-15b and miR-16 modulate multidrug resistance by targeting BCL-2 in human gastric cancer cell. Int J Cancer. 2008;123:372–9.
Bellacosa A, Kumar CC, Di Cristofano A, Testa JR. Activation of AKT kinases in cancer: implications for therapeutic targeting. Adv Cancer Res. 2005;94:29–86.
Miura Y, Ohnami S, Yoshida K, Ohashi M, Nakano M, Fukuhara M, et al. Intraperitoneal injection of adenovirus expressing antisense K-ras RNA suppresses peritoneal dissemination of hamster syngeneic pancreatic cancer without systemic toxicity. Cancer Lett. 2005;218:53–62.
Trujillo MA, Oneal MJ, Davydova J, Bergert E, Yamamoto M, Morris 3rd JC. Construction of an MUC-1 promoter driven, conditionally replicating adenovirus that expresses the sodium iodide symporter for gene therapy of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11:R53.
Young LS, Searle PF, Onion D, Mautner V. Viral gene therapy strategies: from basic science to clinical application. J Pathol. 2006;208:299–318.
Samuels Y et al. High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science. 2004;304:554.
Torbett NE, Luna-Moran A, Knight ZA, Houk A, Moasser M, Weiss W, et al. A chemical screen in diverse breast cancer cell lines reveals genetic enhancers and suppressors of sensitivity to PI3K isoform-selective inhibition. Biochem J. 2008;415:97–110.
Wee S, Wiederschain D, Maira SM, Loo A, Miller C, deBeaumont R, et al. PTEN-deficient cancers depend on PIK3CB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:13057–62.
Cui B, Tao J, Yang Y. Studies on the expression patterns of class I PI3K catalytic subunits and its prognostic significance in colorectal cancer. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2012;62:47–54.
Zhu Y-F, Yu B-H, Li D-L, Ke H-L, Guo X-Z, Xiao X-Y. PI3K expression and PIK3CA mutations are related to colorectal cancer metastases. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(28):3745–51.
Wen F, He S, Sun C, Li T, Wu S. PIK3CA and PIK3CB expression and relationship with multidrug resistance in colorectal carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(11):8295–303.
TANG H, LIU X, WANG Z, et al. Interaction of hsa-miR-381 and glioma suppressor LRRC4 is involved in glioma growth. Brain Res. 2011;1390:21–32.
D’Incalci M. Adjuvant 5-FU based chemotherapy for colon cancer: match or miss the mismatch. Eur J Cancer. 2009;45(3):316–7.
Watanabe T. Chemoradiotherapy and adjuvant chemotherapy for rectal cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 2008;13(6):488–97.
Saseinul S, RBerardi R, SSalvagni S, et al. A combination of gefitinib and FOLFOX-4 as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer patients. A GISCAD multicentre phase II study including a biological analysis of EGFR overexpression amplification and NF-κB activation. Br J Can. 2008;98:71–6.
Palumbo I, Piattoni S, Valentini V, Marini V, et al. Gefitinib enhances the effects of combined radiotherapy and 5-fluorouracil in a colorectal cancer cell line. Int J Color Dis. 2014;29:31–41.
Kindler HL, Friberg G, Skoog L, Wade-Oliver K, Vokes EE. Phase I/II trial of gefitinib and oxaliplatin in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Am J Clin Oncol. 2005;28(4):340–4.
Mao C, Yang ZY, Hu XF, Chen Q, Tang JL. PIK3CA exon 20 mutations as a potential biomarker for resistance to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies in KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Oncol. 2012;23:1518–25.
Bardelli A, Siena S. Molecular mechanisms of resistance to cetuximab and panitumumab in colorectal cancer. Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1254–61.
Zheng T, Wang J, Chen X, Liu LX. Role of microRNA in anticancer drug resistance. Int J Cancer. 2009;126:2–10.
Xie X, Tang B, Zhou J, Gao Q, Zhang P, et al. Inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway increases the chemosensitivity of gastric cancer to vincristine. Oncol Rep. 2013;30:773–82.
Liu L, Ning X, Sun L, Zhang H, Shi Y, Guo C, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha contributes to hypoxia-induced chemoresistance in gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2008;99:121–8.
Jamieson S, Flanagan JU, Kolekar S, Buchanan C, Kendall JD, Lee WJ, et al. A drug targeting only p110α can block phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling and tumour growth in certain cell types. Biochem J. 2011;438:53–62.
Sui H, Fan ZZ, Li Q. Signal transduction pathways and transcriptional mechanisms of ABCB1/Pgp-mediated multiple drug resistance in human cancer cells. J Int Med Res. 2012;40:426–35.
El-Readi MZ, Hamdan D, Farrag N, et al. Inhibition of P-glycoprotein activity by limonin and other secondary metabolites from Citrus species in human colon and leukaemia cell lines. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010;626:139–45.
Barancík M, Bohácová V, Sedlák J, Sulová Z, Breier A. LY294,002, a specific inhibitor of PI3K/Akt kinase pathway, antagonizes P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2006;29:426–34.
Kuo MT, Liu Z, Wei Y, Lin-Lee YC, Tatebe S, Mills GB, et al. Induction of human MDR1 gene expression by 2-acetylaminofluorene is mediated by effectors of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway that activate NF-κB signaling. Oncogene. 2002;21:1945–54.
García MG, Alaniz LD, Cordo Russo RI, Alvarez E, Hajos SE. PI3K/Akt inhibition modulates multidrug resistance and activates NF-kB in murine lymphoma cell lines. Leuk Res. 2009;33(2):288–96.
Owonikoko TK, Khuri FR. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway: biomarkers of success and tribulation. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2013;33:395–401.
Carnero A. The PKB/AKT pathway in cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16:34–44.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Scientific and Technological Project of Shandong Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, S., Wen, F., Li, Y. et al. PIK3CA and PIK3CB silencing by RNAi reverse MDR and inhibit tumorigenic properties in human colorectal carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 37, 8799–8809 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4691-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4691-5