Abstract
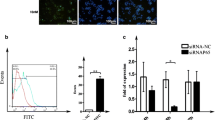
Multidrug resistance (MDR) in various kinds of cancers represents a true obstacle which hinders the successes of most of current available chemotherapies. ATP-binding cassette (ABC) trasporter proteins have been shown to contribute to the majority of MDR in various types of malignancies. c-myc has recently been reported to participate, at least partly, in MDR to some types of cancers. This study aimed to test whether c-myc could play a role, solely or with coordination with other ABCs, in the resistance of HepG2 cells to doxorubicin (Dox). MDR has been induced in wild-type HepG2 and has been verified both on gene and protein levels. Various assays including efflux assays as well as siRNA targeting ABCB1 and c-myc have been employed to explore the role of both candidate molecules in MDR in HepG2. Results obtained, with regard to ABCB1 silencing on HepG2/Dox cells, have shown that ABCB1-deficient cells exhibited a significant reduction in ABCC1 expression as compared to ABCB1-sufficient cells. However, these cells did not show a significant reduction in other tested ABCs (ABCC5 and ABCC10) while c-myc silencing had no significant effect on any of the studied ABCs. Moreover, silencing of ABCB1 on HepG2 significantly increased fluorescent calcein retention in HepG2 cells as compared to the control cells while downregulation of c-myc did not have any effect on fluorescent calcein retention. Altogether, this work clearly demonstrates that c-myc has no role in MDR of HepG2 to Dox which has been shown to be ABCB1-mediated in a mechanism which might involve ABCC1.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gottesman MM, Fojo T, Bates SE. Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP dependent transporters. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:48–58.
Gong J, Jaiswal R, Mathys JM, Combes V, Grau G, Bebawy M. Microparticles and their emerging role in cancer multidrug resistance. Cancer Treat Rev. 2012;38:226–34.
Wang Z, Xu Y, Meng X, Watari F, Liu H. Suppression of c-Myc is involved in multi-walled carbon nanotubes’ down-regulation of ATP-binding cassette transporters in human colon adenocarcinoma cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015;282(1):42–51.
Kim D, Kim M, Kim H, Leea J, Baea J, Kim D, et al. Suppression of multidrug resistance by treatment with TRAIL in human ovarian and breast cancer cells with high level of c-Myc. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1812;2011:796–805.
Sumi TN, Tsuneyoshi N, Nakatsuji N, Suemori H. Apoptosis and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells induced by sustained activation of c-Myc. Oncogene. 2007;26:5564–76.
Hoffman B, Liebermann DA. Apoptotic signaling by c-MYC. Oncogene. 2008;27:6462–72.
Porro A, Iraci N, Soverini S, Diolaiti D, Gherardil S, Terragna C, et al. c-MYC oncoprotein dictates transcriptional profiles of ATP-binding cassette transporter genes in chronic myelogenous leukemia CD34 hematopoietic progenitor cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2011;9(8):1054–66.
Kugimiya N, Nishimoto A, Hosoyama T, Ueno K, Enoki T, Li TS, et al. The c-MYC-ABCB5 axis plays a pivotal role in 5-fluorouracil resistance in human colon cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2015. doi:10.1111/jcmm.12531.
Tiwaria AK, Sodania K, Daia C, Abuznaitb AH, Singha S, Xiaoa Z, et al. Nilotinib potentiates anticancer drug sensitivity in murine ABCB1-, ABCG2-, and ABCC10-multidrug resistance xenograft models Amit K. Chena Z. Cancer Lett. 2013;328(2):307–17.
Zhang X, Yashiro M, Qiu H, Nishii T, Matsuzaki T, Hirakawa K. The role of c-myc in regulating mdr1 gene expression in tumor cell line KB. Anticancer Res. 2010;30:915–21.
Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-Dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–54.
Tiberghien F, Loor F. Ranking of P-glycoprotein substrates and inhibitors by a calcein-AM fluorometry screening assay. Anticancer Drug. 1996;7(5):568–78.
Tiwari AK, Sodani K, Chen ZS. Current advances in modulation of ABC transporter-mediated multidrug resistance in cancer. Int J Toxicol Pharmcol Res. 2009;1:1–6.
Tsuruo T, Naito M, Tomida A, Fujita N, Mashima T, Sakamoto H, et al. Molecular targeting therapy of cancer: drug resistance, apoptosis and survival signal. Cancer Sci. 2003;94:15–21.
Wang X, Campos CR, Peart JC, Smith LK, Boni JL, Cannon RE, et al. Nrf2 upregulates ATP binding cassette transporter expression and activity at the blood–brain and blood–spinal cord barriers. J Neurosci. 2014;34(25):8585–93.
Lee CH. Reversing agents for ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters: application in modulating multidrug resistance (MDR). Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2004;4:43–52.
Leonessa F, Clarke R. ATP binding cassette transporters and drug resistance in breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2003;10:43–73.
Albihn A, Johnsen JI, Henriksson MA. MYC in oncogenesis and as a target for cancer therapies. Adv Cancer Res. 2010;107:163–224.
Nieminen AI, Partanen JI, Klefstrom J. c-Myc blazing a trail of death: coupling of the mitochondrial and death receptor apoptosis pathways by c-Myc. Cell Cycle. 2007;6:2464–72.
He Y, Zhang J, et al. The role of c-myc in regulating mdr1 gene expression in tumor cell line KB. Chin Med J. 2000;113(9):848–51.
Yang X, Cai H, et al. Inhibition of c-Myc by let-7b mimic reverses mutidrug resistance in gastric cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2015;33(4):1723–30.
Xia C, Tian C, et al. c-Myc plays part in drug resistance mediated by bone marrow stromal cells in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res. 2014;39(1):92–9.
Borel F, Logtenstein R, Koornneef A, Maczuga P, Ritsema T, Petry H, et al. In vivo knock-down of multidrug resistance transporters ABCC1 and ABCC2 by AAV-delivered shRNAs and by artificial miRNAs. J RNAi Gene Silenc. 2011;7:434–42.
Qiu J, Zhang Y, Li Y, Zhao Y, Zhang W, Jiang Q, et al. Trametinib modulates cancer multidrug resistance by targeting ABCB1 transporter. Oncotargets. 2015;6(17):15495–509.
Cole SP, Bhardwaj G, Gerlach JH, Mackie JE, Grant CE, Almquist KC, et al. Overexpression of a transporter gene in a multidrug-resistant human lung cancer cell line. Science. 1992;258:1650–4.
Kubota T, Furukawa H, Tanino A, Suto Y, Otan M, Watanabe T, et al. Resistant mechanisms of anthracyclines: pirarubicin might partly break through the P-glycoprotein-mediated drugresistance of human breast cancer tissues. Breast Cancer. 2001;8:333–8.
Nooter K, Westerman AM, Flens MJ, Zaman GJ, Scheper RJ, van Wingerden KE, et al. Expression of the multidrug resistance- associated protein (MRP) gene in human cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 1995;1:1301–10.
Flens MJ, Zaman GJ, van der Valk P, Izquierdo MA, Schroeijers AB, Scheffer LG, et al. Tissue distribution of the multidrug resistance protein. Am J Pathol. 1996;148:1237–47.
Chen ZS, Tiwari AK. Multidrug resistance proteins (MRPs/ABCCs) in cancer chemotherapy and genetic diseases. FEBS J. 2011;278:3226–45.
Deeley RG, Westlake C, Cole SP. Transmembrane transport of endo- and xenobiotics by mammalian ATP-binding cassette multidrug resistance proteins. Physiol Rev. 2006;86:849–899.29.
Sau A, PellizzariTregno F, Valentino F, Federici G, Caccuri AM. Glutathione transferases and development of new principles to overcome drug resistance. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2010;500:116–22.
Mao Q, Deeley RG, Cole SP. Functional reconstitution of substrate transport by purified multidrug resistance protein MRP1 (ABCC1) in phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:34166–72.
Wang L, Deng Q, Wang J, Bai X, Xiao X, Hai-Rong LV, et al. Effect of CIK on multidrug-resistance reversal and increasing the sensitivity of ADR in K562/ADR cells. Oncol Lett. 2014;8(4):1778–82.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Science and Technology Development Fund (STDF), Egypt, Basic and Applied Research Grant (Project ID 4361). We thank Ghada H. El-sayed, Heba K. Nabih, Eman M. Abdel Motaleb, and Alaa Shahin for technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yahya, S.M.M., Hamed, A.R., Emara, M. et al. Differential effects of c-myc and ABCB1 silencing on reversing drug resistance in HepG2/Dox cells. Tumor Biol. 37, 5925–5932 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4426-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4426-7