Abstract
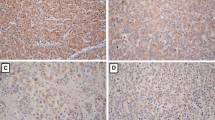
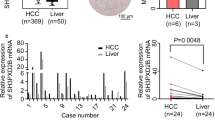
The member 3a of Wingless-type MMTV integration site family (Wnt3a) as an oncogene is overexpressed in many kinds of tumors with a worse outcome. However, the mechanism and alteration of Wnt3a expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have not been clarified. In this study, the levels of Wnt3a expression were investigated in 80 HCC tissues or sera of 186 patients with chronic liver diseases. The incidence of hepatic Wnt3a expression in HCC tissues was 96.25 % and significantly higher (χ 2 = 48.818, P < 0.001) than that in their surrounding tissues (46.25 %). The higher level (>800 ng/L) of circulating Wnt3a expression was found in 92.5 % HCC patients and significantly related (P < 0.05) to alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level, liver cirrhosis, hepatitis B virus infection, poor differentiation, tumor node metastasis, and extra-hepatic metastasis. The level of Wnt3a expression in HCC patients was obviously higher (P < 0.001) than that in any group of cases with benign liver diseases. The diagnostic specificity or the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was 94.34 % or 0.994 in Wnt3a and 69.81 % or 0.710 in AFP for HCC, respectively. The present data suggested that Wnt3a expression associated with tumor progression should be a novel specific biomarker for diagnosis and differentiation of HCC.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AFP:
-
Alpha-fetoprotein
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- HBV:
-
Hepatitis B virus
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- HCV:
-
Hepatitis C virus
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic curve
- TMA:
-
Tissue microarray
- Wnt3a:
-
Member 3a of Wingless-type MMTV integration site family
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Bruix J, Gores GJ, Mazzaferro V. Hepatocellular carcinoma: clinical frontiers and perspectives. Gut. 2014;63:844–85.
El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:1118–27.
Muñoz A, Chen JG, Egner PA, Marshall ML, Johnson JL, Schneider MF, et al. Predictive power of hepatitis B 1762T/1764A mutations in plasma for hepato-cellular carcinoma risk in Qidong, China. Carcinogenesis. 2011;32:860–5.
Yao DF, Horie C, Horie T, Shimizu I, Meng XY, Ito S. Virological features of hepatitis C virus infection in patients with liver diseases in the inshore area of the Yangtze River. Tokushima J Exp Med. 1994;41:49–56.
Ming L, Thorgeirsson SS, Gail MH, Lu P, Harris CC, Wang N, et al. Dominant role of hepatitis B virus and cofactor role of aflatoxin in hepatocarcinogenesis in Qidong, China. Hepatology. 2002;36:1214–20.
Maluccio M, Covey A. Recent progress in understanding, diagnosing, and treating hepatocellular carcinoma. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:394–9.
Wang L, Yao M, Dong Z, Zhang Y, Yao D. Circulating specific biomarkers in diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and its metastasis monitoring. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:9–20.
Li S, Yao D, Wang L, Wu W, Qiu L, Yao M, et al. Expression characteristics of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and its clinical values in diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepat Mon. 2011;11:821–8.
Yao DF, Jiang D, Huang Z, Lu J, Tao Q, Yu Z, et al. Abnormal expression of hepatoma specific gamma-glutamyl transferase and alteration of gamma- glutamyl transferase gene methylation status in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2000;88:761–9.
Wu CS, Lee TY, Chou RH, Yen CJ, Huang WC, Wu CY, et al. Development of a highly sensitive glycan microarray for quantifying AFP-L3 for early prediction of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 2014;9:e99959.
Yao M, Yao DF, Bian YZ, Zhang CG, Qiu LW, Wu W, et al. Oncofetal antigen glypican-3 as a promising early diagnostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2011;10:289–94.
Yao M, Pan LH, Yao DF. Glypican-3 as a specific biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2015;14:122–3.
Wen Y, Han J, Chen J, Dong J, Xia Y, Liu J, et al. Plasma miRNAs as early biomarkers for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2015;137:1679–90.
Rogacki K, Kasprzak A, Stepinski A. Alterations of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinomas associated with hepatitis C virus. Pol J Pathol. 2015;66:9–21.
Pez F, Lopez A, Kim M, Wands JR, Caron de Fromentel C, Merle P. Wnt signaling and hepatocarcinogenesis: molecular targets for the development of innovative anticancer drugs. J Hepatol. 2013;59:1107–17.
Gao C, Xiao G, Hu J. Regulation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling by post- translational modifications. Cell Biosci. 2014;4:13.
Willert K, Nusse R. Wnt proteins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012;4:a007864.
Lamb R, Ablett MP, Spence K, Landberg G, Sims AH, Clarke RB. Wnt pathway activity in breast cancer sub-types and stem-like cells. PLoS One. 2013;8:e67811.
Neth P, Ciccarella M, Egea V, Hoelters J, Jochum M, Ries C. Wnt signaling regulates the invasion capacity of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2006;24:1892–903.
Fox SA, Richards AK, Kusumah I, Perumal V, Bolitho EM, Mutsaers SE, et al. Expression profile and function of Wnt signaling mechanisms in malignant mesothelioma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;440:82–7.
Kaur N, Chettiar S, Rathod S, Rath P, Muzumdar D, Shaikh ML, et al. Wnt3a mediated activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling promotes tumor progression in glioblastoma. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013;54:44–57.
Verras M, Brown J, Li X, Nusse R, Sun Z. Wnt3a growth factor induces androgen receptor-mediated transcription and enhances cell growth in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64:8860–6.
Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. Updated standards for the diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2012;20:419–26.
OY. Management of clinical diagnosis, and antiviral therapy for HBV-related cirrhosis. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2014;22:327–35.
Gao Q, Qiu SJ, Fan J, Zhou J, Wang XY, Xiao YS, et al. Intratumoral balance of regulatory and cytotoxic T cells is associated with prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:2586–93.
Zhang Y, Zhang S, Wang X, Liu J, Yang L, He S, et al. Prognostic significance of FOXP1 as an oncogene in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 2012;65:528–33.
Qian J, Yao D, Dong Z, Wu W, Qiu L, Yao N, et al. Characteristics of hepatic igf-ii expression and monitored levels of circulating igf-ii mRNA in metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010;134:799–806.
Wei Y, Shen N, Wang Z, Yang G, Yi B, Yang N, et al. Sorafenib sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cell to cisplatin via suppression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013;381:139–44.
Zhang Q, Bai X, Chen W, Ma T, Hu Q, Liang C, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling enhances hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma via crosstalk with hif-1α signaling. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34:962–73.
Nalesso G, Sherwood J, Bertrand J, Pap T, Ramachandran M, De Bari C, et al. WNT-3A modulates articular chondrocyte phenotype by activating both canonical and noncanonical pathways. J Cell Biol. 2011;193:551–64.
Lai JP, Oseini AM, Moser CD, Yu C, Elsawa SF, Hu C, et al. The oncogenic effect of sulfatase 2 in human hepatocellular carcinoma is mediated in part by glypican 3-dependent Wnt activation. Hepatology. 2010;52:1680–9.
Yang T, Cai SY, Zhang J, Lu JH, Lin C, Zhai J, et al. Krüppel-like factor 8 is a new Wnt/beta-catenin signaling target gene and regulator in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 2012;7:e39668.
Liu J, Ding X, Tang J, Cao Y, Hu P, Zhou F, et al. Enhancement of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling activity by HCV core protein promotes cell growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 2011;6:e27496.
Liu J, Wang Z, Tang J, Tang R, Shan X, Zhang W, et al. Hepatitis C virus core protein activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling through multiple regulation of upstream molecules in the SMMC-7721 cell line. Arch Virol. 2011;156:1013–23.
Hv T, Bock CT, Velavan TP. Genetic insights on host and hepatitis B virus in liver diseases. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2014;762:65–75.
Zhang XD, Wang Y, Ye LH. Hepatitis B virus X protein accelerates the development of hepatoma. Cancer Biol Med. 2014;11:182–90.
Suarez MI, Uribe D, Jaramillo CM, Osorio G, Perez JC, Lopez R, et al. Wnt/beta- catenin signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinomas cases from Colombia. Ann Hepatol. 2015;14:64–74.
Yao M, Wang L, Yao Y, Gu HB, Yao DF. Biomarker-based microRNA therapeutic strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2014;2:253–8.
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation (81200634), the Projects of Medical Science (2014-YY-028, H201102, BL2012053, PADA, and Qinglan Program), Jiangsu Province and the International S.&T. Cooperation Program (2013DFA32150) of China, and we thank T. FitzGibbon, M.D. for the comments on earlier drafts of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Liuhong Pan and Min Yao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, L., Yao, M., Zheng, W. et al. Abnormality of Wnt3a expression as novel specific biomarker for diagnosis and differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 37, 5561–5568 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4413-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4413-z