Abstract
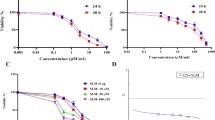
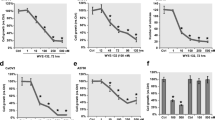
Ovarian cancer (OC) is a deadly disease, and despite improvements in treatment, overall 5-year survival is low. Glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3β is a multifunctional serine/threonine kinase. We wished to ascertain if the GSK-3β inhibitor (2Z,3E)-6-bromoindirubin-3′-oxime, known as “BIO,” can suppress OC development. The OC cell lines A2780 and OVCAR3 were exposed to BIO. At different time points, cell proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle, and cell invasion/cell migration assays were carried out. Phalloidin staining was undertaken to observe lamellipodia formation. Real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and western blotting were used to assess expression of messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein of GSK-3β, cyclin D1, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9, and p21. BIO suppressed the proliferation, invasion, and migration of OC cells; reduced lamellipodia formation; and induced G1 arrest of the cell cycle. BIO exposure led to a significant downregulation of mRNA and protein expression of cyclin D1 and MMP9 in comparison with untreated control cells. In contrast, BIO exposure upregulated mRNA and protein expression of p21 in comparison with untreated control cells. Besides, GSK-3β small interfering RNA (siRNA) transfection in ovarian cancer cells also downregulated GSK-3β, cyclin D1, and MMP9 protein expression while upregulated p21 expression. These data suggest that BIO, as an inhibitor of GSK-3β, can suppress OC development. Therefore, BIO could be a candidate drug for the treatment of OC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mantia-Smaldone GM, Edwards RP, Vlad AM. Targeted treatment of recurrent platinum-resistant ovarian cancer: current and emerging therapies. Cancer Manag Res. 2011;3:25–38.
Lengyel E. Ovarian cancer development and metastasis. Am J Pathol. 2010;177:1053–64.
Ji K, Ye L, Mason MD, Jiang WG. The Kiss-1/Kiss-1R complex as a negative regulator of cell motility and cancer metastasis (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2013;32:747–54.
Embi N, Rylatt DB, Cohen P. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Separation from cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase and phosphorylase kinase. Eur J Biochem / FEBS. 1980;107:519–27.
Kotliarova S, Pastorino S, Kovell LC, Kotliarov Y, Song H, Zhang W, et al. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition induces glioma cell death through c-MYC, nuclear factor-kappaB, and glucose regulation. Cancer Res. 2008;68:6643–51.
Tang QL, Xie XB, Wang J, Chen Q, Han AJ, Zou CY, et al. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta, NF-kappaB signaling, and tumorigenesis of human osteosarcoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012;104:749–63.
Madhunapantula SV, Sharma A, Gowda R, Robertson GP. Identification of glycogen synthase kinase 3alpha as a therapeutic target in melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013;26:886–99.
Salim T, Sjolander A, Sand-Dejmek J. Nuclear expression of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and lack of membranous beta-catenin is correlated with poor survival in colon cancer. Int J Cancer. 2013;133:807–15.
Tsai KH, Hsien HH, Chen LM, Ting WJ, Yang YS, Kuo CH, et al. Rhubarb inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell metastasis via GSK-3-beta activation to enhance protein degradation and attenuate nuclear translocation of beta-catenin. Food Chem. 2013;138:278–85.
Boulahja R, Ouach A, Bourg S, Bonnet P, Lozach O, Meijer L, et al. Advances in tetrahydropyrido[1,2-a]isoindolone (valmerins) series: potent glycogen synthase kinase 3 and cyclin dependent kinase 5 inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. 2015;101:274–87.
Kunnimalaiyaan S, Gamblin TC, Kunnimalaiyaan M. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitor AR-A014418 suppresses pancreatic cancer cell growth via inhibition of GSK-3-mediated Notch1 expression. HPB (Oxford). 2015;17(9):770–6.
Woodard C, Liao G, Goodwin CR, Hu J, Xie Z, Dos Reis TF, et al. A screen for extracellular signal-regulated kinase-primed glycogen synthase kinase 3 substrates identifies the p53 inhibitor Iaspp. J Virol. 2015;89(18):9232–41.
Singh SP, Tao S, Fields TA, Webb S, Harris RC, Rao R. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition attenuates fibroblast activation and development of fibrosis following renal ischemia-reperfusion in mice. Dis Model Mech. 2015;8(8):931–40.
Atkinson JM, Rank KB, Zeng Y, Capen A, Yadav V, Manro JR, et al. Activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway for the treatment of melanoma—application of LY2090314, a novel selective inhibitor of glycogen synthase kinase-3. PLoS One. 2015;10(4):e0125028.
Moroi AJ, Watson SP. Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase enhance C-type lectin-like receptor 2-mediated platelet activation by inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3α/β. J Thromb Haemost. 2015;13(6):1139–50.
Kim KM, Lee KS, Lee GY, Jin H, Durrance ES, Park HS, et al. Anti-diabetic efficacy of KICG1338, a novel glycogen synthase kinase-3β inhibitor, and its molecular characterization in animal models of type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015;409:1–10.
Park SM, Ki SH, Han NR, Cho IJ, Ku SK, Kim SC, et al. Tacrine, an oral acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, induced hepatic oxidative damage, which was blocked by liquiritigenin through GSK3-beta inhibition. Biol Pharm Bull. 2015;38(2):184–92.
Arfeen M, Patel R, Khan T, Bharatam PV. Molecular dynamics simulation studies of GSK-3beta ATP competitive inhibitors: understanding the factors contributing to selectivity. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2015; 1–55.
Nicolaou KA, Liapis V, Evdokiou A, Constantinou C, Magiatis P, Skaltsounis AL, et al. Induction of discrete apoptotic pathways by bromo-substituted indirubin derivatives in invasive breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;425:76–82.
Liu L, Nam S, Tian Y, Yang F, Wu J, Wang Y, et al. 6-Bromoindirubin-3′-oxime inhibits JAK/STAT3 signaling and induces apoptosis of human melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 2011;71:3972–9.
Cao H, Chu Y, Lv X, Qiu P, Liu C, Zhang H, et al. GSK3 inhibitor-BIO regulates proliferation of immortalized pancreatic mesenchymal stem cells (iPMSCs). PLoS One. 2012;7:e31502.
Dastjerdi FV, Zeynali B, Tafreshi AP, Shahraz A, Chavoshi MS, Najafabadi IK, et al. Inhibition of GSK-3beta enhances neural differentiation in unrestricted somatic stem cells. Cell Biol Int. 2012;36:967–2.
Ougolkov AV, Fernandez-Zapico ME, Savoy DN, Urrutia RA, Billadeau DD. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta participates in nuclear factor kappaB-mediated gene transcription and cell survival in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65:2076–81.
Bilim V, Ougolkov A, Yuuki K, Naito S, Kawazoe H, Muto A, et al. Glycogen synthase kinase-3: a new therapeutic target in renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2009;101:2005–14.
Cao Q, Lu X, Feng YJ. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta positively regulates the proliferation of human ovarian cancer cells. Cell Res. 2006;16:671–7.
Cao Q, Feng YJ. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK-3beta) promotes proliferation of ovarian cancer cells in vitro. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2006;28:804–9.
Chien AJ, Moore EC, Lonsdorf AS, Kulikauskas RM, Rothberg BG, Berger AJ, et al. Activated Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in melanoma is associated with decreased proliferation in patient tumors and a murine melanoma model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:1193–8.
Yuhua Z, Han C, Jiyuan L, Wei Z, Lin Q, Xiufa T. Expression and clinical significance of nuclear factor κB/B cell lymphoma-2 signal pathway and glycogen synthase kinase 3β in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015;33(1):11–5.
Campa VM, Baltziskueta E, Bengoa-Vergniory N, Gorroño-Etxebarria I, Wesołowski R, Waxman J, et al. A screen for transcription factor targets of glycogen synthase kinase-3 highlights an inverse correlation of NFκB and androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 2014;5(18):8173–87.
Gao X, He Y, Gao LM, Feng J, Xie Y, Liu X, et al. Ser9-phosphorylated GSK3β induced by 14-3-3ζ actively antagonizes cell apoptosis in a NF-κB dependent manner. Biochem Cell Biol. 2014;92(5):349–56.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Authors’ contributions
LZ conceived the study and analyzed interpretation. AS Y and LZ carried out the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the first and final draft of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, AS., Zhao, L. Effects of the GSK-3β inhibitor (2Z,3E)-6-bromoindirubin-3′-oxime upon ovarian cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 37, 4857–4864 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4344-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4344-8