Abstract
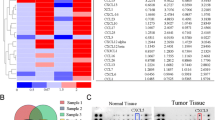
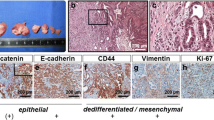
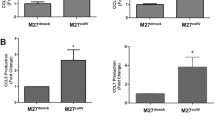
C-C chemokine receptor type 1 (CCR1) and chemokine C-C motif receptor-like 2 (CCRL2) have not yet been sufficiently investigated for their role in colorectal cancer (CRC). Here, we investigated their expression in rat and human CRC samples, their modulation of expression in a rat liver metastasis model, as well as the effects on cellular properties resulting from their knockdown. One rat and five human colorectal cancer cell lines were used. CC531 rat colorectal cells were injected via the portal vein into rats and re-isolated from rat livers after defined periods. Following mRNA isolation, the gene expression was investigated by microarray. In addition, all cell lines were screened for mRNA expression of CCR1 and CCRL2 by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Cell lines with detectable expression were used for knockdown experiments; and the respective influence was determined on the cells’ proliferation, scratch closure, and colony formation. Finally, specimens from the primaries of 50 patients with CRC were monitored by quantitative RT-PCR for CCR1 and CCRL2 expression levels. The microarray studies showed peak increases of CCR1 and CCRL2 in the early phase of liver colonization. Knockdown was sufficient at mRNA but only moderate at protein levels and resulted in modest but significant inhibition of proliferation (p < 0.05), scratch closure, and colony formation (p < 0.05). All human CRC samples were positive for CCR1 and CCRL2 and showed a significant pairwise correlation (p < 0.0004), but there was no correlation with tumor stage or age of patients. In summary, the data point to an important role of CCR1 and CCRL2 under conditions of organ colonization and both chemokine receptors qualify as targets of treatment during early colorectal cancer liver metastasis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brenner H, Kloor M, Pox CP. Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 2014;383:1490–502.
Kattan MW, Wheeler TM, Scardino PT. Postoperative nomogram for disease recurrence after radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 1999;17:1499–507.
Gallagher DJ, Kemeny N. Metastatic colorectal cancer: from improved survival to potential cure. Oncology. 2010;78:237–48.
Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC. Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:563–72.
Duffy MJ, McGowan PM, Gallagher WM. Cancer invasion and metastasis: changing views. J Pathol. 2008;214:283–93.
Deryugina EI, Quigley JP. Matrix metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006;25:9–34.
Wang CL, Sun BS, Tang Y, Zhuang HQ, Cao WZ. CCR1 knockdown suppresses human non-small cell lung cancer cell invasion. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009;135:695–701.
Lazennec G, Richmond A. Chemokines and chemokine receptors: new insights into cancer-related inflammation. Trends Mol Med. 2010;16:133–44.
Kruizinga RC, Bestebroer J, Berghuis P, de Haas CJ, Links TP, de Vries EG, et al. Role of chemokines and their receptors in cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15:3396–416.
Erreni M, Bianchi P, Laghi L, Mirolo M, Fabbri M, Locati M, et al. Expression of chemokines and chemokine receptors in human colon cancer. Methods Enzymol. 2009;460:105–21.
Horuk R. Chemokine receptor antagonists: overcoming developmental hurdles. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8:23–33.
Pease JE, Horuk R. Chemokine receptor antagonists: part 1. Exp Opin Ther Patents. 2009;19:39–58.
Pease JE, Horuk R. Chemokine receptor antagonists: part 2. Exp Opin Ther Patents. 2009;19:199–221.
Strieter RM. Chemokines: not just leukocyte chemoattractants in the promotion of cancer. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:285–6.
Vandercappellen J, Van Damme J, Struyf S. The role of CXC chemokines and their receptors in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2008;267:226–44.
Luster AD. Chemokines–chemotactic cytokines that mediate inflammation. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:436–45.
Wang JM, Deng X, Gong W, Su S. Chemokines and their role in tumor growth and metastasis. J Immunol Methods. 1998;220:1–17.
Zlotnik A, Yoshie O. Chemokines: a new classification system and their role in immunity. Immunity. 2000;12:121–7.
D’Ambrosio D, Panina-Bordignon P, Sinigaglia F. Chemokine receptors in inflammation: an overview. J Immunol Methods. 2003;273:3–13.
Weber C, Weber KS, Klier C, Gu S, Wank R, Horuk R, et al. Specialized roles of the chemokine receptors CCR1 and CCR5 in the recruitment of monocytes and T(H)1-like/CD45RO(+) T cells. Blood. 2001;97:1144–6.
Fioretti F, Fradelizi D, Stoppacciaro A, Ramponi S, Ruco L, Minty A, et al. Reduced tumorigenicity and augmented leukocyte infiltration after monocyte chemotactic protein-3 (MCP-3) gene transfer: perivascular accumulation of dendritic cells in peritumoral tissue and neutrophil recruitment within the tumor. J Immunol. 1998;161:342–6.
Gao JL, Wynn TA, Chang Y, Lee EJ, Broxmeyer HE, Cooper S, et al. Impaired host defense, hematopoiesis, granulomatous inflammation and type 1-type 2 cytokine balance in mice lacking CC chemokine receptor 1. J Exp Med. 1997;185:1959–68.
Revesz L, Bollbuck B, Buhl T, Eder J, Esser R, Feifel R, et al. Novel CCR1 antagonists with oral activity in the mouse collagen induced arthritis. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005;15:5160–4.
Shahrara S, Proudfoot AE, Woods JM, Ruth JH, Amin MA, Park CC, et al. Amelioration of rat adjuvant-induced arthritis by Met-RANTES. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:1907–19.
Anders HJ, Ninichuk V, Schlondorff D. Progression of kidney disease: blocking leukocyte recruitment with chemokine receptor CCR1 antagonists. Kidney Int. 2006;69:29–32.
Ninichuk V, Anders HJ. Chemokine receptor CCR1: a new target for progressive kidney disease. Am J Nephrol. 2005;25:365–72.
Vielhauer V, Berning E, Eis V, Kretzler M, Segerer S, Strutz F, et al. CCR1 blockade reduces interstitial inflammation and fibrosis in mice with glomerulosclerosis and nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int. 2004;66:2264–78.
Ajuebor MN, Hogaboam CM, Le T, Proudfoot AE, Swain MG. CCL3/MIP-1alpha is pro-inflammatory in murine T cell-mediated hepatitis by recruiting CCR1-expressing CD4(+) T cells to the liver. Eur J Immunol. 2004;34:2907–18.
Yang X, Lu P, Fujii C, Nakamoto Y, Gao JL, Kaneko S, et al. Essential contribution of a chemokine, CCL3, and its receptor, CCR1, to hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Int J Cancer J Int Cancer. 2006;118:1869–76.
Reichel CA, Khandoga A, Anders HJ, Schlondorff D, Luckow B, Krombach F. Chemokine receptors Ccr1, Ccr2, and Ccr5 mediate neutrophil migration to postischemic tissue. J Leukoc Biol. 2006;79:114–22.
Bonville CA, Lau VK, DeLeon JM, Gao JL, Easton AJ, Rosenberg HF, et al. Functional antagonism of chemokine receptor CCR1 reduces mortality in acute pneumovirus infection in vivo. J Virol. 2004;78:7984–9.
Ness TL, Carpenter KJ, Ewing JL, Gerard CJ, Hogaboam CM, Kunkel SL. CCR1 and CC chemokine ligand 5 interactions exacerbate innate immune responses during sepsis. J Immunol. 2004;173:6938–48.
Yun JJ, Whiting D, Fischbein MP, Banerji A, Irie Y, Stein D, et al. Combined blockade of the chemokine receptors CCR1 and CCR5 attenuates chronic rejection. Circulation. 2004;109:932–7.
Gao W, Topham PS, King JA, Smiley ST, Csizmadia V, Lu B, et al. Targeting of the chemokine receptor CCR1 suppresses development of acute and chronic cardiac allograft rejection. J Clin Investig. 2000;105:35–44.
Yoshimura T, Oppenheim JJ. Chemokine-like receptor 1 (CMKLR1) and chemokine (C-C motif) receptor-like 2 (CCRL2); two multifunctional receptors with unusual properties. Exp Cell Res. 2011;317:674–84.
Otero K, Vecchi A, Hirsch E, Kearley J, Vermi W, Del Prete A, et al. Nonredundant role of CCRL2 in lung dendritic cell trafficking. Blood. 2010;116:2942–9.
Migeotte I, Franssen JD, Goriely S, Willems F, Parmentier M. Distribution and regulation of expression of the putative human chemokine receptor HCR in leukocyte populations. Eur J Immunol. 2002;32:494–501.
Georges RB, Adwan H, Hamdi H, Hielscher T, Linnemann U, Berger MR. The insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 3 and 7 are associated with colorectal cancer and liver metastasis. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011;12:69–79.
Georges R, Bergmann F, Hamdi H, Zepp M, Eyol E, Hielscher T, et al. Sequential biphasic changes in claudin1 and claudin4 expression are correlated to colorectal cancer progression and liver metastasis. J Cell Mol Med. 2012;16:260–72.
Team RDC. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria R Foundation for Statistical Computing. 2011.
Muller A, Homey B, Soto H, Ge N, Catron D, Buchanan ME, et al. Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature. 2001;410:50–6.
Ghadjar P, Coupland SE, Na IK, Noutsias M, Letsch A, Stroux A, et al. Chemokine receptor CCR6 expression level and liver metastases in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1910–6.
Ghadjar P, Rubie C, Aebersold DM, Keilholz U. The chemokine CCL20 and its receptor CCR6 in human malignancy with focus on colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer J Int Cancer. 2009;125:741–5.
Rubie C, Frick VO, Pfeil S, Wagner M, Kollmar O, Kopp B, et al. Correlation of IL-8 with induction, progression and metastatic potential of colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol WJG. 2007;13:4996–5002.
Rubie C, Frick VO, Wagner M, Schuld J, Graber S, Brittner B, et al. ELR+ CXC chemokine expression in benign and malignant colorectal conditions. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:178.
Rubie C, Frick VO, Ghadjar P, Wagner M, Justinger C, Faust SK, et al. Cxc receptor-4 mRNA silencing abrogates cxcl12-induced migration of colorectal cancer cells. J Transl Med. 2011;9:22.
Brand S, Olszak T, Beigel F, Diebold J, Otte JM, Eichhorst ST, et al. Cell differentiation dependent expressed CCR6 mediates ERK-1/2, SAPK/JNK, and Akt signaling resulting in proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 2006;97:709–23.
Juremalm M, Nilsson G. Chemokine receptor expression by mast cells. Chem Immunol Allergy. 2005;87:130–44.
Schober A, Zernecke A. Chemokines in vascular remodeling. Thromb Haemost. 2007;97:730–7.
Williams IR. Chemokine receptors and leukocyte trafficking in the mucosal immune system. Immunol Res. 2004;29:283–92.
Vaday GG, Peehl DM, Kadam PA, Lawrence DM. Expression of CCL5 (RANTES) and CCR5 in prostate cancer. Prostate. 2006;66:124–34.
Moller C, Stromberg T, Juremalm M, Nilsson K, Nilsson G. Expression and function of chemokine receptors in human multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2003;17:203–10.
Wu X, Fan J, Wang X, Zhou J, Qiu S, Yu Y, et al. Downregulation of CCR1 inhibits human hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;355:866–71.
Shimada T, Matsumoto M, Tatsumi Y, Kanamaru A, Akira S. A novel lipopolysaccharide inducible C-C chemokine receptor related gene in murine macrophages. FEBS Lett. 1998;425:490–4.
Brouwer N, Zuurman MW, Wei T, Ransohoff RM, Boddeke HW, Biber K. Induction of glial L-CCR mRNA expression in spinal cord and brain in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Glia. 2004;46:84–94.
Zuurman MW, Heeroma J, Brouwer N, Boddeke HW, Biber K. LPS-induced expression of a novel chemokine receptor (L-CCR) in mouse glial cells in vitro and in vivo. Glia. 2003;41:327–36.
Zabel BA, Nakae S, Zuniga L, Kim JY, Ohyama T, Alt C, et al. Mast cell-expressed orphan receptor CCRL2 binds chemerin and is required for optimal induction of IgE-mediated passive cutaneous anaphylaxis. J Exp Med. 2008;205:2207–20.
Oostendorp J, Hylkema MN, Luinge M, Geerlings M, Meurs H, Timens W, et al. Localization and enhanced mRNA expression of the orphan chemokine receptor L-CCR in the lung in a murine model of ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation. J Histochem Cytochem Off J Histochem Soc. 2004;52:401–10.
Kitamura T, Kometani K, Hashida H, Matsunaga A, Miyoshi H, Hosogi H, et al. SMAD4-deficient intestinal tumors recruit CCR1+ myeloid cells that promote invasion. Nat Genet. 2007;39:467–75.
Hirai H, Fujishita T, Kurimoto K, Miyachi H, Kitano S, Inamoto S, et al. CCR1-mediated accumulation of myeloid cells in the liver microenvironment promoting mouse colon cancer metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2014;31:977–89.
Reufsteck C, Lifshitz-Shovali R, Zepp M, Bauerle T, Kubler D, Golomb G, et al. Silencing of skeletal metastasis-associated genes impairs migration of breast cancer cells and reduces osteolytic bone lesions. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2012;29:441–56.
Kovacheva M, Zepp M, Berger SM, Berger MR. Sustained conditional knockdown reveals intracellular bone sialoprotein as essential for breast cancer skeletal metastasis. Oncotarget. 2014;5:5510–22.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Israa G. Akram and Rania Georges contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akram, I.G., Georges, R., Hielscher, T. et al. The chemokines CCR1 and CCRL2 have a role in colorectal cancer liver metastasis. Tumor Biol. 37, 2461–2471 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4089-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4089-4