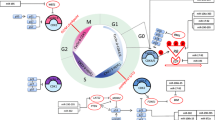
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNA molecules which regulate the target gene expression posttranscriptionally. Increasing studies have shown that microRNAs play important roles in multiple biological pathways. For instance, aberrant expression of microRNA-224 (miR-224) plays a vital role in tumor biology in various types of human cancer. Here, we aim to summarize the molecular mechanisms that lead to the overexpression of miR-224 in cancers, analyze the effect of miR-224 on tumor biology, and reveal the clinical significance of miR-224. MiR-224 regulates its targets by modulating messenger RNA (mRNA) stability and/or protein translation, and it would provide new insight into molecular targeting cancer treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shukla GC, Singh J, Barik S. MicroRNAs: processing, maturation, target recognition and regulatory functions. Mol Cell Pharmacol. 2011;3(3):83–92.
Ameres SL, Zamore PD. Diversifying microRNA sequence and function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14(8):475–88.
Berindan-Neagoe I, Monroig PC, Pasculli B, Calin GA. MicroRNAome genome: a treasure for cancer diagnosis and therapy. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(5):311–36.
Chen WX, Hu Q, Qiu MT, Zhong SL, Xu JJ, Tang JH, et al. miR-221/222: promising biomarkers for breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 2013;34(3):1361–703.
Kong YW, Ferland-McCollough D, Jackson TJ, Bushell M. microRNAs in cancer management. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(6):249–58.
Wang Z, Li Y, Kong D, Ahmad A, Banerjee S, Sarkar FH. Cross-talk between mirna and notch signaling pathways in tumor development and progression. Cancer Lett. 2010;292(2):141–8.
Wang Y, Ren JW, Gao Y, Ma JZ, Toh HC, Chow P, et al. MicroRNA-224 targets SMAD family member 4 to promote cell proliferation and negatively influence patient survival. PLoS One. 2013;8(7):e68744.
Wang Y, Toh HC, Chow P, Chung AY, Meyers DJ, Cole PA, et al. MicroRNA-224 is up-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma through epigenetic mechanisms. FASEB J. 2012;26(7):3032–41.
Scisciani C, Vossio S, Guerrieri F, Schinzari V, De Iaco R, D’Onorio de Meo P, et al. Transcriptional regulation of miR-224 upregulated in human HCCs by NFkB inflammatory pathways. J Hepatol. 2012;56(4):855–61.
Knoll S, Fürst K, Kowtharapu B, Schmitz U, Marquardt S, Wolkenhauer O, et al. E2F1 induces miR-224/452 expression to drive EMT through TXNIP downregulation. EMBO Rep. 2014;15(12):1315–29.
Ning QL, Jiang XY. Angiotensin II upregulated the expression of microRNA-224 but not microRNA-21 in adult rat cardiac fibroblasts. Biomed Rep. 2013;1(5):776–80.
Yao GD, Yin MM, Jie L, Tian H, Liu L, Li X, Sun F. MicroRNA-224 is involved in transforming growth factor-beta-mediated mouse granulosa cell proliferation and granulosa cell function by targeting Smad4. Mol Endocrinol. 2010;24(3):540–51.
Hwang HW, Baxter LL, Loftus SK, Cronin JC, Trivedi NS, Borate B, Pavan WJ. Distinct microRNA expression signatures are associated with melanoma subtypes and are regulated by HIF1A. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2014;27(5):777–87.
Liang M, Yao GD, Yin MM, Lu M, Tian H, Liu L, et al. Transcriptional cooperation between p53 and NF-κB p65 regulates microRNA-224 transcription in mouse ovarian granulosa cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013;370(1–2):119–29.
Zhu S, Sachdeva M, Wu F, Lu Z, Mo YY. Ubc9 promotes breast cell invasion and metastasis in a sumoylation-independent manner. Oncogene. 2010;29(12):1763–72.
Yang W, Lee DY, Ben-David Y. The roles of microRNAs in tumorigenesis and angiogenesis. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2011;3(2):140–55.
Zhang WY, Dahlberg JE, Tam W. MicroRNAs in tumorigenesis: a primer. Am J Pathol. 2007;171(3):728–38.
Sumbul AT, Gogebakan B, Ergun S, Yengil E, Batmaci CY, Tonyali O, Yaldiz M. miR-204-5p expression in colorectal cancer: an autophagy-associated gene. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(12):12713–9.
Olaru AV, Yamanaka S, Vazquez C, Mori Y, Cheng Y, Abraham JM, et al. MicroRNA-224 negatively regulates p21 expression during late neoplastic progression in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013;19(3):471–80.
Waga S, Li R, Stillman B. p53-induced p21 controls DNA replication. Leukemia. 1997;11(3):321–3.
Lan SH, Wu SY, Zuchini R, Lin XZ, Su IJ, Tsai TF, et al. Autophagy suppresses tumorigenesis of hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma through degradation of microRNA-224. Hepatology. 2014;59(2):505–17.
Zhang GJ, Zhou H, Xiao HX, Li Y, Zhou T. Up-regulation of miR-224 promotes cancer cell proliferation and invasion and predicts relapse of colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2013;13(1):104.
Skaftnesmo KO, Prestegarden L, Micklem DR, Lorens JB. MicroRNAs in tumorigenesis. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2007;8(6):320–5.
Wu XJ, Pu XM, Zhao ZF, Zhao YN, Kang XJ, Wu WD, et al. The expression profiles of microRNAs in Kaposi’s sarcoma. Tumour Boil. 2015;36(1):437–46.
Liao WT, Li TT, Wang ZG, Wang SY, He MR, Ye YP, et al. MicroRNA-224 promotes cell proliferation and tumor growth in human colorectal cancer by repressing PHLPP1 and PHLPP2. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(17):4662–72.
Ma DL, Tao XC, Gao F, Fan C, Wu D. miR-224 functions as an onco-miRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activating AKT signaling. Oncol Lett. 2012;4(3):483–8.
Lin ZY, Huang YQ, Zhang YQ, Han ZD, He HC, Ling XH, et al. MicroRNA-224 inhibits progression of human prostate cancer by downregulating TRIB1. Int J Cancer. 2014;135(3):541–50.
Seher TC, Leptin M. Tribbles, a cell-cycle brake that coordinates proliferation and morphogenesis during Drosophila gastrulation. Curr Biol. 2000;10(11):623–9.
Hegedus Z, Czibula A, Kiss-Toth E. Tribbles: a family of kinase-like proteins with potent signaling regulatory function. Cell Signal. 2007;19(2):238–50.
Liu H, Li P, Li B, Sun P, Zhang J, Wang B, Jia B. RKIP suppresses gastric cancer cell proliferation and invasion and enhances apoptosis regulated by microRNA-224. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(10):10095–103.
Al-Mulla F, Bitar MS, Taqi Z, Yeung KC. RKIP: much more than Raf kinase inhibitory protein. J Cell Physiol. 2013;228(8):1688–702.
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Burge CB. Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell. 2003;115(7):787–98.
Zhang YZ, Takahashi S, Tasaka A, Yoshima T, Ochi H, Chayama K. Involvement of microRNA-224 in cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and anti-apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28(3):565–75.
Wang Y, Lee AT, Ma JZ, Wang J, Ren J, Yang Y, et al. Profiling microRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma reveals microRNA-224 up-regulation and apoptosis inhibitor-5 as a microRNA-224-specific target. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(19):13205–15.
Koci L, Chlebova K, Hyzdalova M, Hofmanova J, Jira M, Kysela P, et al. Apoptosis inhibitor 5 (API-5; AAC-11; FIF) is upregulated in human carcinomas in vivo. Oncol Lett. 2012;3(4):913–6.
Wang M, Deng X, Ying Q, Jin T, Li M, Liang C. MicroRNA-224 targets ERG2 and contributes to malignant progressions of meningioma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;460(2):354–61.
Chen W, Cai F, Zhang B, Barekati Z, Zhong XY. The level of circulating mirna-10b and mirna-373 in detecting lymph node metastasis of breast cancer: potential biomarkers. Tumour Biol. 2013;34(1):455–62.
Ke TW, Hsu HL, Wu YH, Chen WT, Cheng YW, Cheng CW. MicroRNA-224 suppresses colorectal cancer cell migration by targeting Cdc42. Dis Markers. 2014;2014:617150.
Callow MG, Clairvoyant F, Zhu S, Schryver B, Whyte DB, Bischoff JR, et al. Requirement for PAK4 in the anchorage-independent growth of human cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(1):550–8.
Li Q, Wang G, Shan JL, Yang ZX, Wang HZ, Feng J, et al. MicroRNA-224 is upregulated in HepG2 cells and involved in cellular migration and invasion. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25(1):164–71.
Zhang HJ, Siu MK, Yeung MC, Jiang LL, Mak VC, Ngan HY, et al. Overexpressed PAK4 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of choriocarcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2011;32(5):765–71.
Kaneyoshi T, Nakatsukasa H, Higashi T, Fujiwara K, Naito I, Nouso K, et al. Actual invasive potential of human hepatocellular carcinoma revealed by in situ gelatin zymography. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7(12):4027–32.
Li Q, Ding CC, Chen C, Zhang Z, Xiao H, Xie F, et al. miR-224 promotion of cell migration and invasion by targeting homeobox D 10 gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;29(4):835–42.
Xu XT, Xu Q, Tong JL, Zhu MM, Nie F, Chen X, et al. MicroRNA expression profiling identifies miR-328 regulates cancer stem cell-like SP cells in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2012;106(7):1320–30.
Yuan KF, Xie K, Fox J, Zeng H, Gao H, Huang C, Wu M. Decreased levels of miR-224 and the passenger strand of miR-221 increase MBD2, suppressing maspin and promoting colorectal tumor growth and metastasis in mice. Gastroenterology. 2013;145(4):853–64.
Bailey CM, Khalkhali-Ellis Z, Seftor EA, Hendrix MJ. Biological functions of maspin. J Cell Physiol. 2006;209(3):617–24.
Goto Y, Nishikawa R, Kojima S, Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Inoguchi S, et al. Tumour-suppressive microRNA-224 inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion via targeting oncogenic TPD52 in prostate cancer. FEBS Lett. 2014;588(10):1973–82.
Ummanni R, Teller S, Junker H, Zimmermann U, Venz S, Scharf C, Giebel J, et al. Altered expression of tumor protein D52 regulates apoptosis and migration of prostate cancer cells. FEBS J. 2008;275:5703–13.
Huang L, Ting D, Lin X, Zimmermann U, Venz S, Scharf C, et al. MicroRNA-224 targets RKIP to control cell invasion and expression of metastasis genes in human breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;425(2):127–33.
Keller ET, Fu Z, Brennan M. The role of Raf kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP)In health and disease. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004;68:1049–53.
Trakul N, Rosner MR. Modulation of the MAP kinase signaling cascade by Raf kinase inhibitory protein. Cell Res. 2005;15:19–23.
Boguslawska J, Wojcicka A, Piekielko-Witkowska A, Master A, Nauman A. MiR-224 targets the 3′UTR of type 1 5′-iodothyronine deiodinase possibly contributing to tissue hypothyroidism in renal cancer. PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24541.
Boguslawska J, Piekielko-Witkowska A, Wojcicka A, Kedzierska H, Poplawski P, Nauman A. Regulatory feedback loop between T3 and microRNAs in renal cancer. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014;384(1–2):61–70.
Wang H, Zhu LJ, Yang YC, Wang ZX, Wang R. MiR-224 promotes the chemoresistance of human lung adenocarcinoma cells to cisplatin via regulating G1/S transition and apoptosis by targeting p21 (WAF1/CIP1). Br J Cancer. 2014;111(2):339–54.
Mencia N, Selga E, Noe V, Ciudad CJ. Underexpression of miR-224 in methotrexate resistant human colon cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011;82(11):1572–82.
Li HY, Li Y, Liu D, Sun H, Liu J. miR-224 is critical for celastrol-induced inhibition of migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;32(2):448–58.
Upraity S, Shaikh S, Padul V, Shirsat NV. MiR-224 expression increases radiation sensitivity of glioblastoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;448(2):225–30.
Gyöngyösi B, Végh E, Járay B, Szekely E, Fassan M, Bodoky G, et al. Pretreatment microRNA level and outcome in sorafenib-treated hepatocellular carcinoma. J Histochem Cytochem. 2014;62(8):547–55.
Zhao H, Bi T, Qu Z, Jiang J, Cui S, Wang Y. Expression of miR-224-5p is associated with the original cisplatin resistance of ovarian papillary serous carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2014;32(3):1003–12.
Song GQ, Song GR, Ni HY, Gu L, Liu H, Chen B, et al. Deregulated expression of miR-224 and its target gene: CD59 predicts outcome of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with R-CHOP. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2014;14(7):659–70.
Shen SN, Wang LF, Jia YF, Hao YQ, Zhang L, Wang H. Upregulation of microrna-224 is associated with aggressive progression and poor prognosis in human cervical cancer. Diagn Pathol. 2013;8:69.
Zhuang LP, Meng ZQ. Serum miR-224 reflects stage of hepatocellular carcinoma and predicts survival. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:731781.
Fu H, He HC, Han ZD, Wan YP, Luo HW, Huang YQ, et al. MicroRNA-224 and its target CAMKK2 synergistically influence tumor progression and patient prognosis in prostate cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014;36(3):1983–91.
Zhu D, Chen H, Yang XG, Chen W, Wang L, Xu J, Yu L. Decreased microRNA-224 and its clinical significance in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Diagn Pathol. 2014;9(1):198.
Lu S, Wang S, Geng S, Ma S, Liang Z, Jiao B. Upregulation of microRNA-224 confers a poor prognosis in glioma patients. Clin Transl Oncol. 2013;15(7):569–74.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81272470).
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W., Fan, Xm., Mao, L. et al. MicroRNA-224: as a potential target for miR-based therapy of cancer. Tumor Biol. 36, 6645–6652 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3883-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3883-3