Abstract
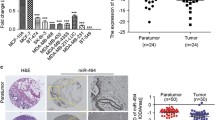
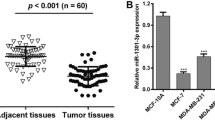
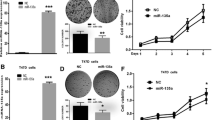
Studies have shown that microRNAs (miRNAs) are involved in the malignant progression of human cancer. However, little is known about the potential role of miRNAs in breast carcinogenesis. miR-124 expression in breast cancer tissue was measured by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Target prediction algorithms and luciferase reporter gene assays were used to investigate the target of miR-124. Breast cancer cells growth was regulated by overexpression or knockdown miR-124. At the end of the study, tumor-bearing mice were tested to confirm the function of miR-124 in breast cancer. In this study, we demonstrated that the expression of miR-124 was significantly downregulated in breast cancer tissues compared with matched adjacent non-neoplastic tissues. We identified and confirmed that cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) was a direct target of miR-124. Overexpression of miR-124 suppressed CDK4 protein expression and attenuated cell viability, proliferation, and cell cycle progression in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-435S breast cancer cells in vitro. Overexpression of CDK4 partially rescued the inhibitory effect of miR-124 in the breast cancer cells. Moreover, we found that miR-124 overexpression effectively repressed tumor growth in xenograft animal experiments. Our results demonstrate that miR-124 functions as a growth-suppressive miRNA and plays an important role in inhibiting tumorigenesis by targeting CDK4.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Desantis C, Ma J, Bryan L, Jemal A: Breast cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 2013.
Pagani O, Senkus E, Wood W, Colleoni M, Cufer T, Kyriakides S, et al. International guidelines for management of metastatic breast cancer: can metastatic breast cancer be cured? J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010;102:456–63.
van den Hurk CJ, Eckel R, van de Poll-Franse LV, Coebergh JW, Nortier JW, Holzel D, et al. Unfavourable pattern of metastases in m0 breast cancer patients during 1978-2008: a population-based analysis of the Munich Cancer Registry. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;128:795–805.
Negrini M, Calin GA. Breast cancer metastasis: a microrna story. Breast Cancer Res. 2008;10:203.
Huang Q, Gumireddy K, Schrier M, le Sage C, Nagel R, Nair S, et al. The micrornas mir-373 and mir-520c promote tumour invasion and metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:202–10.
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Weinberg RA. Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microrna-10b in breast cancer. Nature. 2007;449:682–8.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, et al. Microrna expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005;435:834–8.
Pillai RS. Microrna function: multiple mechanisms for a tiny rna? RNA. 2005;11:1753–61.
Slack FJ, Weidhaas JB. Microrna in cancer prognosis. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2720–2.
Wang V, Wu W. Microrna-based therapeutics for cancer. BioDrugs. 2009;23:15–23.
Krichevsky AM, King KS, Donahue CP, Khrapko K, Kosik KS. A microrna array reveals extensive regulation of micrornas during brain development. RNA. 2003;9:1274–81.
Xia H, Cheung WK, Ng SS, Jiang X, Jiang S, Sze J, et al. Loss of brain-enriched mir-124 microrna enhances stem-like traits and invasiveness of glioma cells. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:9962–71.
Hunt S, Jones AV, Hinsley EE, Whawell SA, Lambert DW. Microrna-124 suppresses oral squamous cell carcinoma motility by targeting itgb1. FEBS Lett. 2011;585:187–92.
Furuta M, Kozaki KI, Tanaka S, Arii S, Imoto I, Inazawa J. Mir-124 and mir-203 are epigenetically silenced tumor-suppressive micrornas in hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2010;31:766–76.
Zheng F, Liao YJ, Cai MY, Liu YH, Liu TH, Chen SP, et al. The putative tumour suppressor microrna-124 modulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell aggressiveness by repressing rock2 and ezh2. Gut. 2012;61:278–89.
Deng X, Ma L, Wu M, Zhang G, Jin C, Guo Y, et al. Mir-124 radiosensitizes human glioma cells by targeting cdk4. J Neurooncol. 2013;114:263–74.
Zhang T, Wang J, Zhai X, Li H, Li C, Chang J. Mir-124 retards bladder cancer growth by directly targeting cdk4. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2014;46:1072–9.
Wolfel T, Hauer M, Schneider J, Serrano M, Wolfel C, Klehmann-Hieb E, et al. Meyer zum Buschenfelde KH, Beach D: a p16ink4a-insensitive cdk4 mutant targeted by cytolytic t lymphocytes in a human melanoma. Science. 1995;269:1281–4.
Schmidt EE, Ichimura K, Reifenberger G, Collins VP. Cdkn2 (p16/mts1) gene deletion or cdk4 amplification occurs in the majority of glioblastomas. Cancer Res. 1994;54:6321–4.
He J, Allen JR, Collins VP, Allalunis-Turner MJ, Godbout R, Day 3rd RS, et al. Cdk4 amplification is an alternative mechanism to p16 gene homozygous deletion in glioma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1994;54:5804–7.
Curtin JA, Fridlyand J, Kageshita T, Patel HN, Busam KJ, Kutzner H, et al. Distinct sets of genetic alterations in melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2135–47.
Costello JF, Plass C, Arap W, Chapman VM, Held WA, Berger MS, et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (cdk6) amplification in human gliomas identified using two-dimensional separation of genomic DNA. Cancer Res. 1997;57:1250–4.
Yu Q, Sicinska E, Geng Y, Ahnstrom M, Zagozdzon A, Kong Y, et al. Requirement for cdk4 kinase function in breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2006;9:23–32.
Landis MW, Pawlyk BS, Li T, Sicinski P, Hinds PW. Cyclin d1-dependent kinase activity in murine development and mammary tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 2006;9:13–22.
Puyol M, Martin A, Dubus P, Mulero F, Pizcueta P, Khan G, et al. A synthetic lethal interaction between k-ras oncogenes and cdk4 unveils a therapeutic strategy for non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2010;18:63–73.
Choi YJ, Li X, Hydbring P, Sanda T, Stefano J, Christie AL, et al. The requirement for cyclin d function in tumor maintenance. Cancer Cell. 2012;22:438–51.
Anders L, Ke N, Hydbring P, Choi YJ, Widlund HR, Chick JM, et al. A systematic screen for cdk4/6 substrates links foxm1 phosphorylation to senescence suppression in cancer cells. Cancer Cell. 2011;20:620–34.
Zou X, Ray D, Aziyu A, Christov K, Boiko AD, Gudkov AV, et al. Cdk4 disruption renders primary mouse cells resistant to oncogenic transformation, leading to arf/p53-independent senescence. Genes Dev. 2002;16:2923–34.
Ruas M, Gregory F, Jones R, Poolman R, Starborg M, Rowe J, et al. Cdk4 and cdk6 delay senescence by kinase-dependent and p16ink4a-independent mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27:4273–82.
Michaud K, Solomon DA, Oermann E, Kim JS, Zhong WZ, Prados MD, et al. Pharmacologic inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 arrests the growth of glioblastoma multiforme intracranial xenografts. Cancer Res. 2010;70:3228–38.
Rane SG, Cosenza SC, Mettus RV, Reddy EP. Germ line transmission of the cdk4(r24c) mutation facilitates tumorigenesis and escape from cellular senescence. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:644–56.
Calin GA, Croce CM. Microrna signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:857–66.
Iorio MV, Croce CM. Microrna dysregulation in cancer: Diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics. A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol Med. 2012;4:143–59.
Zhu S, Wu H, Wu F, Nie D, Sheng S, Mo YY. Microrna-21 targets tumor suppressor genes in invasion and metastasis. Cell Res. 2008;18:350–9.
Makeyev EV, Zhang J, Carrasco MA, Maniatis T. The microrna mir-124 promotes neuronal differentiation by triggering brain-specific alternative pre-mrna splicing. Mol Cell. 2007;27:435–48.
Cao X, Pfaff SL, Gage FH. A functional study of mir-124 in the developing neural tube. Genes Dev. 2007;21:531–6.
Han ZB, Yang Z, Chi Y, Zhang L, Wang Y, Ji Y, et al. Microrna-124 suppresses breast cancer cell growth and motility by targeting cd151. Cell Physiol Biochem: Int J Exp Cell Physiol, Biochem Pharmacol. 2013;31:823–32.
Li L, Luo J, Wang B, Wang D, Xie X, Yuan L, et al. Microrna-124 targets flotillin-1 to regulate proliferation and migration in breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 2013;12:163.
Li W, Zang W, Liu P, Wang Y, Du Y, Chen X, et al. Microrna-124 inhibits cellular proliferation and invasion by targeting ets-1 in breast cancer. Tumour Biol: J Int Soc Oncodevelopmental Biol Med. 2014;35:10897–904.
Liang YJ, Wang QY, Zhou CX, Yin QQ, He M, Yu XT, et al. Mir-124 targets slug to regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of breast cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34:713–22.
Huang Z, Choi BK, Mujoo K, Fan X, Fa M, Mukherjee S, Owiti N, Zhang N, An Z: The e3 ubiquitin ligase nedd4 negatively regulates her3/erbb3 level and signaling. Oncogene 2014.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81272323), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK2012590), the Technology Project of Changzhou Social Development (CE20125019, CE20125024, CE20135044), and the key project of the Changzhou Health Bureau (ZD201201, ZD201307).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author contributions
T.B. and C.Q. provided the original idea and were responsible for the study design, analysis and interpretation of data, statistical analyses, and writing of the manuscript; T.B., D.X., L.Y., N.X., K.Q., and Y.W. were responsible for the analysis and interpretation of data and statistical analysis; C.T., W.L., Y.N., and J.D. were responsible for technical, material support and statistical analyses; S.W. was responsible for data collection and technical supports; All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 283 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, T., Xu, D., Tu, C. et al. miR-124 inhibits cell proliferation in breast cancer through downregulation of CDK4. Tumor Biol. 36, 5987–5997 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3275-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3275-8