Abstract
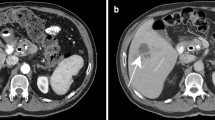
Hepatic inflammatory pseudotumors (HIPT) are rare benign neoplasms with unknown etiology and a great potential for mimicry, challenging diagnostics, and treatment features. The aim of the study was to retrospectively analyze the imaging, pathological, and clinical features of HIPT in our large cohort of patients in order to increase the understanding and suggest a scoring system for treatment approaches. Retrospective study analyzed 114 HIPT cases recorded from July 2006 to July 2012, when surgery was performed. Data were compared with chi-square test. In our study population, the mean age was 53.14 ± 10.98 years, with 69 male and 45 female patients. Most presented symptoms were abdominal pain (59/144, 41.0 %), fever (48/114, 42.1 %), abdominal distension (35/144, 24.3 %), and weight loss (12/144, 8.3 %). Laboratory examinations were normal. Sixteen cases were HBsAg positive and 8 had liver cirrhosis. Most of the tumors were located in the right lobe (79/114, 69.3 %), 33 in the left lobe, and 2 in the caudal lobe. Three imaging modalities, such as ultrasonography (US), computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), were compared and showed significant differences in sensitivity and sensibility. HIPT diagnostics are challenging, and conservative treatment should be prioritized as soon as the diagnosis is made. CT and MRI seem to have comparable diagnostic sensitivity. We propose a guideline for consideration of operative approach.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim YW, Lee JG, Kim KS, Yoon DS, Lee WJ, Kim BR, et al. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver treated by hepatic resection: a case report. Yonsei Med J. 2006;47(1):140–3.
Ntinas A, Kardassis D, Miliaras D, Tsinoglou K, Dimitriades A, Vrochides D. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver: a case report and review of the literature. J Med Case Rep. 2011;5:196. doi:10.1186/1752-1947-5-196.
Pack GT, Baker HW. Total right hepatic lobectomy: report of a case. Ann Surg. 1953;138(2):253–8.
Hoosein MM, Tapuria N, Standish RA, Koti RS, Webster GJ, Millar AD, et al. Inflammatory pseudotumour of the liver: the residuum of a biliary cystadenoma? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;19(4):333–6. doi:10.1097/MEG.0b013e328010b128.
Tang L, Lai EC, Cong WM, Li AJ, Fu SY, Pan ZY, et al. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the liver: a cohort study. World J Surg 23. 2010;34(2):309–13. doi:10.1007/s00268-009-0330-x.
Faraj W, Ajouz H, Mukherji D, Kealy G, Shamseddine A, Khalife M. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver: a rare pathological entity. World J Surg Oncol. 2011;9:5. doi:10.1186/1477-7819-9-5.
Geramizadeh B, Tahamtan MR, Bahador A, Sefidbakht S, Modjalal M, Nabai S, et al. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver: two case reports and a review of the literature. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2009;52(2):210–2.
Ogawa T, Yokoi H, Kawarada Y. A case of inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver causing elevated serum CA19-9 levels. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93(12):2551–5. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.00717.x.
Elpek GO. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the liver: a diagnostic challenge. J Clin Translat Hepatol. 2014;2(1):53–7. doi:10.14218/jcth.2013.00023.
Yan FH, Zhou KR, Jiang YP, Shi WB. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver—13 cases of MRI findings. World J Gastroenterol. 2001;7 (3):422–4.
Koea JB, Broadhurst GW, Rodgers MS, McCall JL. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver: demographics, diagnosis, and the case for nonoperative management. J Am Coll Surg. 2003;196(2):226–35. doi:10.1016/s1072-7515(02)01495-3.
Someren A. “Inflammatory pseudotumor” of liver with occlusive phlebitis: report of a case in a child and review of the literature. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978;69(2):176–81.
Milias K, Madhavan KK, Bellamy C, Garden OJ, Parks RW. Inflammatory pseudotumors of the liver: experience of a specialist surgical unit. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24(9):1562–6. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2009.05951.x.
Ueda J, Yoshida H, Taniai N, Onda M, Hayashi H, Tajiri T. Inflammatory pseudotumor in the liver associated with intrahepatic bile duct stones mimicking malignancy. J Nippon Med School = Nippon Ika Daigaku zasshi. 2009;76(3):154–9.
Zavaglia C, Barberis M, Gelosa F, Cimino G, Minola E, Mondazzi L, et al. Inflammatory pseudotumour of the liver with malignant transformation. Report of two cases. Italian J Gastroenterol. 1996;28(3):152–9.
Pecorella I, Ciardi A, Memeo L, Trombetta G, de Quarto A, de Simone P, et al. Inflammatory pseudotumour of the liver—evidence for malignant transformation. Pathol Res Pract. 1999;195(2):115–20. doi:10.1016/s0344-0338(99)80083-1.
Nagarajan S, Jayabose S, McBride W, Prasadh I, Tanjavur V, Marvin MR, et al. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor of the liver in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2013;57(3):277–80. doi:10.1097/MPG.0b013e31829e0b3b.
Tsou YK, Lin CJ, Liu NJ, Lin CC, Lin CH, Lin SM. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver: report of eight cases, including three unusual cases, and a literature review. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;22 (12):2143–7. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04514.x.
Sari A, Tunakan M, Unsal B, Ekinci N, Rezanko T, Elcin F, et al. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver diagnosed by needle biopsy: report of three cases (one with neuroendocrine tumor of the rectum and lung). Turkish J Gastroenterol: Off J Turkish Soc Gastroenterol. 2010;21(3):308–12.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xiaoyu Yang, Junjun Zhu, Fengfeng Cai and Aijun Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Zhu, J., Biskup, E. et al. Inflammatory pseudotumors of the liver: experience of 114 cases. Tumor Biol. 36, 5143–5148 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3167-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3167-y