Abstract
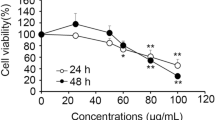
Mushroom Huaier has become a focus of interest in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Presently, we isolated and purified one polysaccharide from this mushroom. This study aimed to investigate the effects of SP1 on tumor growth and metastasis in a HCC xenograft model and explore its possible mechanism of action. Our results showed that SP1 not only significantly inhibited the proliferation of SMMC-7721 cells in vitro at the concentration ranging from 0 to 800 μg/ml but also suppressed the HCC tumor growth and metastatic nodules to the lung in SMMC-7721-bearing mice by oral administration at three doses of 30, 60, and 120 mg/kg. Concomitantly, immunohistochemistry analysis of tumor tissues identified that SP1 administration at three doses significantly inhibited the in vivo cancer cell proliferation and microvessel density (MVD) formation, evidenced by a low proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) and CD34 expression, but increased the percentage of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL)-positive cells. Keeping in line with this observation, SP1 treatment decreased serum matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 2 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels, downregulated the protein expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha, VEGF, MMP2, bcl-2, N-cadherin, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), and metadherin (MTDH), and upregulated bax and NE-cadherin protein expression in tumor tissues. Taken together, our data suggest that SP1 appears to be a promising chemopreventive agent for the tumorigenesis and metastasis in patients with HCC, especially at advanced stages.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108.
Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2003;362:1907–17.
Wang J, Zheng X, Zeng G, Zhou Y, Yuan H. Purified vitexin compound 1 inhibits growth and angiogenesis through activation of FOXO3a by inactivation of Akt in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 2014;33:441–8.
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Borras J. Epidemiology of primary liver cancer. Semin Liver Dis. 1999;19:271–85.
Bruix J, Sherman M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2005;42:1208–36.
Drake CG, Antonarakis ES. Update: immunological strategies for prostate cancer. Curr Urol Rep. 2010;11:202–7.
Kellof GJ. Perspective on cancer chemoprevention research and drug development. Adv Cancer Res. 2000;78:199–334.
Cohen I, Tagliaferri M, Tripathy D. Traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 2002;29:563–74.
Li L, Ye S, Wang Y. Progress on experimental research and clinical application of Trametes robiniophila. Bull Chin Cancer. 2007;2:016.
Zhang T, Wang K, Zhang J, Wang X, Chen Z, Ni C, et al. Huaier aqueous extract inhibits colorectal cancer stem cell growth partially via downregulation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncol Lett. 2013;5:1171–6.
Ren J, Zheng C, Feng G, Liang H, Xia X, Fang J, et al. Inhibitory effect of extract of fungi of Huaier on hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Huazhong Univ Sci Techn Med Sci. 2009;29:198–201.
Zhang N, Kong X, Yan S, Yuan C, Yang Q. Huaier aqueous extract inhibits proliferation of breast cancer cells by inducing apoptosis. Cancer Sci. 2010;101:2375–83.
Xu X, Wei Q, Wang K, Ling Q, Xie H, Zhou L, et al. Anticancer effects of Huaier are associated with down-regulation of P53. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2011;12:2251–4.
Guo Y, Cheng P, Chen Y, Zhou X, Yu P, Li Y. Studies on the constituents of polysaccharide from the hyphae of Trametes robiniophila (II)—identification of polysaccharide from the hyphae of Trametes robiniophila and determination of its molar ratio. J China Pharm Univ. 1992;23:155–7.
Guo Y, Cheng P, Chen Y, Zhou X, Yu P, Li Y. Isolation and analysis of the polysaccharide of Huaier mycelium. Chin J Biochem Pharm. 1993;63:56–9.
Zheng J, Li C, Wu X, Liu M, Sun X, Yang Y, et al. Huaier polysaccharides suppresses hepatocarcinoma MHCC97-H cell metastasis via inactivation of EMT and AEG-1 pathway. Int J Biol Macromol. 2014;64:106–10.
Li C, Wu X, Zhang H, Yang G, Hao M, Sheng S, et al. A Huaier polysaccharide inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis. Tumour Biol. 2014. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2775-2.
Staub AM. Removal of protein-Sevag method. Methods Carbohydr Chem. 1965;5:5–6.
Liu X, Zu YG, Fu YJ, Yao LP, Gu CB, Wang W, et al. Antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity towards cancer cells of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil. Eur Food Res Technol. 2009;229:247–53.
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR, Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis—correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:1–8.
Haifeng J, Yanglin P, Lijie H, Huihong Z, Xiaohua L, Lina Z, et al. p75 neurotrophin receptor inhibits invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2007;5:423–33.
Han MH, Lee WS, Lu JN, Kim G, Jung JM, Ryu CH, et al. Citrus aurantium L. exhibits apoptotic effects on U937 human leukemia cells partly through inhibition of Akt. Int J Oncol. 2012;40:2090–6.
Liu S, Yu M, He Y, Xiao L, Wang F, Song C, et al. Melittin prevents liver cancer cell metastasis through inhibition of the Rac1-dependent pathway. Hepatology. 2008;47:1964–73.
Sun HC, Tang ZY, Li XM, Zhou YN, Sun BR, Ma ZC. Immunohistochemical study of angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma: its relationship with prognosis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1999;125:419–26.
Martínez A. A new family of angiogenic factors. Cancer Lett. 2006;236:157–63.
Jakob C, Sterz J, Zavrski I, Heider U, Kleeberg L, Fleissner C, et al. Angiogenesis in multiple myeloma. Eur J Cancer. 2006;42:1581–90.
Pang RW, Joh JW, Johnson PJ, Monden M, Pawlik TM, Poon RT. Biology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15:962–71.
Barr MP, Bouchier-Hayes DJ, Harmey JJ. Vascular endothelial growth factor is an autocrine survival factor for breast tumour cells under hypoxia. Int J Oncol. 2008;32:41–8.
Tzao C, Lee SC, Tung HJ, Hsu HS, Hsu WH, Sun GH, et al. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-D as outcome predictors in resected esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Markers. 2008;25:141–8.
Lin C, McGough R, Aswad B, Block JA, Terek R. Hypoxia induces HIF-1alpha and VEGF expression in chondrosarcoma cells and chondrocytes. J Orthop Res. 2004;22:1175–81.
Shimamura T, Saito S, Morita K, Kitamura T, Morimoto M, Kiba T, et al. Detection of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma biopsy specimens. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000;15:640–6.
Ng KT, Guo DY, Cheng Q, Geng W, Ling CC, Li CX, et al. A garlic derivative, S-allylcysteine (SAC), suppresses proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e31655.
Wang L, Tang ZY, Qin LX, Wu XF, Sun HC, Xue Q, et al. gh-dose and long-term therapy with interferon-alfa inhibits tumor growth and recurrence in nude mice bearing human hepatocellular carcinoma xenografts with high metastatic potential. Hepatol. 2000;32:43–8.
Cho JY, Chung HC, Noh SH, Roh JK, Min JS, Kim BS. High level of urokinase-type plasminogen activator is a new prognostic marker in patients with gastric carcinoma. Cancer. 1997;79:878–83.
Simpson-Haidaris PJ, Rybarczyk B. Tumors and fibrinogen. The role of fibrinogen as an extracellular matrix protein. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;936:406–12.
Zucker S, Vacirca J. Role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in colorectal cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2004;23:101–17.
Sugita K. Recent advances in inhibitors of metalloproteinases for cancer therapy. IDrugs. 1999;2:327–39.
Wojtowicz-Praga S. Clinical potential of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Drugs Res Dev. 1999;1:117–29.
Sarrió D, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Hardisson D, Cano A, Moreno-Bueno G, Palacios J. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer relates to the basal-like phenotype. Cancer Res. 2008;68:989–97.
Fransvea E, Angelotti U, Antonaci S, Giannelli G. Blocking transforming growth factor-beta up-regulates E-cadherin and reduces migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology. 2008;47:1557–66.
Yu H, Pardoll D, Jove R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:798–809.
Long M, Hao M, Dong K, Shen J, Wang X, Lin F, et al. AEG-1 overexpression is essential for maintenance of malignant state in human AML cells via up-regulation of Akt1 mediated by AURKA activation. Cell Signal. 2013;25:1438–46.
Yang SF, Wang SN, Wu CF, Yeh YT, Chai CY, Chunag SC, et al. Altered p-STAT3 (tyr705) expression is associated with histological grading and intratumour microvessel density in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 2007;60:642–8.
Srivastava J, Siddiq A, Emdad L, Santhekadur PK, Chen D, Gredler R, et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis: novel insights from a mouse model. Hepatology. 2012;56:1782–91.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81201779 and No. 81101691).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yanmei Zou and Xiaomin Qin contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, Y., Xiong, H., Xiong, H. et al. A polysaccharide from mushroom Huaier retards human hepatocellular carcinoma growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis in nude mice. Tumor Biol. 36, 2929–2936 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2923-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2923-8