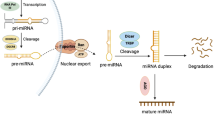
Abstract
With cancer being a major cause of death worldwide, microRNAs (miRNAs) have been investigated as novel and non-invasive biomarkers for cancer diagnosis. Recently, microRNA-21 (miR-21) attracts much attention for its aberrant expression and has been widely studied in various cancers. However, the inconsistent results from studies make it hard to evaluate the diagnostic value of miR-21 in cancer diagnosis, which lead us to conduct this meta-analysis. We conducted a comprehensive literature search in the Medline, Embase, PubMed, CNKI, and Web of Science before July 1, 2014. STATA 12.0 software was used for calculation and statistical analysis. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratio (PLR, NLR), and diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) were used to assess the diagnostic performance of miR-21 for cancers. Seventy-three studies in 60 articles were involved in this meta-analysis, with a total of 4684 patients with cancer and 3108 controls. The overall parameters were calculated from all the included studies: sensitivity of 0.78 (95 % confidence interval (CI) 0.74–0.81), specificity of 0.83 (95 % CI 0.80–0.86), PLR of 4.5 (95 % CI 3.8–5.4), NLR of 0.27 (95 % CI 0.23–0.32); DOR of 17 (95 % CI 12–23), and area under the curve (AUC) of 0.88 (95 % CI 0.84–0.90). In addition, we performed subgroup analyses based on ethnicity, cancer types, and sample types. Results from subgroup analysis showed that cancer types and sample types were the sources of heterogeneity in our meta-analysis. The overall diagnostic value of miR-21 is not very high for cancer diagnosis; however, it is affected significantly by the types of cancer and specimen. MiR-21 has a relatively high diagnostic value for detecting breast cancer, and miR-21 assays based on plasma, serum, and tissue achieved relatively higher accuracy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chan SH, Wu CW, Li AF, Chi CW, Lin WC. miR-21 microRNA expression in human gastric carcinomas and its clinical association. Anticancer Res. 2008;28:907–11.
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K, et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 2008;18:997–1006. doi:10.1038/cr.2008.282.
Bhardwaj A, Arora S, Prajapati VK, Singh S, Singh AP. Cancer “stemness”-regulating microRNAs: role, mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Curr Drug Targets. 2013;14:1175–84.
Breitkreutz D, Hlatky L, Rietman E, Tuszynski JA. Molecular signaling network complexity is correlated with cancer patient survivability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:9209–12. doi:10.1073/pnas.1201416109.
Wang Q, Wu X, Wu T, Li GM, Shi Y. Clinical significance of RKIP mRNA expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:4377–80. doi:10.1007/s13277-013-1575-4.
Tran B, Rosenthal MA. Survival comparison between glioblastoma multiforme and other incurable cancers. J Clin Neurosci. 2010;17:417–21. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2009.09.004.
El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2557–76. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2007.04.061.
Song MY, Pan KF, Su HJ, Zhang L, Ma JL, Li JY, et al. Identification of serum microRNAs as novel non-invasive biomarkers for early detection of gastric cancer. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e33608. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0033608.
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. doi:10.3322/caac.20107.
O’Byrne KJ, Gatzemeier U, Bondarenko I, Barrios C, Eschbach C, Martens UM, et al. Molecular biomarkers in non-small-cell lung cancer: a retrospective analysis of data from the phase 3 FLEX study. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:795–805. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70189-9.
Mar-Aguilar F, Mendoza-Ramirez JA, Malagon-Santiago I, Espino-Silva PK, Santuario-Facio SK, Ruiz-Flores P, et al. Serum circulating microRNA profiling for identification of potential breast cancer biomarkers. Dis Markers. 2013;34:163–9. doi:10.3233/dma-120957.
Yang X, Guo Y, Du Y, Yang J, Li S, Liu S, et al. Serum microRNA-21 as a diagnostic marker for lung carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2014;9:e97460. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0097460.
Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Rutjes AW, Scholten RJ, Bossuyt PM, Zwinderman AH. Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2005;58:982–90. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2005.02.022.
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. doi:10.3322/caac.21208.
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30.
Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, Aharonov R, Gilad S, Barad O, et al. Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat Genet. 2005;37:766–70. doi:10.1038/ng1590.
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155:529–36. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009.
Wu R, Jiang Y, Wu Q, Li Q, Cheng D, Xu L, et al. Diagnostic value of microRNA-21 in the diagnosis of lung cancer: evidence from a meta-analysis involving 11 studies. Tumour Biol. 2014. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2106-7.
Wang Y, Gao X, Wei F, Zhang X, Yu J, Zhao H, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating miR-21 for cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gene. 2014;533:389–97. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2013.09.038.
Yu L, Todd NW, Xing L, Xie Y, Zhang H, Liu Z, et al. Early detection of lung adenocarcinoma in sputum by a panel of microRNA markers. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2870–8. doi:10.1002/ijc.25289.
Zeng Z, Wang J, Zhao L, Hu P, Zhang H, Tang X, et al. Potential role of microRNA-21 in the diagnosis of gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2013;8:e73278. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0073278.
Zhang B, Wang Q, Pan X. MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in animals and plants. J Cell Physiol. 2007;210:279–89. doi:10.1002/jcp.20869.
Hamza TH, Arends LR, van Houwelingen HC, Stijnen T. Multivariate random effects meta-analysis of diagnostic tests with multiple thresholds. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2009;9:73. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-9-73.
Xie H, Chu Z, Wang H. Serum microRNA expression profile as a biomarker in diagnosis and prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Pediatr. 2012;30:421–4.
Kishimoto T, Eguchi H, Nagano H, Kobayashi S, Akita H, Hama N, et al. Plasma miR-21 is a novel diagnostic biomarker for biliary tract cancer. Cancer Sci. 2013;104:1626–31. doi:10.1111/cas.12300.
Zaravinos A, Radojicic J, Lambrou GI, Volanis D, Delakas D, Stathopoulos EN, et al. Expression of miRNAs involved in angiogenesis, tumor cell proliferation, tumor suppressor inhibition, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and activation of metastasis in bladder cancer. J Urol. 2012;188:615–23. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2012.03.122.
Asaga S, Kuo C, Nguyen T, Terpenning M, Giuliano AE, Hoon DS. Direct serum assay for microRNA-21 concentrations in early and advanced breast cancer. Clin Chem. 2011;57:84–91. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2010.151845.
Gao J, Zhang Q, Xu J, Guo L, Li X. Clinical significance of serum miR-21 in breast cancer compared with CA153 and CEA. Chin J Cancer Res. 2013;25:743–8. doi:10.3978/j.issn. 1000-9604.2013.12.04.
Lee CH, Kuo WH, Lin CC, Oyang YJ, Huang HC, Juan HF. MicroRNA-regulated protein-protein interaction networks and their functions in breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:11560–606. doi:10.3390/ijms140611560.
Mar-Aguilar F, Luna-Aguirre CM, Moreno-Rocha JC, Araiza-Chavez J, Trevino V, Rodriguez-Padilla C, et al. Differential expression of miR-21, miR-125b and miR-191 in breast cancer tissue. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2013;9:53–9. doi:10.1111/j.1743-7563.2012.01548.x.
Ng EK, Li R, Shin VY, Jin HC, Leung CP, Ma ES, et al. Circulating microRNAs as specific biomarkers for breast cancer detection. PLoS One. 2013;8:e53141. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0053141.
Wang B, Zhang Q. The expression and clinical significance of circulating microRNA-21 in serum of five solid tumors. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012;138:1659–66. doi:10.1007/s00432-012-1244-9.
Selaru FM, Olaru AV, Kan T, David S, Cheng Y, Mori Y, et al. MicroRNA-21 is overexpressed in human cholangiocarcinoma and regulates programmed cell death 4 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3. Hepatology. 2009;49:1595–601. doi:10.1002/hep.22838.
Kanaan Z, Rai SN, Eichenberger MR, Roberts H, Keskey B, Pan J, et al. Plasma MiR-21: A potential diagnostic marker of colorectal cancer. Ann Surg. 2012;256:544–51.
Koga Y, Yasunaga M, Takahashi A, Kuroda J, Moriya Y, Akasu T, et al. MicroRNA expression profiling of exfoliated colonocytes isolated from feces for colorectal cancer screening. Cancer Prev Res. 2010;3:1435–42.
Kuriyama S, Hamaya Y, Yamada T, Sugimoto M, Osawa S, Sugimoto K, et al. Fecal microrna assays as a marker for colorectal cancer screening. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:S770.
Liu GH, Zhou ZG, Chen R, Wang MJ, Zhou B, Li Y, et al. Serum miR-21 and miR-92a as biomarkers in the diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2013;34:2175–81. doi:10.1007/s13277-013-0753-8.
Luo X, Stock C, Burwinkel B, Brenner H. Identification and evaluation of plasma microRNAs for early detection of colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e62880. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062880.
Toiyama Y, Takahashi M, Hur K, Nagasaka T, Tanaka K, Inoue Y, et al. Serum miR-21 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105:849–59.
Wu CW, Ng SSM, Dong YJ, Ng SC, Leung WW, Lee CW, et al. Detection of miR-92a and miR-21 in stool samples as potential screening biomarkers for colorectal cancer and polyps. Gut. 2012;61:739–45.
Zanutto S, Pizzamiglio S, Ghilotti M, Bertan C, Ravagnani F, Perrone F, et al. Circulating miR-378 in plasma: a reliable, haemolysis-independent biomarker for colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2014;110:1001–7. doi:10.1038/bjc.2013.819.
Xie ZJ, Chen G, Zhang XC, Li DF, Huang J, Li ZJ. Saliva supernatant miR-21: a novel potential biomarker for esophageal cancer detection. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13:6145–9.
Ye M, Ye P, Zhang W, Rao J, Xie Z. Diagnostic values of salivary versus and plasma microRNA-21 for early esophageal cancer. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2014;34:885–9.
Cui L, Zhang X, Ye G, Zheng T, Song H, Deng H, et al. Gastric juice MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers for the screening of gastric cancer. Cancer. 2013;119:1618–26. doi:10.1002/cncr.27903.
Li BS, Zhao YL, Guo G, Li W, Zhu ED, Luo X, et al. Plasma microRNAs, miR-223, miR-21 and miR-218, as novel potential biomarkers for gastric cancer detection. PLoS One. 2012;7:e41629. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041629.
Shiotani A, Murao T, Kimura Y, Matsumoto H, Kamada T, Kusunoki H, et al. Identification of serum miRNAs as novel non-invasive biomarkers for detection of high risk for early gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 2013;109:2323–30. doi:10.1038/bjc.2013.596.
Zheng Y, Cui L, Sun W, Zhou H, Yuan X, Huo M, et al. MicroRNA-21 is a new marker of circulating tumor cells in gastric cancer patients. Cancer Biomark. 2011;10:71–7. doi:10.3233/cbm-2011-0231.
Akers JC, Ramakrishnan V, Kim R, Skog J, Nakano I, Pingle S, et al. MiR-21 in the extracellular vesicles (EVs) of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): a platform for glioblastoma biomarker development. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e78115. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0078115.
Wang F, Sun GP, Zou YF, Hao JQ, Zhong F, Ren WJ. MicroRNAs as promising biomarkers for gastric cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2012;11:259–67. doi:10.3233/cbm-2012-00284.
Liu AM, Yao TJ, Wang W, Wong KF, Lee NP, Fan ST, et al. Circulating miR-15b and miR-130b in serum as potential markers for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open. 2012;2:e000825. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2012-000825.
Qin Z, Zhu X, Huang Y. Circulating microRNA-21 as a novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. SiChuan Med J. 2013;34:1463–5.
Tomimaru Y, Eguchi H, Nagano H, Wada H, Kobayashi S, Marubashi S, et al. Circulating microRNA-21 as a novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012;56:167–75. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2011.04.026.
Xu J, Wu C, Che X, Wang L, Yu D, Zhang T, et al. Circulating microRNAs, miR-21, miR-122, and miR-223, in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma or chronic hepatitis. Mol Carcinog. 2011;50:136–42. doi:10.1002/mc.20712.
Abd-El-Fattah AA, Sadik NA, Shaker OG, Aboulftouh ML. Differential microRNAs expression in serum of patients with lung cancer, pulmonary tuberculosis, and pneumonia. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013;67:875–84. doi:10.1007/s12013-013-9575-y.
Le HB, Zhu WY, Chen DD, He JY, Huang YY, Liu XG, et al. Evaluation of dynamic change of serum miR-21 and miR-24 in pre- and post-operative lung carcinoma patients. Med Oncol. 2012;29:3190–7. doi:10.1007/s12032-012-0303-z.
Li Y, Li W, Ouyang Q, Hu S, Tang J. Detection of lung cancer with blood microRNA-21 expression levels in Chinese population. Oncol Lett. 2011;2:991–4. doi:10.3892/ol.2011.351.
Ma J, Li N, Guarnera M, Jiang F. Quantification of plasma miRNAs by digital PCR for cancer diagnosis. Biomark Insights. 2013;8:127–36. doi:10.4137/bmi.s13154.
Mozzoni P, Banda I, Goldoni M, Corradi M, Tiseo M, Acampa O, et al. Plasma and EBC microRNAs as early biomarkers of non-small-cell lung cancer. Biomarkers. 2013;18:679–86. doi:10.3109/1354750x.2013.845610.
Shen J, Liao J, Guarnera MA, Fang H, Cai L, Stass SA, et al. Analysis of microRNAs in sputum to improve computed tomography for lung cancer diagnosis. J Thorac Oncol. 2014;9:33–40. doi:10.1097/jto.0000000000000025.
Shen J, Todd NW, Zhang H, Yu L, Lingxiao X, Mei Y, et al. Plasma microRNAs as potential biomarkers for non-small-cell lung cancer. Lab Investig. 2011;91:579–87. doi:10.1038/labinvest.2010.194.
Tang D, Shen Y, Wang M, Yang R, Wang Z, Sui A, et al. Identification of plasma microRNAs as novel noninvasive biomarkers for early detection of lung cancer. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2013;22:540–8. doi:10.1097/CEJ.0b013e32835f3be9.
Wei J, Liu LK, Gao W, Zhu CJ, Liu YQ, Cheng T, et al. Reduction of plasma microRNA-21 is associated with chemotherapeutic response in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Chin J Cancer Res. 2011;23:123–8. doi:10.1007/s11670-011-0123-2.
Xie Y, Todd NW, Liu Z, Zhan M, Fang H, Peng H, et al. Altered miRNA expression in sputum for diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2010;67:170–6. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2009.04.004.
Baraniskin A, Kuhnhenn J, Schlegel U, Chan A, Deckert M, Gold R, et al. Identification of microRNAs in the cerebrospinal fluid as marker for primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system. Blood. 2011;117:3140–6. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-09-308684.
Mao X, Sun Y, Tang J. Serum miR-21 is a diagnostic and prognostic marker of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neurol Sci. 2014;35:233–8.
Liu X, Luo HN, Tian WD, Lu J, Li G, Wang L, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of plasma microRNA deregulation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013;14:1133–42. doi:10.4161/cbt.26170.
Gombos K, Horvath R, Szele E, Juhasz K, Gocze K, Somlai K, et al. miRNA expression profiles of oral squamous cell carcinomas. Anticancer Res. 2013;33:1511–7.
Ouyang L, Liu P, Yang S, Ye S, Xu W, Liu X. A three-plasma miRNA signature serves as novel biomarkers for osteosarcoma. Med Oncol. 2013;30:340. doi:10.1007/s12032-012-0340-7.
Dillhoff M, Liu J, Frankel W, Croce C, Bloomston M. MicroRNA-21 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and a potential predictor of survival. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008;12:2171–6. doi:10.1007/s11605-008-0584-x.
Habbe N, Koorstra JB, Mendell JT, Offerhaus GJ, Ryu JK, Feldmann G, et al. MicroRNA miR-155 is a biomarker of early pancreatic neoplasia. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009;8:340–6.
Liu JQ, Gao J, Ren Y, Wang XW, Wang WW, Lu H. Diagnostic value of plasma miR-21 in pancreatic cancer. World Chin J Digestol. 2011;19:860–3.
Ryu JK, Matthaei H, Dal Molin M, Hong SM, Canto MI, Schulick RD, et al. Elevated microRNA miR-21 levels in pancreatic cyst fluid are predictive of mucinous precursor lesions of ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreatology. 2011;11:343–50. doi:10.1159/000329183.
Wang J, Chen J, Chang P, LeBlanc A, Li D, Abbruzzesse JL, et al. MicroRNAs in plasma of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients as novel blood-based biomarkers of disease. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2009;2:807–13. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.capr-09-0094.
Yaman Agaoglu F, Kovancilar M, Dizdar Y, Darendeliler E, Holdenrieder S, Dalay N, et al. Investigation of miR-21, miR-141, and miR-221 in blood circulation of patients with prostate cancer. Tumour Biol. 2011;32:583–8. doi:10.1007/s13277-011-0154-9.
Faragalla H, Youssef YM, Scorilas A, Khalil B, White NM, Mejia-Guerrero S, et al. The clinical utility of miR-21 as a diagnostic and prognostic marker for renal cell carcinoma. J Mol Diagn. 2012;14:385–92. doi:10.1016/j.jmoldx.2012.02.003.
Silva-Santos RM, Costa-Pinheiro P, Luis A, Antunes L, Lobo F, Oliveira J, et al. MicroRNA profile: a promising ancillary tool for accurate renal cell tumour diagnosis. Br J Cancer. 2013;109:2646–53. doi:10.1038/bjc.2013.552.
Meng X, Liu Y, Liu B. Glutathione S-transferase M1 null genotype meta-analysis on gastric cancer risk. Diagn Pathol. 2014;9:122. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-9-122.
Keutgen XM, Filicori F, Crowley MJ, Wang Y, Scognamiglio T, Hoda R, et al. A panel of four miRNAs accurately differentiates malignant from benign indeterminate thyroid lesions on fine needle aspiration. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:2032–8. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-11-2487.
Mazeh H, Levy Y, Mizrahi I, Appelbaum L, Ilyayev N, Halle D, et al. Differentiating benign from malignant thyroid nodules using micro ribonucleic acid amplification in residual cells obtained by fine needle aspiration biopsy. J Surg Res. 2013;180:216–21. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2012.04.051.
Lee H, Choi HJ, Kang CS, Lee HJ, Lee WS, Park CS. Expression of miRNAs and PTEN in endometrial specimens ranging from histologically normal to hyperplasia and endometrial adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol. 2012;25:1508–15. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2012.111.
Tsukamoto O, Miura K, Mishima H, Abe S, Kaneuchi M, Higashijima A et al. Identification of endometrioid endometrial carcinoma-associated microRNAs in tissue and plasma. Gynecol Oncol. 2014;132:715–21. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2014.01.029.
Kumarswamy R, Volkmann I, Thum T. Regulation and function of miRNA-21 in health and disease. RNA Biol. 2011;8:706–13. doi:10.4161/rna.8.5.16154.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National 12th Five-Year Special Grand Project for Infectious Diseases (2012ZX10002004-005).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, L., Wan, Z., Ma, Y. et al. The clinical utility of microRNA-21 as novel biomarker for diagnosing human cancers. Tumor Biol. 36, 1993–2005 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2806-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2806-z