Abstract
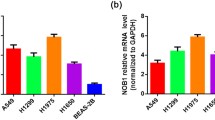
Dual-specificity phosphatase 6 (DUSP6/MKP-3) is a mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase that regulates extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) activity via feedback mechanisms, with an increasingly recognized role in tumour biology. The aim of this study was to explore the role of DUSP6 expression in the prognosis of human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). DUSP6 expression levels were evaluated by real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in 60 NSCLC samples from patients who underwent pulmonary resection at 12 de Octubre University Hospital. We performed a statistical analysis to investigate the correlation of DUSP6 expression and the clinical outcomes. We found that 66.7 % of the tumour samples show the downregulation of DUSP6 at the messenger RNA (mRNA) levels compared to benign epithelial lung tissues and 55 % of them show at least twofold downregulation of DUSP6 gene expression. Patients were classified into three groups according to their DUSP6 expression levels and those with very low levels (at least twofold downregulation) had the worst outcomes. Using the value of twice below the mean value in benign epithelial lung tissue as a cutoff, the overall survival of patients with very low DUSP6 levels was significantly lower than that in the rest of patients (31.9 ± 18.8 months vs. not reached, P = 0.049). This was most pronounced in adenocarcinoma histology and high-stage tumour samples. Our results suggest that DUSP6 gene expression in tumour samples may be a prognostic marker in NSCLC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013. doi:10.3322/caac.21166.
Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E, Lortet-Tieulent J, Rosso S, Coebergh JW, Comber H, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer. 2013. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2012.12.027.
Malvezzi M, Bertuccio P, Levi F, La Vecchia C, Negri E. European cancer mortality predictions for the year 2013. Ann Oncol. 2013. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdt010.
O’Reilly KE, Rojo F, She QB, Solit D, Mills GB, Smith D, et al. mTOR inhibition induces upstream receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and activates Akt. Cancer Res. 2006. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2925.
Shaw AT, Meissner A, Dowdle JA, Crowley D, Magendantz M, Ouyang C, et al. Sprouty-2 regulates oncogenic K-ras in lung development and tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. 2007. doi:10.1101/gad.1526207.
Zhang Z, Kobayashi S, Borczuk AC, Leidner RS, Laframboise T, Levine AD, et al. Dual specificity phosphatase 6 (DUSP6) is an ETS-regulated negative feedback mediator of oncogenic ERK signaling in lung cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 2010. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgq020.
Ostman A, Hellberg C, Bohmer FD. Protein-tyrosine phosphatases and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006. doi:10.1038/nrc1837.
Julien SG, Dube N, Hardy S, Tremblay ML. Inside the human cancer tyrosine phosphatome. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011. doi:10.1038/nrc2980.
Patterson KI, Brummer T, O’Brien PM, Daly RJ. Dual-specificity phosphatases: critical regulators with diverse cellular targets. Biochem J. 2009. doi:10.1042/BJ20082234.
Wong VC, Chen H, Ko JM, Chan KW, Chan YP, Law S, et al. Tumor suppressor dual-specificity phosphatase 6 (DUSP6) impairs cell invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-associated phenotype. Int J Cancer. 2013. doi:10.1002/ijc.25970.
Camps M, Nichols A, Gillieron C, Antonsson B, Muda M, Chabert C, et al. Catalytic activation of the phosphatase MKP-3 by ERK2 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Science. 1998. doi:10.1126/science.280.5367.1262.
Liu S, Sun JP, Zhou B, Zhang ZY. Structural basis of docking interactions between ERK2 and MAP kinase phosphatase 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. doi:10.1073/pnas.0510506103.
Arkell RS, Dickinson RJ, Squires M, Hayat S, Keyse SM, Cook SJ. DUSP6/MKP-3 inactivates ERK1/2 but fails to bind and inactivate ERK5. Cell Signal. 2008. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.12.014.
Keyse SM. Dual-specificity MAP, kinase phosphatases (MKPs) and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008. doi:10.1007/s10555-008-9123-1.
Jurek A, Amagasaki K, Gembarska A, Heldin CH, Lennartsson J. Negative and positive regulation of MAPK phosphatase 3 controls platelet-derived growth factor-induced Erk activation. J Biol Chem. 2009. doi:10.1074/jbc.M808490200.
Pulido R, Hooft van Huijsduijnen R. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: dual-specificity phosphatases in health and disease. FEBS J. 2008. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06250.x.
Marchetti S, Gimond C, Roux D, Gothie E, Pouyssegur J, Pages G. Inducible expression of a MAP kinase phosphatase-3-GFP chimera specifically blunts fibroblast growth and ras-dependent tumor formation in nude mice. J Cell Physiol. 2004. doi:10.1002/jcp.10465.
Okudela K, Yazawa T, Woo T, Sakaeda M, Ishii J, Mitsui H, et al. Down-regulation of DUSP6 expression in lung cancer: its mechanism and potential role in carcinogenesis. Am J Pathol. 2009. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2009.080489.
Chen HY, Yu SL, Chen CH, Chang GC, Chen CY, Yuan A, et al. A five-gene signature and clinical outcome in non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2007. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa060096.
Sato M, Vaughan MB, Girard L, Peyton M, Lee W, Shames DS, et al. Multiple oncogenic changes (K-RAS(V12), p53 knockdown, mutant EGFRs, p16 bypass, telomerase) are not sufficient to confer a full malignant phenotype on human bronchial epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 2006. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2521.
Furukawa T, Sunamura M, Motoi F, Matsuno S, Horii A. Potential tumor suppressive pathway involving DUSP6/MKP-3 in pancreatic cancer. Am J Pathol. 2003. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64315-5.
Xu S, Furukawa T, Kanai N, Sunamura M, Horii A. Abrogation of DUSP6 by hypermethylation in human pancreatic cancer. J Hum Genet. 2005. doi:10.1007/s10038-005-0235-y.
Chan DW, Liu VW, Tsao GS, Yao KM, Furukawa T, Chan KK, et al. Loss of MKP3 mediated by oxidative stress enhances tumorigenicity and chemoresistance of ovarian cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 2008. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgn167.
Lee JU, Huang S, Lee MH, Lee SE, Ryu MJ, Kim SJ, et al. Dual specificity phosphatase 6 as a predictor of invasiveness in papillary thyroid cancer. Eur J Endocrinol. 2013. doi:10.1530/EJE-12-0010.
Zhang H, Guo Q, Wang C, Yan L, Fu Y, Fan M, et al. Dual-specificity phosphatase 6 (Dusp6), a negative regulator of FGF2/ERK1/2 signaling, enhances 17β-estradiol-induced cell growth in endometrial adenocarcinoma cell. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2013.02.007.
Messina S, Frati L, Leonetti C, Zuchegna C, Di Zazzo E, Calogero A, et al. Dual-specificity phosphatase DUSP6 has tumor-promoting properties in human glioblastomas. Oncogene. 2011. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.99.
Arora D, Kothe S, van den Eijnden M, Hooft van Huijsduijnen R, Heidel F, Fischer T, et al. Expression of protein-tyrosine phosphatases in acute myeloid leukemia cells: FLT3 ITD sustains high levels of DUSP6 expression. Cell Commun Signal. 2013. doi:10.1186/1478-811X-10-19.
Suwinski R, Klusek A, Tyszkiewicz T, Kowalska M, Szczesniak-Klusek B, Gawkowska-Suwinska M, et al. Gene expression from bronchoscopy obtained tumour samples as a predictor of outcome in advanced inoperable lung cancer. PLoS One. 2013. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041379.
Bermudez O, Marchetti S, Pages G, Gimond C. Post-translational regulation of the ERK phosphatase DUSP6/MKP3 by the mTOR pathway. Oncogene. 2008. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1211040.
Marchetti S, Gimond C, Chambard JC, Touboul T, Roux D, Pouyssegur J, et al. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases phosphorylate mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 3/DUSP6 at serines 159 and 197, two sites critical for its proteasomal degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.2.854-864.2005.
Roberts PJ, Der CJ. Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 2007. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210422.
Cui Y, Parra I, Zhang M, Hilsenbeck SG, Tsimelzon A, Furukawa T, et al. Elevated expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 3 in breast tumors: a mechanism of tamoxifen resistance. Cancer Res. 2006. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3243.
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by Fundación Médica Mutua Madrileña (Madrid, Spain) grant 2008/107 and by Comunidad de Madrid (Biomedicina S2010/BMD-2326, Inmunothercan-CM). VD-G is supported by Fundación Mutua Madrileña 2010/018, AA-L by Red Temática de Investigación Corporativa del Cáncer (RTICC, ISCIII, Spain), CP by Ministerio de Sanidad y Política Social (TRA-151, Spain) and MTA-O by Instituto de Salud Carlos III (Programa Post-Formación Sanitaria Especializada FIS-CM 06/00231). We thank Dr. Juan Carlos Rubio (Genomic Department, Instituto de Investigación Hospital 12 de Octubre, Madrid) and Alberto Muro (Translational Oncology, Instituto de Investigación Hospital 12 de Octubre, Madrid) for their technical support.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Díaz-García, C.V., Agudo-López, A., Pérez, C. et al. Prognostic value of dual-specificity phosphatase 6 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Tumor Biol. 36, 1199–1206 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2729-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2729-8