Abstract
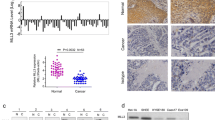
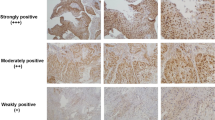
VGLL4, a member of the Vestigial-like (VGLL) proteins, has been reported to be dysregulated in several cancer types. However, its function in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) remains poorly understood. Here, it was found that the expression level of VGLL4 was decreased in ESCC tissues. Moreover, forced expression of VGLL4 in ESCC cells inhibited cell growth and migration, while knockdown of VGLL4 expression promoted the tumorigenecity of ESCC cells. Mechanistically, VGLL4 regulated the growth and motility of ESCC cells through downregulating the expression of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), a known oncogene in the progression of ESCC. Taken together, our study suggested that downregulation of VGLL4 was very important in the progression of ESCC, and restoring the function of VGLL4 might be a promising therapeutic strategy for ESCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shimada H, Nabeya Y, Okazumi S, et al. Prediction of survival with squamous cell carcinoma antigen in patients with resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Surgery. 2003;133(5):486–94.
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63(1):11–30.
Metzger R, Schneider PM, Warnecke-Eberz U, Brabender J, Holscher AH. Molecular biology of esophageal cancer. Onkologie. 2004;27(2):200–6.
He LR, Liu MZ, Li BK, et al. Overexpression of AIB1 predicts resistance to chemoradiotherapy and poor prognosis in patients with primary esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2009;100(9):1591–6.
Chen HH, Mullett SJ, Stewart AF. Vgl-4, a novel member of the vestigial-like family of transcription cofactors, regulates alpha1-adrenergic activation of gene expression in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(29):30800–6.
Mielcarek M, Gunther S, Kruger M, Braun T. VITO-1, a novel vestigial related protein is predominantly expressed in the skeletal muscle lineage. Gene Expr Patterns. 2002;2(3–4):305–10.
Mielcarek M, Piotrowska I, Schneider A, Gunther S, Braun T. VITO-2, a new SID domain protein, is expressed in the myogenic lineage during early mouse embryonic development. Gene Expr Patterns. 2009;9(3):129–37.
Pobbati AV, Hong W. Emerging roles of TEAD transcription factors and its coactivators in cancers. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012;14(5):390–8.
Pobbati AV, Chan SW, Lee I, Song H, Hong W. Structural and functional similarity between the Vgll1-TEAD and the YAP-TEAD complexes. Structure. 2012;20(7):1135–40.
Richardson AL, Wang ZC, De Nicolo A, et al. X chromosomal abnormalities in basal-like human breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2006;9(2):121–32.
Helias-Rodzewicz Z, Perot G, Chibon F, et al. YAP1 and VGLL3, encoding two cofactors of TEAD transcription factors, are amplified and overexpressed in a subset of soft tissue sarcomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2012;49(12):1161–71.
Jin HS, Park HS, Shin JH, et al. A novel inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP)-interacting protein, Vestigial-like (Vgl)-4, counteracts apoptosis-inhibitory function of IAPs by nuclear sequestration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;412(3):454–9.
Tajonar A, Maehr R, Hu G, et al. Brief report: VGLL4 is a novel regulator of survival in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 2012;31(12):2833–41.
Mann KM, Ward JM, Yew CC, et al. Sleeping Beauty mutagenesis reveals cooperating mutations and pathways in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(16):5934–41.
Jiao S, Wang H, Shi Z, et al. A peptide mimicking VGLL4 function acts as a YAP antagonist therapy against gastric cancer. Cancer Cell. 2014;25(2):166–80.
Zhang W, Gao Y, Li P, et al. VGLL4 functions as a new tumor suppressor in lung cancer by negatively regulating the YAP-TEAD transcriptional complex. Cell Res. 2013;24(3):331–43.
Xie JJ, Xu LY, Wu JY, et al. Involvement of CYR61 and CTGF in the fascin-mediated proliferation and invasiveness of esophageal squamous cell carcinomas cells. Am J Pathol. 2012;176(2):939–51.
Deng YZ, Chen PP, Wang Y, et al. Connective tissue growth factor is overexpressed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and promotes tumorigenicity through beta-catenin-T-cell factor/Lef signaling. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(50):36571–81.
Fujii M, Toyoda T, Nakanishi H, et al. TGF-beta synergizes with defects in the Hippo pathway to stimulate human malignant mesothelioma growth. J Exp Med. 2012;209(3):479–94.
Zhao B, Ye X, Yu J, et al. TEAD mediates YAP-dependent gene induction and growth control. Genes Dev. 2008;22(14):1962–71.
Li LY, Li EM, Wu ZY, et al. Connective tissue growth factor expression in precancerous lesions of human esophageal epithelium and prognostic significance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 2012. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2050.2010.01147.x.
Xie JJ, Xu LY, Xie YM, et al. Roles of ezrin in the growth and invasiveness of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 2009;124(11):2549–58.
Sutter AP, Hopfner M, Huether A, Maaser K, Scherubl H. Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor by erlotinib (Tarceva) for the treatment of esophageal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2006;118(7):1814–22.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81201840 and 81372523), the Health Bureau Foundation of Shanghai (20124Y152), and Chenxing Young Scholarship of Shanghai Jiao Tong University.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Wei Jiang, Feng Yao, and Jing He contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, W., Yao, F., He, J. et al. Downregulation of VGLL4 in the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 36, 1289–1297 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2701-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2701-7