Abstract
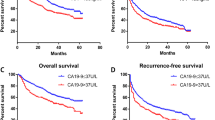
Serum levels of carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA 19-9) were shown to be associated with poorer prognosis in several cancers, but the prognostic role of CA 19-9 levels in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma was unclear. A retrospective cohort of 97 patients with resectable hepatocellular carcinoma was performed to assess the prognostic role of CA 19-9 levels on overall survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. Both Kaplan-Meier product-limit method and multivariate analysis were performed to determine the prognostic role of CA 19-9 levels. The results indicated that among those 97 patients, 24 (24.7 %) had elevated preoperative CA 19-9 levels (≥37 U/mL). Elevated serum CA 19-9 levels did not correlate with patient age, gender, tumor size, tumor stage, diabetes, and hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Kaplan-Meier product-limit method showed that patients with elevated CA 19-9 levels had poorer survival than those with normal CA 19-9 levels (log-rank test P < 0.001). Multivariate analysis showed that elevated CA 19-9 level was a significantly independent predictor of poorer overall survival (hazard ratio [HR] = 2.56; 95 % confidence interval [95 % CI] 1.41–4.64, P = 0.002). In addition, tumor stages and multiple tumors were also independent predictors of poorer overall survival in hepatocellular carcinoma (P < 0.01). In conclusion, serum CA 19-9 levels have an independent prognostic role in patients with resectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Elevated CA 19-9 level is significantly associated with poorer overall survival in hepatocellular carcinoma.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li G, Zheng Z. Toll-like receptor 3 genetic variants and susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinoma and HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2013;34(3):1589–94.
Breuhahn K, Gores G, Schirmacher P. Strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy and diagnostics: lessons learned from high throughput and profiling approaches. Hepatology. 2011;53(6):2112–21.
Tanaka M, Katayama F, Kato H, Tanaka H, Wang J, Qiao YL, et al. Hepatitis b and c virus infection and hepatocellular carcinoma in China: a review of epidemiology and control measures. J Epidemiol. 2011;21(6):401–16.
Aravalli RN, Steer CJ, Cressman EN. Molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2008;48(6):2047–63.
Kaseb AO, Morris JS, Hassan MM, Siddiqui AM, Lin E, Xiao L, et al. Clinical and prognostic implications of plasma insulin-like growth factor-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(29):3892–9.
Li W, Cai HX, Ge XM, Li K, Xu WD, Shi WH. Prognostic significance of BMP7 as an oncogene in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2013;34(2):669–74.
Villanueva A, Minguez B, Forner A, Reig M, Llovet JM. Hepatocellular carcinoma: novel molecular approaches for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. Annu Rev Med. 2010;61(1):317–28.
Galli C, Basso D, Plebani M. Ca 19-9: handle with care. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2013;51(7):1369–83.
Goonetilleke KS, Siriwardena AK. Systematic review of carbohydrate antigen (ca 19-9) as a biochemical marker in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2007;33(3):266–70.
John AR, Haghighi KS, Taniere P, Esmat ME, Tan YM, Bramhall SR. Is a raised CA 19-9 level diagnostic for a cholangiocarcinoma in patients with no history of sclerosing cholangitis? Dig Surg. 2006;23(5–6):319–24.
Zhang S, Chen Y, Zhu Z, Ding Y, Ren S, Zuo Y. Differential expression of carbohydrate antigen 19-9 in human colorectal cancer: a comparison with colon and rectal cancers. Mol Clin Oncol. 2013;1(6):1072–8.
Mohri Y, Tanaka K, Ohi M, Saigusa S, Yasuda H, Toiyama Y, et al. Identification of prognostic factors and surgical indications for metastatic gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 2014;14(6):409.
Tsuji M, Kashihara T, Terada N, Mori H. An immunohistochemical study of hepatic atypical adenomatous hyperplasia, hepatocellular carcinoma, and cholangiocarcinoma with alpha-fetoprotein, carcinoembryonic antigen, ca19-9, epithelial membrane antigen, and cytokeratins 18 and 19. Pathol Int. 1999;49(4):310–7.
Kim KH, Lee SG, Park EH, Hwang S, Ahn CS, Moon DB, et al. Surgical treatments and prognoses of patients with combined hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16(3):623–9.
Pissaia Jr A, Bernard D, Scatton O, Soubrane O, Conti F, Calmus Y. Significance of serum tumor markers carcinoembryonic antigen, ca 19-9, ca 125, and ca 15-3 in pre-orthotopic liver transplantation evaluation. Transplant Proc. 2009;41(2):682–4.
Tao LY, Cai L, He XD, Liu W, Qu Q. Comparison of serum tumor markers for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma. Am Surg. 2010;76(11):1210–3.
Ballehaninna UK, Chamberlain RS. Biomarkers for pancreatic cancer: promising new markers and options beyond CA 19-9. Tumor Biol. 2013;34(6):3279–92.
Bauer TM, El-Rayes BF, Li X, Hammad N, Philip PA, Shields AF, et al. Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 is a prognostic and predictive biomarker in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer who receive gemcitabine-containing chemotherapy: a pooled analysis of 6 prospective trials. Cancer. 2013;119(2):285–92.
Narita Y, Taniguchi H, Komori A, Nitta S, Yamaguchi K, Kondo C, et al. Ca19-9 level as a prognostic and predictive factor of bevacizumab efficacy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients undergoing oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014;73(2):409–16.
Liu SL, Song ZF, Hu QG, Shan D, Hu SB, Li J, et al. Serum carbohydrate antigen (ca) 19-9 as a prognostic factor in cholangiocarcinoma: a meta-analysis. Front Med China. 2010;4(4):457–62.
Xiao J, He X, Wang Z, Hu J, Sun F, Qi F, et al. Serum carbohydrate antigen 19-9 and prognosis of patients with gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(2):1331–4.
Uchino K, Tateishi R, Shiina S, Kanda M, Masuzaki R, Kondo Y, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma with extrahepatic metastasis: clinical features and prognostic factors. Cancer. 2011;117(19):4475–83.
Villanueva A, Llovet JM. Targeted therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2011;140(5):1410–26.
Villanueva A, Hoshida Y, Battiston C, Tovar V, Sia D, Alsinet C, et al. Combining clinical, pathology, and gene expression data to predict recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2011;140(5):1501–12.
Zhou H, Huang H, Shi J, Zhao Y, Dong Q, Jia H, et al. Prognostic value of interleukin 2 and interleukin 15 in peritumoral hepatic tissues for patients with hepatitis b-related hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. Gut. 2010;59(12):1699–708.
Zhao YM, Wang L, Dai Z, Wang DD, Hei ZY, Zhang N, et al. Validity of plasma macrophage migration inhibitory factor for diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2011;129(10):2463–72.
Ding T, Xu J, Zhang Y, Guo RP, Wu WC, Zhang SD, et al. Endothelium-coated tumor clusters are associated with poor prognosis and micrometastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. Cancer. 2011;117(21):4878–89.
Zhou L, Zhang N, Li QJ, Sun W, Zhang Y, Wang DS, et al. Association between high levels of notch 1 expression and high invasion and poor overall survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2013;34(1):543–53.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81200328) and Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (12ZR1424100).
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Huang, T., Zhang, F. et al. Prognostic role of serum carbohydrate antigen 19-9 levels in patients with resectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 36, 2257–2261 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2435-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2435-6