Abstract
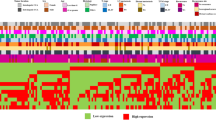
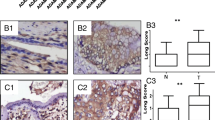
The activation of Ephrin (Eph) receptors, the largest tyrosine kinase families of cell surface receptor, has recently been addressed in human cholangiocarcinoma (CCA). Therefore, the present study aimed to investigate the role of Eph receptors and its ligands in CCA. Of all 50 cases of human CCA tested, immunohistochemical staining demonstrated that EphB2, EphB4, ephrinB1, and ephrinB2 were 100 % positive in CCA tissues with overexpressions of the above proteins as 56, 56, 70, and 48 % of cases, respectively. High expression of EphB2 was significantly correlated with the metastatic status of patients (P = 0.027). We also found that the high co-expression level of EphB2/ephrinB1 or EphB2/ephrinB2 were significantly correlated with the metastatic status of the patients (P = 0.034 and P = 0.024). Furthermore, we showed that the high co-expression level of EphB4/MVD and ephrinB1/MVD were significantly correlated with the metastasis status of CCA patients (P = 0.012 and P = 0.029). We further demonstrated that the EphB2 suppression using siRNA significantly reduced CCA cell migration by decreasing the phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and paxillin. In conclusion, the upregulation of EphB2 receptors and its specific ligands (ephrinB1 and ephrinB2) leads to CCA metastasis. Suppression of EphB2 expression as well as inhibition of its downstream signaling proteins might serve as possible therapeutic strategies in human CCA.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vatanasapt V, Sriamporn S, Vatanasapt P. Cancer control in Thailand. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2002;32(Suppl):S82–91.
Dechakhamphu S, Pinlaor S, Sitthithaworn P, Bartsch H, Yongvanit P. Accumulation of miscoding etheno-DNA adducts and highly expressed DNA repair during liver fluke-induced cholangiocarcinogenesis in hamsters. Mutat Res. 2010;691:9–16.
Dechakhamphu S, Pinlaor S, Sitthithaworn P, Nair J, Bartsch H, Yongvanit P. Lipid peroxidation and etheno DNA adducts in white blood cells of liver fluke-infected patients: protection by plasma alpha-tocopherol and praziquantel. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010;19:310–8.
Dechakhamphu S, Yongvanit P, Nair J, Pinlaor S, Sitthithaworn P, Bartsch H. High excretion of etheno adducts in liver fluke-infected patients: protection by praziquantel against DNA damage. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008;17:1658–64.
Pinlaor S, Yongvanit P, Hiraku Y, Ma N, Semba R, Oikawa S, et al. 8-nitroguanine formation in the liver of hamsters infected with opisthorchis viverrini. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;309:567–71.
Thamavit W, Bhamarapravati N, Sahaphong S, Vajrasthira S, Angsubhakorn S. Effects of dimethylnitrosamine on induction of cholangiocarcinoma in opisthorchis viverrini-infected syrian golden hamsters. Cancer Res. 1978;38:4634–9.
Thanan R, Murata M, Pinlaor S, Sithithaworn P, Khuntikeo N, Tangkanakul W, et al. Urinary 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2′-deoxyguanosine in patients with parasite infection and effect of antiparasitic drug in relation to cholangiocarcinogenesis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008;17:518–24.
Loilome W, Juntana S, Namwat N, Bhudhisawasdi V, Puapairoj A, Sripa B, et al. Prkar1a is overexpressed and represents a possible therapeutic target in human cholangiocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2011;129:34–44.
Loilome W, Yongvanit P, Wongkham C, Tepsiri N, Sripa B, Sithithaworn P, et al. Altered gene expression in opisthorchis viverrini-associated cholangiocarcinoma in hamster model. Mol Carcinog. 2006;45:279–87.
Techasen A, Loilome W, Namwat N, Takahashi E, Sugihara E, Puapairoj A, et al. Myristoylated alanine-rich c kinase substrate phosphorylation promotes cholangiocarcinoma cell migration and metastasis via the protein kinase c-dependent pathway. Cancer Sci. 2010;101:658–65.
Dokduang H, Juntana S, Techasen A, Namwat N, Yongvanit P, Khuntikeo N, et al. Survey of activated kinase proteins reveals potential targets for cholangiocarcinoma treatment. Tumour Biol. 2013;34:3519–28.
Loilome W, Bungkanjana P, Techasen A, Namwat N, Yongvanit P, Puapairoj A, et al. Activated macrophages promote Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in cholangiocarcinoma cells. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:5357–67.
Yothaisong S, Dokduang H, Techasen A, Namwat N, Yongvanit P, Bhudhisawasdi V, et al. Increased activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is associated with cholangiocarcinoma metastasis and PI3K/mTOR inhibition presents a possible therapeutic strategy. Tumour Biol. 2013;34:3637–48.
Mosch B, Reissenweber B, Neuber C, Pietzsch J. Eph receptors and ephrin ligands: important players in angiogenesis and tumor angiogenesis. J Oncol. 2010;2010:135285.
Pasquale EB. Eph-ephrin bidirectional signaling in physiology and disease. Cell. 2008;133:38–52.
Pasquale EB. Eph receptors and ephrins in cancer: bidirectional signalling and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:165–80.
Surawska H, Ma PC, Salgia R. The role of ephrins and eph receptors in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004;15:419–33.
Nakada M, Niska JA, Miyamori H, McDonough WS, Wu J, Sato H, et al. The phosphorylation of EphB2 receptor regulates migration and invasion of human glioma cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64:3179–85.
Wang SD, Rath P, Lal B, Richard JP, Li Y, Goodwin CR, et al. EphB2 receptor controls proliferation/migration dichotomy of glioblastoma by interacting with focal adhesion kinase. Oncogene. 2012;31:5132–43.
Sikkema AH, den Dunnen WF, Hulleman E, van Vuurden DG, Garcia-Manero G, Yang H, et al. EphB2 activity plays a pivotal role in pediatric medulloblastoma cell adhesion and invasion. Neuro Oncol. 2012;14:1125–35.
Kinch MS, Moore MB, Harpole Jr DH. Predictive value of the EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase in lung cancer recurrence and survival. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:613–8.
Lawrenson ID, Wimmer-Kleikamp SH, Lock P, Schoenwaelder SM, Down M, Boyd AW, et al. Ephrin-A5 induces rounding, blebbing and de-adhesion of EphA3-expressing 293T and melanoma cells by CrkII and Rho-mediated signalling. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:1059–72.
Liu W, Jung YD, Ahmad SA, McCarty MF, Stoeltzing O, Reinmuth N, et al. Effects of overexpression of ephrin-B2 on tumour growth in human colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2004;90:1620–6.
Macrae M, Neve RM, Rodriguez-Viciana P, Haqq C, Yeh J, Chen C, et al. A conditional feedback loop regulates ras activity through EphA2. Cancer Cell. 2005;8:111–8.
Adams RH, Wilkinson GA, Weiss C, Diella F, Gale NW, Deutsch U, et al. Roles of ephrinB ligands and EphB receptors in cardiovascular development: demarcation of arterial/venous domains, vascular morphogenesis, and sprouting angiogenesis. Genes Dev. 1999;13:295–306.
Brantley-Sieders DM, Zhuang G, Hicks D, Fang WB, Hwang Y, Cates JM, et al. The receptor tyrosine kinase EphA2 promotes mammary adenocarcinoma tumorigenesis and metastatic progression in mice by amplifying ErbB2 signaling. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:64–78.
Kuijper S, Turner CJ, Adams RH. Regulation of angiogenesis by Eph-ephrin interactions. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2007;17:145–51.
Sawamiphak S, Seidel S, Essmann CL, Wilkinson GA, Pitulescu ME, Acker T, et al. Ephrin-B2 regulates VEGFR2 function in developmental and tumour angiogenesis. Nature. 2010;465:487–91.
Wang HU, Chen ZF, Anderson DJ. Molecular distinction and angiogenic interaction between embryonic arteries and veins revealed by ephrin-B2 and its receptor Eph-B4. Cell. 1998;93:741–53.
Chiu ST, Chang KJ, Ting CH, Shen HC, Li H, Hsieh FJ. Over-expression of EphB3 enhances cell-cell contacts and suppresses tumor growth in HT-29 human colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:1475–86.
Oricchio E, Nanjangud G, Wolfe AL, Schatz JH, Mavrakis KJ, Jiang M, et al. The Eph-receptor A7 is a soluble tumor suppressor for follicular lymphoma. Cell. 2011;147:554–64.
Jamnongkan W, Techasen A, Thanan R, Duenngai K, Sithithaworn P, Mairiang E, et al. Oxidized alpha-1 antitrypsin as a predictive risk marker of opisthorchiasis-associated cholangiocarcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2013;34:695–704.
Namwat N, Puetkasichonpasutha J, Loilome W, Yongvanit P, Techasen A, Puapairoj A, et al. Downregulation of reversion-inducing-cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs (RECK) is associated with enhanced expression of matrix metalloproteinases and cholangiocarcinoma metastases. J Gastroenterol. 2011;46:664–75.
Kimura H, Nakajima T, Kagawa K, Deguchi T, Kakusui M, Katagishi T, et al. Angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma as evaluated by CD34 immunohistochemistry. Liver. 1998;18:14–9.
Nanashima A, Shibata K, Nakayama T, Tobinaga S, Araki M, Kunizaki M, et al. Relationship between microvessel count and postoperative survival in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:2123–9.
Jones G, Jurkiewicz MJ, Bostwick J, Wood R, Bried JT, Culbertson J, et al. Management of the infected median sternotomy wound with muscle flaps. The emory 20-year experience. Ann Surg. 1997;225:766–76. discussion 776-768.
Lackmann M, Boyd AW. Eph, a protein family coming of age: more confusion, insight, or complexity? Sci Signal. 2008;1:re2.
Merlos-Suarez A, Batlle E. Eph-ephrin signalling in adult tissues and cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008;20:194–200.
Nievergall E, Lackmann M, Janes PW. Eph-dependent cell-cell adhesion and segregation in development and cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012;69:1813–42.
Miao H, Burnett E, Kinch M, Simon E, Wang B. Activation of EphA2 kinase suppresses integrin function and causes focal-adhesion-kinase dephosphorylation. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:62–9.
Parrinello S, Napoli I, Ribeiro S, Wingfield Digby P, Fedorova M, Parkinson DB, et al. EphB signaling directs peripheral nerve regeneration through Sox2-dependent schwann cell sorting. Cell. 2010;143:145–55.
Yokote H, Fujita K, Jing X, Sawada T, Liang S, Yao L, et al. Trans-activation of EphA4 and FGF receptors mediated by direct interactions between their cytoplasmic domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:18866–71.
Tanaka M, Ohashi R, Nakamura R, Shinmura K, Kamo T, Sakai R, et al. Tiam1 mediates neurite outgrowth induced by ephrin-B1 and EphA2. EMBO J. 2004;23:1075–88.
Yang NY, Pasquale EB, Owen LB, Ethell IM. The EphB4 receptor-tyrosine kinase promotes the migration of melanoma cells through Rho-mediated actin cytoskeleton reorganization. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:32574–86.
Iida H, Honda M, Kawai HF, Yamashita T, Shirota Y, Wang BC, et al. EphrinA1 expression contributes to the malignant characteristics of {alpha}-fetoprotein producing hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut. 2005;54:843–51.
Li X, Wang Y, Zhen H, Yang H, Fei Z, Zhang J, et al. Expression of EphA2 in human astrocytic tumors: correlation with pathologic grade, proliferation and apoptosis. Tumour Biol. 2007;28:165–72.
Vaught D, Brantley-Sieders DM, Chen J. Eph receptors in breast cancer: roles in tumor promotion and tumor suppression. Breast Cancer Res. 2008;10:217.
Gerety SS, Anderson DJ. Cardiovascular ephrinB2 function is essential for embryonic angiogenesis. Development. 2002;129:1397–410.
Gerety SS, Wang HU, Chen ZF, Anderson DJ. Symmetrical mutant phenotypes of the receptor ephB4 and its specific transmembrane ligand ephrin-B2 in cardiovascular development. Mol Cell. 1999;4:403–14.
Abengozar MA, de Frutos S, Ferreiro S, Soriano J, Perez-Martinez M, Olmeda D, et al. Blocking ephrinB2 with highly specific antibodies inhibits angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, and tumor growth. Blood. 2012;119:4565–76.
Foubert P, Silvestre JS, Souttou B, Barateau V, Martin C, Ebrahimian TG, et al. Psgl-1-mediated activation of EphB4 increases the proangiogenic potential of endothelial progenitor cells. J Clin Invest. 2007;117:1527–37.
Mansson-Broberg A, Siddiqui AJ, Genander M, Grinnemo KH, Hao X, Andersson AB, et al. Modulation of ephrinB2 leads to increased angiogenesis in ischemic myocardium and endothelial cell proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;373:355–9.
Folkman J, Watson K, Ingber D, Hanahan D. Induction of angiogenesis during the transition from hyperplasia to neoplasia. Nature. 1989;339:58–61.
Tomisaki S, Ohno S, Ichiyoshi Y, Kuwano H, Maehara Y, Sugimachi K. Microvessel quantification and its possible relation with liver metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cancer. 1996;77:1722–8.
Xi HQ, Wu XS, Wei B, Chen L. Aberrant expression of EphA3 in gastric carcinoma: correlation with tumor angiogenesis and survival. J Gastroenterol. 2012;47:785–94.
Zatterstrom UK, Brun E, Willen R, Kjellen E, Wennerberg J. Tumor angiogenesis and prognosis in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Head Neck. 1995;17:312–8.
Mitra SK, Hanson DA, Schlaepfer DD. Focal adhesion kinase: in command and control of cell motility. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:56–68.
Schaller MD. Paxillin: a focal adhesion-associated adaptor protein. Oncogene. 2001;20:6459–72.
Guo DL, Zhang J, Yuen ST, Tsui WY, Chan AS, Ho C, et al. Reduced expression of EphB2 that parallels invasion and metastasis in colorectal tumours. Carcinogenesis. 2006;27:454–64.
Specht S, Isse K, Nozaki I, Lunz 3rd JG, Demetris AJ. Sprr2a expression in cholangiocarcinoma increases local tumor invasiveness but prevents metastasis. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2013;30:877–90.
Acknowledgements
This study is funded by the grant from the Thailand Research Fund (Grant No. MRG5400834) and the Research Assistantship Grant of the Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University (Grant No. AS55203) to WL along with the grants from the Higher Education Research Promotion and National Research University Project of Thailand, Office of the Higher Education Commission, through the Center of Excellence in Specific Health Problems in Greater Mekong Sub-region cluster (SHeP-GMS), Khon Kaen University allocated to WK and WL. We thank Prof. Ross H. Andrews for English language assistance.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
(DOCX 37 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
(DOCX 38 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
(DOCX 35 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khansaard, W., Techasen, A., Namwat, N. et al. Increased EphB2 expression predicts cholangiocarcinoma metastasis. Tumor Biol. 35, 10031–10041 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2295-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2295-0