Abstract
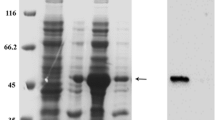
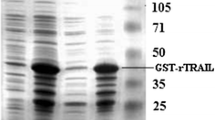
The specific binding peptide pd20 of gastric cancer cells with a high potential for liver metastasis was fused with human tumour necrosis factor (TNF) α, and a prokaryotic expression vector was established to express the pd20–TNFα fusion protein. After purification and identification, the preventive effects of the fusion protein on liver metastasis of gastric cancer were observed in mice. The whole gene synthesis method was used for pd20–TNFα fusion gene preparation, and a pd20–TNFα prokaryotic expression vector was constructed. The vector was induced and expressed in Escherichia coli BL21. The expression products were analysed and verified by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis and Western blot analysis. The Ni-NTA column method was used to purify the fusion protein, and the L929 cytotoxicity method was used to detect biological activity. Flow cytometry apoptosis experiments and invasion assays were performed to observe the effects of the fusion protein on apoptosis and metastasis of gastric cancer cells with high potential for liver metastasis. Thirty nude mice with liver metastasis of gastric cancer were established and then randomly divided into three groups of ten mice each. The Pd20–TNFα recombinant protein (1.2 × 106 U/kg day) or standard TNFα (1.2 × 106 U/kg day) saline was administered via tail vein injection for 7 consecutive days. The pathological changes in various organs of nude mice were observed 4 weeks later. The size of the gastric cancer, the incidence of liver metastasis and the number of liver metastases were measured and calculated. We successfully constructed a Pd20–TNFα recombinant plasmid and prepared the fusion protein. Detection of the pd20–TNFα protein by immunofluorescence showed a very strong expression in liver tissue, suggesting a targeting of the fusion protein to the liver. The L929 cytotoxicity assays showed that the pd20–TNFα fusion purified protein had a significant lethal effect on L929 cells, with a killing activity of up to 7.6 × 106 IU/ml. The apoptosis experiments showed that as the concentration of the fusion protein increased, the early gastric cancer cell apoptosis also increased, with the early apoptosis rate increasing from 5.99 % to 9.04 %. Cell invasion experiments showed that the purified pd20–TNFα fusion protein significantly inhibited the in vitro invasion of XGC9811-L cells, with the penetrating cells being significantly decreased compared with the control group per unit time (P < 0.01). Vector experiments showed that the pd20–TNFα recombinant protein group had significantly reduced cancer lesions and liver metastasis in nude mice compared with the control group. We successfully purified a pd20–TNFα fusion protein and confirmed that it had significant biological activity promoting early gastric cancer cell apoptosis, thereby inhibiting gastric cancer cell invasion.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Couzin J. Tracing the steps of metastasis cancer’s menacing ballet. Science. 2003;299:1002–5.
Pande J, Szewczyk MM, Grover AK. Phage display: concept, innovations, applications and future. Biotechnol Adv. 2010;28(6):849–58.
Rentero I, Heinis C. Screening of large molecule diversities by phage display. Chimia (Aarau). 2011;65(11):843–5.
An P, Lei H, Zhang J, et al. Suppression of tumor growth and metastasis by a VEGFR-1 antagonizing peptide identified from a phage display library. Int J Cancer. 2004;111(2):165–73.
Li ZJ, Cho CH. Peptides as targeting probes against tumor vasculature for diagnosis and drug delivery. J Transl Med. 2012;19:10.
Hu SJ, Guo XN, Fan DM, et al. Phage display selection of peptides that inhibit metastasis ability of gastric cancer cells with high liver-metastatic potential. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;341(4):964–72.
Hu SJ, Guo XN, Yang L, et al. Liver cancer cells with high metastatic potential specificity of phage binding peptide identification. Modern Oncol. 2005;13:158–60.
Chu WM. Tumor necrosis factor. Cancer Lett. 2013;328(2):222–5.
MacGill RS, Davis TA, Macko J. Local gene delivery of tumor necrosis factor alpha can impact primary tumor growth and metastases through a host-mediated response. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2007;24(7):521–31.
Mao W, Zhu X, Tang D, et al. TNF-α expression in the UCB-MSCs as stable source inhibits gastric cancers growth in nude mice. Cancer Invest. 2012;30(6):463–72.
Shaw J, Chen B, Huang WH, et al. The small-molecule TNF-alpha modulator, UTL-5 g, reduces side effects induced by cisplatin and enhances the therapeutic effect of cisplatin in vivo. J Exp Ther Oncol. 2011;9:129–37.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation (No. 81060193) and Ningxia Natural Science Foundation (No. NZ09169).
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, SJ., Jiang, RX., Xie, HH. et al. Purification of a Pd20–TNFα fusion protein that prevents liver metastasis of gastric cancer. Tumor Biol. 35, 7523–7529 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1957-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1957-2