Abstract
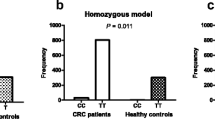
Interleukin (IL) 17A is an inflammatory cytokine expressed by Th 17 cells and plays a role in tissue inflammation by inducing release of proinflammatory and neutrophil-mobilizing cytokines. We have investigated the association between colorectal cancer and polymorphisms of IL17A (rs2275913. G197A). The study was performed in 241 subjects (102 with colorectal cancer and 139 healthy controls). Genotypes were determined by fluorescent-based restriction fragment length polymorphism method. The association between the molecular features at the gene in relation to tumor and patient clinical characteristics was analyzed. There was a significant difference between the genotype frequencies of IL17A G197A of control subjects (GG 68.34 % and GA + AA 31.65 %) and patients with colorectal cancer (GG 47.05 % and GA + AA 52.94 %) (p = 0.001with odds ratio (OR) 2.45 (1.43–4.11)). IL17A G197A polymorphism is particularly associated with colon cancer. Indeed, the IL17A GG genotype could be considered as a protective factor against colon cancer (p = 0.00001) with OR 3.77 (2.04–6.99). We have noted a significant association of IL17A G197A polymorphism not only with tumor localization (p = 0.003) but also with tumor differentiation (p = 0.0005) in CRC patients. We have also showed a significant association of G197A variant with an increased risk of advanced stage (p = 0.005). Our result suggests that the A allele of IL17A gene is involved in susceptibility to colorectal cancer and is associated with clinical features as tumor location, tumor differentiation, and TNM stage. IL17A polymorphism may serve as biomarker of disease location and progression.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- IBD:
-
Inflammatory bowel disease
- UC:
-
Ulcerative colitis
- Th1/17 cells:
-
T helper 1/17 cells
- IL17A/B/C/D/E/F:
-
Interleukin A/B/C/D/E/F
- IL1β/6/8/10:
-
Interleukin IL1β/6/8/10
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor κB
- TNFα:
-
Tumor necrosis factor α
- TNM stage:
-
Tumor node metastasis stage
- ETBF:
-
Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis
- CIHM:
-
CpG island hyper-methylation
- PR:
-
Progesterone receptor
- VEFG:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- p53:
-
Tumor suppressor protein53
References
Vasen HF, van der Meulen-de Jong AE, de Vos Tot Nederveen Cappel WH, Oliveira J. Familial colorectal cancer risk: ESMO clinical recommendations. Ann Oncol. 2009;20 Suppl 4:51–3.
Carter AB, Misyak SA, Hontecillas R, Bassaganya-Riera J. Dietary modulation of inflammation-induced colorectal cancer through PPARgamma. PPAR Res. 2009;2009:498352.
Tanaka T. Development of an inflammation-associated colorectal cancer model and its application for research on carcinogenesis and chemoprevention. Int J Inflamm. 2012;2012:658786.
Bernstein CN, Blanchard JF, Kliewer E, Wajda A. Cancer risk in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based study. Cancer. 2001;91(4):854–62.
Lakatos PL, Lakatos L. Risk for colorectal cancer in ulcerative colitis: changes, causes and management strategies. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14(25):3937–47.
Wilkening S, Tavelin B, Canzian F, Enquist K, Palmqvist R, Altieri A, et al. Interleukin promoter polymorphisms and prognosis in colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29(6):1202–6.
Erdman SE, Poutahidis T. Roles for inflammation and regulatory T cells in colon cancer. Toxicol Pathol. 2010;38(1):76–87.
Colotta F, Allavena P, Sica A, Garlanda C, Mantovani A. Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark of cancer: links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30(7):1073–81.
Clevers H. At the crossroads of inflammation and cancer. Cell. 2004;118(6):671–4.
Sakamoto K, Maeda S, Hikiba Y, Nakagawa H, Hayakawa Y, Shibata W, et al. Constitutive NF-kappaB activation in colorectal carcinoma plays a key role in angiogenesis, promoting tumor growth. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(7):2248–58.
Wang S, Liu Z, Wang L, Zhang X. NF-kappaB signaling pathway, inflammation and colorectal cancer. Cell Mol Immunol. 2009;6(5):327–34.
Lin WW, Karin M. A cytokine-mediated link between innate immunity, inflammation, and cancer. J Clin Invest. 2007;117(5):1175–83.
Macarthur M, Hold GL, El-Omar EM. Inflammation and cancer II. Role of chronic inflammation and cytokine gene polymorphisms in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal malignancy. Am J Physiol. 2004;286(4):G515–20.
Li M, You Q, Wang X. Association between polymorphism of the tumor necrosis factor alpha-308 gene promoter and colon cancer in the Chinese population. Genet Test Mol Biomark. 2011;15(11):743–7.
Cen G, Wu W. Association between tumor necrosis factor-alpha 857C/T polymorphism and gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 2013;47(9):1119–33.
Ito H, Kaneko K, Makino R, Konishi K, Kurahashi T, Yamamoto T, et al. Interleukin-1beta gene in esophageal, gastric and colorectal carcinomas. Oncol Rep. 2007;18(2):473–81.
El-Omar EM, Carrington M, Chow WH, McColl KE, Bream JH, Young HA, et al. Interleukin-1 polymorphisms associated with increased risk of gastric cancer. Nature. 2000;404(6776):398–402.
Cacev T, Radosevic S, Krizanac S, Kapitanovic S. Influence of interleukin-8 and interleukin-10 on sporadic colon cancer development and progression. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29(8):1572–80.
Lu W, Pan K, Zhang L, Lin D, Miao X, You W. Genetic polymorphisms of interleukin (IL)-1B, IL-1RN, IL-8, IL-10 and tumor necrosis factor alpha and risk of gastric cancer in a Chinese population. Carcinogenesis. 2005;26(3):631–6.
Landi S, Moreno V, Gioia-Patricola L, Guino E, Navarro M, de Oca J, et al. Association of common polymorphisms in inflammatory genes interleukin (IL)6, IL8, tumor necrosis factor alpha, NFKB1, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma with colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2003;63(13):3560–6.
Shibata T, Tahara T, Hirata I, Arisawa T. Genetic polymorphism of interleukin-17A and -17 F genes in gastric carcinogenesis. Hum Immunol. 2009;70(7):547–51.
McGovern DP, Rotter JI, Mei L, Haritunians T, Landers C, Derkowski C, et al. Genetic epistasis of IL23/IL17 pathway genes in Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009;15(6):883–9.
Yamada H. Current perspectives on the role of IL-17 in autoimmune disease. J Inflamm Res. 2010;3:33–44.
Kawaguchi M, Adachi M, Oda N, Kokubu F, Huang SK. IL-17 cytokine family. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;114(6):1265–73. quiz 74.
Kolls JK, Linden A. Interleukin-17 family members and inflammation. Immunity. 2004;21(4):467–76.
Kim SW, Kim ES, Moon CM, Park JJ, Kim TI, Kim WH, et al. Genetic polymorphisms of IL-23R and IL-17A and novel insights into their associations with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 2011;60(11):1527–36.
Zhang X, Yu P, Wang Y, Jiang W, Shen F, Wang Y, et al. Genetic polymorphisms of interleukin 17A and interleukin 17 F and their association with inflammatory bowel disease in a Chinese Han population. Inflamm Res. 2013;62(8):743–50.
Kim ES, Kim SW, Moon CM, Park JJ, Kim TI, Kim WH, et al. Interactions between IL17A, IL23R, and STAT4 polymorphisms confer susceptibility to intestinal Behcet’s disease in Korean population. Life Sci. 2012;90(19–20):740–6.
Nordang GB, Viken MK, Hollis-Moffatt JE, Merriman TR, Forre OT, Helgetveit K, et al. Association analysis of the interleukin 17A gene in Caucasian rheumatoid arthritis patients from Norway and New Zealand. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009;48(4):367–70.
Arisawa T, Tahara T, Shibata T, Nagasaka M, Nakamura M, Kamiya Y, et al. The influence of polymorphisms of interleukin-17A and interleukin-17 F genes on the susceptibility to ulcerative colitis. J Clin Immunol. 2008;28(1):44–9.
Wu X, Zeng Z, Chen B, Yu J, Xue L, Hao Y, et al. Association between polymorphisms in interleukin-17A and interleukin-17 F genes and risks of gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(1):86–92.
Tahara T, Shibata T, Nakamura M, Yamashita H, Yoshioka D, Okubo M, et al. Effect of polymorphisms of IL-17A, -17 F and MIF genes on CpG island hyper-methylation (CIHM) in the human gastric mucosa. Int J Mol Med. 2009;24(4):563–9.
Quan Y, Zhou B, Wang Y, Duan R, Wang K, Gao Q, et al. Association between IL17 polymorphisms and risk of cervical cancer in Chinese women. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:258293.
Zhou B, Zhang P, Wang Y, Shi S, Zhang K, Liao H, et al. Interleukin-17 gene polymorphisms are associated with bladder cancer in a Chinese Han population. Mol Carcinog. 2012;52(11):871–8.
Steiner GE, Newman ME, Paikl D, Stix U, Memaran-Dagda N, Lee C, et al. Expression and function of pro-inflammatory interleukin IL-17 and IL-17 receptor in normal, benign hyperplastic, and malignant prostate. Prostate. 2003;56(3):171–82.
Zhu X, Mulcahy LA, Mohammed RA, Lee AH, Franks HA, Kilpatrick L, et al. IL-17 expression by breast-cancer-associated macrophages: IL-17 promotes invasiveness of breast cancer cell lines. Breast Cancer Res. 2008;10(6):R95.
Zhang B, Rong G, Wei H, Zhang M, Bi J, Ma L, et al. The prevalence of Th17 cells in patients with gastric cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;374(3):533–7.
Le Gouvello S, Bastuji-Garin S, Aloulou N, Mansour H, Chaumette MT, Berrehar F, et al. High prevalence of Foxp3 and IL17 in MMR-proficient colorectal carcinomas. Gut. 2008;57(6):772–9.
Huber AK, Jacobson EM, Jazdzewski K, Concepcion ES, Tomer Y. Interleukin (IL)-23 receptor is a major susceptibility gene for Graves' ophthalmopathy: the IL-23/T-helper 17 axis extends to thyroid autoimmunity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93(3):1077–81.
Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B, Fredriksen T, Mauger S, Bindea G, et al. Clinical impact of different classes of infiltrating T cytotoxic and helper cells (Th1, th2, treg, th17) in patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2011;71(4):1263–71.
Oppmann B, Lesley R, Blom B, Timans JC, Xu Y, Hunte B, et al. Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity. 2000;13(5):715–25.
Wang L, Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Huang S, Wang Z, et al. Association analysis of IL-17A and IL-17 F polymorphisms in Chinese Han women with breast cancer. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(3):e34400.
Suzuki H, Ogawa H, Miura K, Haneda S, Watanabe K, Ohnuma S, et al. IL-23 directly enhances the proliferative and invasive activities of colorectal carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2012;4(2):199–204.
Chae WJ, Gibson TF, Zelterman D, Hao L, Henegariu O, Bothwell AL. Ablation of IL-17A abrogates progression of spontaneous intestinal tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(12):5540–4.
Wu S, Rhee KJ, Albesiano E, Rabizadeh S, Wu X, Yen HR, et al. A human colonic commensal promotes colon tumorigenesis via activation of T helper type 17 T cell responses. Nat Med. 2009;15(9):1016–22.
Tong Z, Yang XO, Yan H, Liu W, Niu X, Shi Y, et al. A protective role by interleukin-17 F in colon tumorigenesis. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(4):e34959.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all the members of ‘Laboratoire Diagnostic Génétique et Moléculaire, Centre Jean Perrin, Clermont Ferrand, France for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Omrane, I., Marrakchi, R., Baroudi, O. et al. Significant association between interleukin-17A polymorphism and colorectal cancer. Tumor Biol. 35, 6627–6632 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1890-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1890-4