Abstract
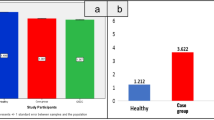
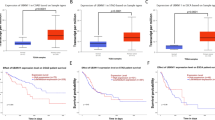
Neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) overexpression has been reported in a variety of human cancers. However, the role of NRP-1 in bladder cancer (BC) remains unclear. The aim of present study was to analyze NRP-1 protein expression in BC tissues and to assess its prognostic significance for BC. NRP-1 messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) and protein expression were determined by real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and immunohistochemistry in specimens of primary cancer and their adjacent noncancerous tissues in BC patients. Additionally, NRP-1 protein expression in 139 archived paraffin-embedded BC samples was analyzed by immunohistochemistry and correlated with clinicopathological characteristics and survival. Student’s t test, Spearman’s rank correlation, Kaplan-Meier plots, and Cox’s proportional hazards regression model were used to analyze the data. By qRT-PCR and immunohistochemistry, the levels of NRP-1 mRNA and protein were significantly higher in BC, compared to that in adjacent noncancerous tissues (P < 0.001). High expression of NRP-1 was significantly associated with histologic grade (P = 0.016) and tumor stage (P = 0.001). Multivariate analysis showed that high expression of NRP-1 was an independent prognostic factor for overall survival. Our study suggests that overexpression of NRP-1 may play an important role in the progression of BC, and NRP-1 expression may serve as a biomarker for poor prognosis for BC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liou LS. Urothelial cancer biomarkers for detection and surveillance. Urology. 2006;67:25–33. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2006.01.034. discussion 33–24.
Smaldone MC, Jacobs BL, Smaldone AM, Hrebinko Jr RL. Long-term results of selective partial cystectomy for invasive urothelial bladder carcinoma. Urology. 2008;72:613–6. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2008.04.052.
He Z, Tessier-Lavigne M. Neuropilin is a receptor for the axonal chemorepellent semaphorin III. Cell. 1997;90:739–51.
Kolodkin AL, Levengood DV, Rowe EG, Tai YT, Giger RJ, Ginty DD. Neuropilin is a semaphorin III receptor. Cell. 1997;90:753–62. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80535-8.
Kitsukawa T, Shimono A, Kawakami A, Kondoh H, Fujisawa H. Overexpression of a membrane protein, neuropilin, in chimeric mice causes anomalies in the cardiovascular system, nervous system and limbs. Development. 1995;121:4309–18.
Kawasaki T, Kitsukawa T, Bekku Y, Matsuda Y, Sanbo M, Yagi T, et al. A requirement for neuropilin-1 in embryonic vessel formation. Development. 1999;126:4895–902.
Miao HQ, Lee P, Lin H, Soker S, Klagsbrun M. Neuropilin-1 expression by tumor cells promotes tumor angiogenesis and progression. FASEB J. 2000;14:2532–9. doi:10.1096/fj.00-0250com.
Ding H, Wu X, Roncari L, Lau N, Shannon P, Nagy A, et al. Expression and regulation of neuropilin-1 in human astrocytomas. Int J Cancer. 2000;88:584–92.
Latil A, Bièche I, Pesche S, Valéri A, Fournier G, Cussenot O, et al. VEGF overexpression in clinically localized prostate tumors and neuropilin-1 overexpression in metastatic forms. Int J Cancer. 2000;89:167–71.
Fakhari M, Pullirsch D, Abraham D, Paya K, Hofbauer R, Holzfeind P, et al. Selective upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors neuropilin-1 and −2 in human neuroblastoma. Cancer. 2002;94:258–63.
Kawakami T, Tokunaga T, Hatanaka H, Kijima H, Yamazaki H, Abe Y, et al. Neuropilin 1 and neuropilin 2 co-expression is significantly correlated with increased vascularity and poor prognosis in nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer. 2002;95:2196–201. doi:10.1002/cncr.10936.
Akagi M, Kawaguchi M, Liu W, McCarty MF, Takeda A, Fan F, et al. Induction of neuropilin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor by epidermal growth factor in human gastric cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 2003;88:796–802. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6600811.
Parikh AA, Liu WB, Fan F, Stoeltzing O, Reinmuth N, Bruns CJ, et al. Expression and regulation of the novel vascular endothelial growth factor receptor neuropilin-1 by epidermal growth factor in human pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer. 2003;98:720–9. doi:10.1002/cncr.11560.
Hansel DE, Wilentz RE, Yeo CJ, Schulick RD, Montgomery E, Maitra A. Expression of neuropilin-1 in high-grade dysplasia, invasive cancer, and metastases of the human gastrointestinal tract. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004;28:347–56.
Bachelder RE, Crago A, Chung J, Wendt MA, Shaw LM, Robinson G, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor is an autocrine survival factor for neuropilin-expressing breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2001;61:5736–40.
Barr MP, Byrne AM, Duffy AM, Condron CM, Devocelle M, Harriott P, et al. A peptide corresponding to the neuropilin-1-binding site on VEGF(165) induces apoptosis of neuropilin-1-expressing breast tumour cells. Br J Cancer. 2005;92:328–33. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6602308.
Bachelder RE, Wendt MA, Mercurio AM. Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes breast carcinoma invasion in an autocrine manner by regulating the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Cancer Res. 2002;62:7203–6.
Bachelder RE, Lipscomb EA, Lin X, Wendt MA, Chadborn NH, Eickholt BJ, et al. Competing autocrine pathways involving alternative neuropilin-1 ligands regulate chemotaxis of carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2003;63:5230–3.
Parikh AA, Fan F, Liu WB, Ahmad SA, Stoeltzing O, Reinmuth N, et al. Neuropilin-1 in human colon cancer: expression, regulation, and role in induction of angiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 2004;164:2139–51.
Tomizawa Y, Sekido Y, Kondo M, Gao B, Yokota J, Roche J, et al. Inhibition of lung cancer cell growth and induction of apoptosis after reexpression of 3p21.3 Candidate tumor suppressor gene SEMA3B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:13954–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.231490898.
Tse C, Xiang RH, Bracht T, Naylor SL. Human semaphorin 3B (SEMA3B) located at chromosome 3p21.3 suppresses tumor formation in an adenocarcinoma cell line. Cancer Res. 2002;62:542–6.
Castro-Rivera E, Ran S, Thorpe P, Minna JD. Semaphorin 3B (SEMA3B) induces apoptosis in lung and breast cancer, whereas VEGF165 antagonizes this effect. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:11432–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.0403969101.
Gospodarowicz MK. Staging of bladder cancer. Semin Surg Oncol. 1994;10:51–9.
Hussain SA, James ND. Molecular markers in bladder cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2005;15:3–9. doi:10.1016/j.semradonc.2004.07.007.
Acknowledgments
This work was also supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30772278 and No. 30973443).
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Wen Cheng, Dian Fu and Zhi-Feng Wei contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, W., Fu, D., Wei, ZF. et al. NRP-1 expression in bladder cancer and its implications for tumor progression. Tumor Biol. 35, 6089–6094 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1806-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1806-3