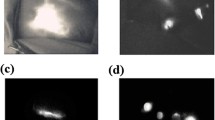
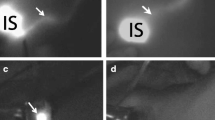
Abstract
Near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence imaging using indocyanine green (ICG) was considered to have the potential to improve sentinel lymph node (SLN) mapping in breast cancer. Herein, we performed a randomized clinical trial to evaluate the effectiveness of ICG fluorescence imaging compared with blue dye imaging in SLN navigation surgery. We also analyzed lymph drainage pathways to identify targets for sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB). Finally, 68 consecutive patients diagnosed with breast cancer and who underwent SLNB between November 2010 and September 2012 were enrolled in the study. The cases were randomly grouped into either the ICG fluorescence or blue dye group, with 36 in the ICG fluorescence group and 32 in the blue dye group. Levels I and II axillary dissection was performed in all cases after SLNB. A single lymph drainage pathway was detected in 21 of 36 (58.3 %) patients, and multiple lymph drainage pathways were detected in 15 of 36 (41.7 %) cases. The detection rate of SLNB was higher by ICG fluorescence than by blue dye (97.2 vs. 81.3 %, p < 0.05), as 3.6 SLNs were detected on average in the ICG fluorescence group compared to 2.1 in the blue dye group. However, the sensitivity and false-negative rate were similar in the two groups. In conclusion, ICG fluorescence was superior to blue dye for the identification of the SLN.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mansel RE, Fallowfield L, Kissin M, et al. Randomized multicenter trial of sentinel node biopsy versus standard axillary treatment in operable breast cancer: the ALMANAC Trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:599–609.
Strver ME, Meijnen P, Van Tienhoven G, et al. Sentinel node identification rate and nodal involvement in the EORTC 10981-22023 Amaros trial. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:185–61.
Erb KM, Julian TB. Completion of axillary dissection for a positive sentinel node: necessary or not? Curr Oncol Rep. 2009;11:15–20.
Giulianno AE, Hunt KK, Ballman KV, et al. Axillary dissection vs no axillary dissection in women with invasive breast cancer and sentinel node metastasis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2011;305:569–75.
Julian TB, Krag D, Brown A, et al. Preliminary technical results of NSABP B-32, a randomized phase III clinical trial to compare sentinel node resection to conventional axillary dissection in clinical node negative breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2004;88:511–2.
Wang L, Yu JM, Wang YS, et al. Preoperative lymphoscintigraphy predicts the successful identification but is not necessary in sentinel lymph nodes biopsy in breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:2215–20.
Noguchi M, Inokuchi M, Zen Y. Complement of peritumonal and subareolar injection in breast cancer sentinel lymph node biopsy. J Surg Oncol. 2009;100:100–5.
Christine B, Teal MD, Jennifer P, et al. Evaluation of the benefit of using blue dye in addition to radioisotope for sentinel lymph node biopsy in patients with breast cancer. Breast J. 2005;6:391–3.
Sandrucci S, Casalegno PS, Percivale P, et al. Sentinel lymph node mapping and biopsy for breast cancer: a review of the literature relative to 4791 procedure. Tumori. 1999;85:425–34.
Stratmann SL, McCarty TM, Kuhn JA. Radiation safety with breast sentinel node biopsy. Am J Surg. 1999;178:454–7.
Sardi A, Spiegler E, Colandrea J, et al. The benefit of using two techniques for sentinel lymph node mapping in breast cancer. Am J Surg. 2002;68:24–8.
Ueno H, Hihara J, Shimizu K, et al. Experiment study on fluorescent microspheres as a tracer for sentinel node detection. Anticancer Res. 2005;25:821–5.
Murawa D, Hirche S, Dresel S, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer guided by indocyanine green fluorescence. Br J Surg. 2009;96:1289–94.
Doubrovsky A, de Wilt JH, Scolyer RA, et al. Sentinel node biopsy provides more accurate staging than elective lymph node dissection in patients with cutaneous melanoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2004;15:829–36.
Xing Y, Foy M, Cox DD, et al. Meta-analysis of sentinel lymph node biopsy after preoperative chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2006;93:539–46.
Derossis AM, Fey J, Yeung H, et al. A trend analysis of the relative value of blue dye and isotope location in 2000 consecutive cases of sentinel node biopsy for breast cancer. J Am Coll Sugar. 2001;193:473–8.
McMasters KM, Wong SL, Martin RCG, et al. Dermal injection of radioactive colloid is superior to peritumoral injection for breast cancer sentinel lymph node biopsy: results of a multi-institutional study. Ann Surg. 2001;233:676–87.
Hung WK, Chan CM, Chong SF, et al. Randomized clinical trial comparing blue dye with combined dye and isotope for sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2005;92:1494–7.
Kang SW, Chung SE, Shin WJ, et al. Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy and late geographic hyperfluorescence on indocyanine green angiography. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009;93:759–64.
Schneider PD. Preoperative assessment of liver function. Surg Clin N Am. 2004;84:355–73.
Kitai T, Inomoto T, Miwa M, et al. Fluorescence navigation with indocyanine green for detecting sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 2005;12:211–5.
Aydogan F, Celik V, Uras C, et al. A comparison of the adverse reactions associated with isosulfan blue versus methylene blue dye in sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast cancer. Am J Surg. 2008;195:277–8.
Hirsche PD, Murawa D, Mohr Z, et al. ICG fluorescent-guided sentinel node biopsy for axillary nodal staging in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;121:373–8.
Polom K, Murawa D, Nowaczyk P, et al. Breast cancer sentinel lymph node mapping using near infrared guided indocyanine green and indocyanine green-human serum albumin in comparison with gamma emitting radioactive colloid tracer. J Cancer Surg. 2012;38:137–42.
Kennedy RJ, Kollias J, Gill PG, et al. Removal of two sentinel nodes accurately stages the axilla in breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2003;90:1349–53.
Megumi T, Tomoharu S, Kassim A, et al. Lymphatic mapping with fluorescence navigation using indocyanine green and axillary surgery in patients with primary breast cancer. Breast. 2012;6:535–41.
Bass SS, Cox CE, Reintgen DS, et al. Learning curves and certification for breast cancer lymphatic mapping. Surg Oncol Clin Am. 1999;8:497–509.
Dupont E, Cox C, Shivers S, et al. Learning curves and breast cancer lymphatic mapping: institutional volume index. J Surg Res. 2001;97:92–6.
Sanidas EE, de Bree E, Tsififif DD, et al. How many cases are enough for accreditation in sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer? Am J Surg. 2003;185:202–10.
Quan ML, McCready D, Temple WJ, et al. Biopsy of lymphatic metastases in breast cancer: lessons learn from sentinel node biopsy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2002;9:467–71.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, W., Zhang, L., Ji, J. et al. Breast cancer sentinel lymph node mapping using near-infrared guided indocyanine green in comparison with blue dye. Tumor Biol. 35, 3073–3078 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1399-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1399-2